Space Physics Aboard Station as Starliner Crew Returns to Houston
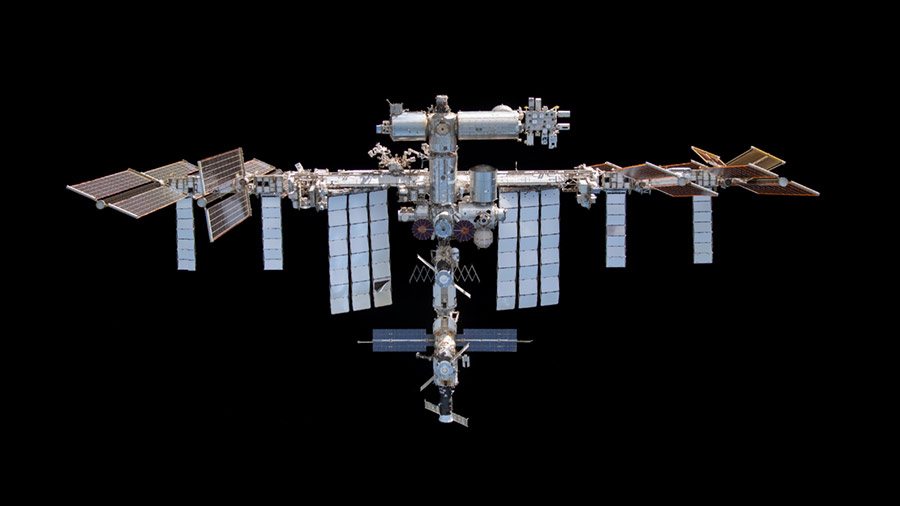

Space physics and life support maintenance topped the schedule at the end of the week for the Expedition 71 crew as the Starliner astronauts return to Houston. 3D printing and cargo operations also rounded out the operations aboard the International Space Station.
The coldest place in the universe may be the Cold Atom Lab located aboard the orbital outpost’s Destiny laboratory module. NASA Flight Engineer Mike Barratt opened up the quantum physics research device Friday morning and inspected its cables and ports as part of broader science hardware replacement work. The ultra-cold laboratory chills atoms to near absolute zero to observe their fundamental characteristics and quantum behaviors.
Barratt then joined NASA Flight Engineers Tracy C. Dyson and Matthew Dominick as they continued life support maintenance in the Tranquility module. Barratt activated the water processing assembly then reinstalled module components to their normal configuration in Tranquility. Dominick and Dyson spent the day in the module replacing hardware that supports the water recovery system which is part of the orbital outpost’s Waste and Hygiene compartment, or bathroom.
NASA Flight Engineer Jeanette Epps assisted Dyson at the end of the day finalizing cleanup activities in Tranquility after the advanced orbital plumbing work was complete. Epps began her shift in the Kibo laboratory module replacing obsolete gas bottles with new types of gas bottles in the Common Gas Supply Equipment rack. The gas supply hardware supplies gases including argon, helium, and carbon dioxide fueling research racks and their experiments inside Kibo.
Working in the orbiting lab’s Roscosmos segment, Commander Oleg Kononenko checked Soyuz communication systems, inspected video equipment, and cleaned vents on broadband hardware. Flight Engineer Nikolai Chub worked on a 3D printing experiment testing the device’s controller and software while printing an object. Chub also stowed trash and obsolete gear inside the Progress 86 resupply ship that is due to undock at the end of the month. Flight Engineer Alexander Grebenkin spent his day checking smoke detectors in the Nauka science module.
On the ground at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, preparations continue ahead of the agency’s Boeing Crew Flight Test launch to the microgravity laboratory. NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams, still in quarantine ahead of the flight test, will return to Houston this weekend as work progresses on a valve replacement on the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket Centaur upper stage. Crew will return to NASA Kennedy prior to the next launch opportunity, which is targeted for no earlier than 6:16 p.m. EDT on Friday, May 17, from Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida.
Wilmore and Williams are the first to launch aboard Boeing’s Starliner to the space station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. The astronauts will spend about a week at the orbiting laboratory before returning to Earth and making a parachute and airbag-assisted landing in the southwestern United States.
After successful completion of the mission, NASA will finalize certification of Starliner and its systems for crewed rotation missions to the space station. The Starliner capsule, with a diameter of 15 feet (4.56 meters) and the capability to steer automatically or manually, will carry four astronauts, or a mix of crew and cargo, for NASA missions to low Earth orbit.
For the latest on Boeing’s Crew Flight Test please visit NASA’s blog.
Learn more about station activities by following the space station blog, @space_station and @ISS_Research on X, as well as the ISS Facebook and ISS Instagram accounts.
Get weekly video highlights at: https://roundupreads.jsc.nasa.gov/videoupdate/
Get the latest from NASA delivered every week. Subscribe here: www.nasa.gov/subscribe
Powered by WPeMatico
Mark Garcia