NASA Celebrates Hispanic Heritage Month 2023
In honor of Hispanic Heritage Month, we recognize Hispanic astronauts who have flown in space. The table below lists these individuals of various nationalities who have made significant contributions to their space programs. The first Hispanic astronauts completed short flights to a Soviet space station and aboard the space shuttle. In the past 23 years, many more have completed flights to the International Space Station and contributed to its assembly, operations, and research activities.
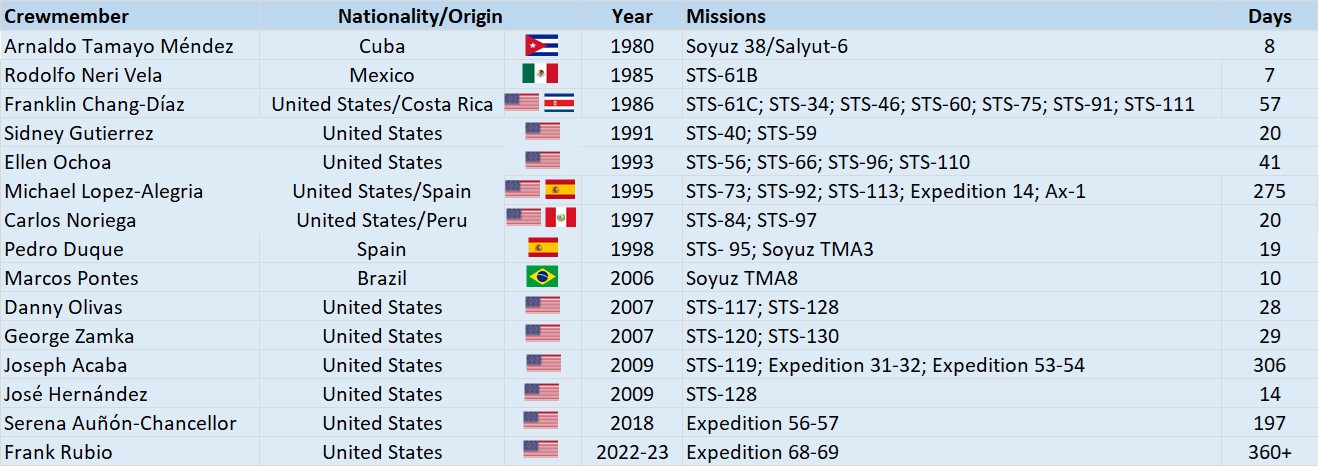
Table of Hispanic astronauts who have flown in space.
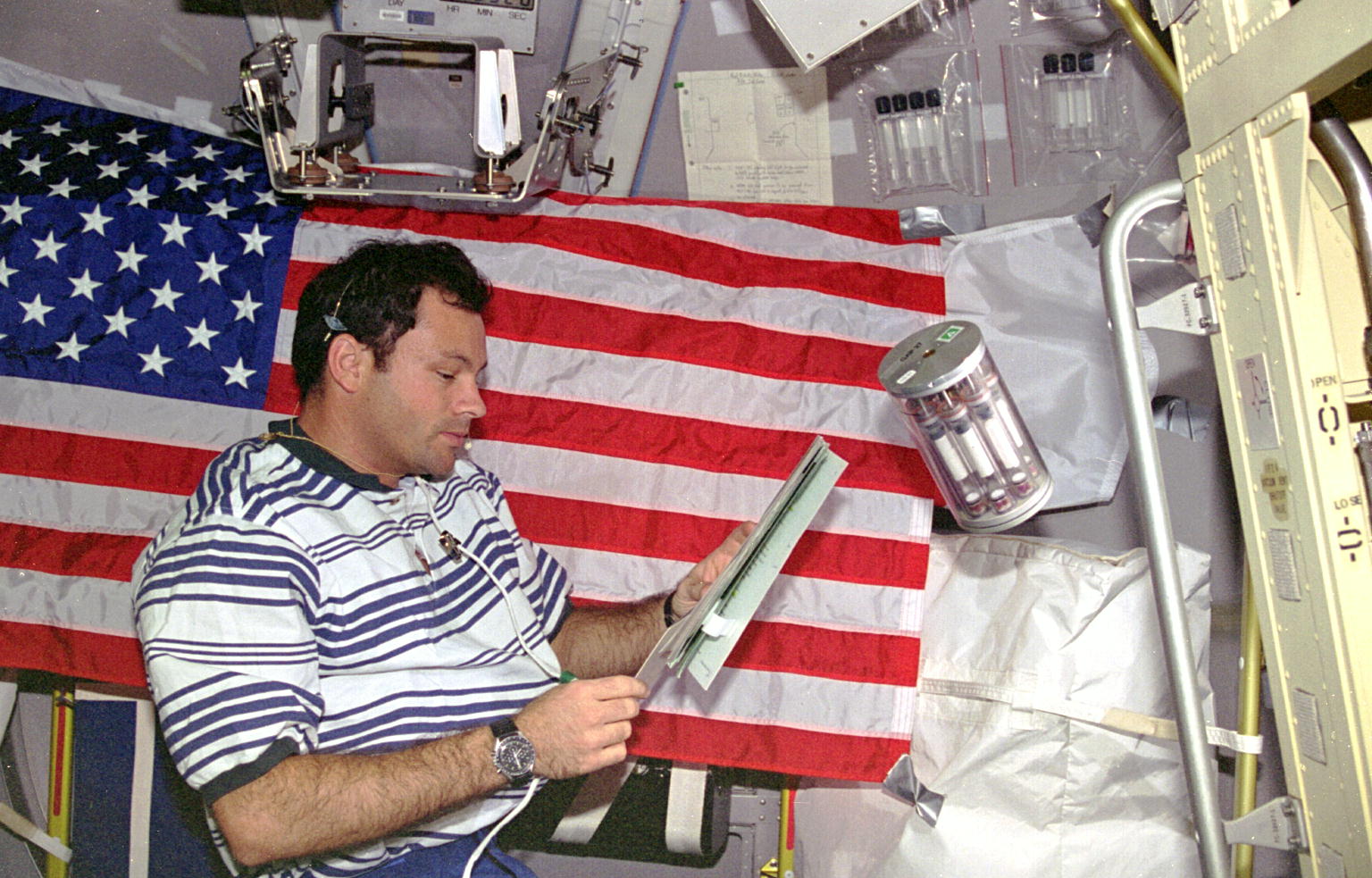
Arnaldo Tamayo Méndez of Cuba holds the title of the first person of Hispanic heritage to fly in space. He spent eight days aboard the Salyut-6 space station in September 1980 as part of the Soviet Union’s Interkosmos program to fly cosmonauts from friendly socialist countries. The first Hispanic to fly on the space shuttle, Payload Specialist Rodolfo Neri Vela of Mexico, also introduced tortillas to astronauts’ on board menus during his flight on STS-61B in November 1985. Tortillas continue to be a staple on the space station today, for everything from breakfast tacos, to burgers, sandwiches, and pizzas. Selected as an astronaut in 1980, Costa Rican-born Franklin R. Chang-Díaz holds the honor as the first Hispanic American in space. He flew in space a record-tying seven times, including one visit to the Russian space station Mir and one to the International Space Station.
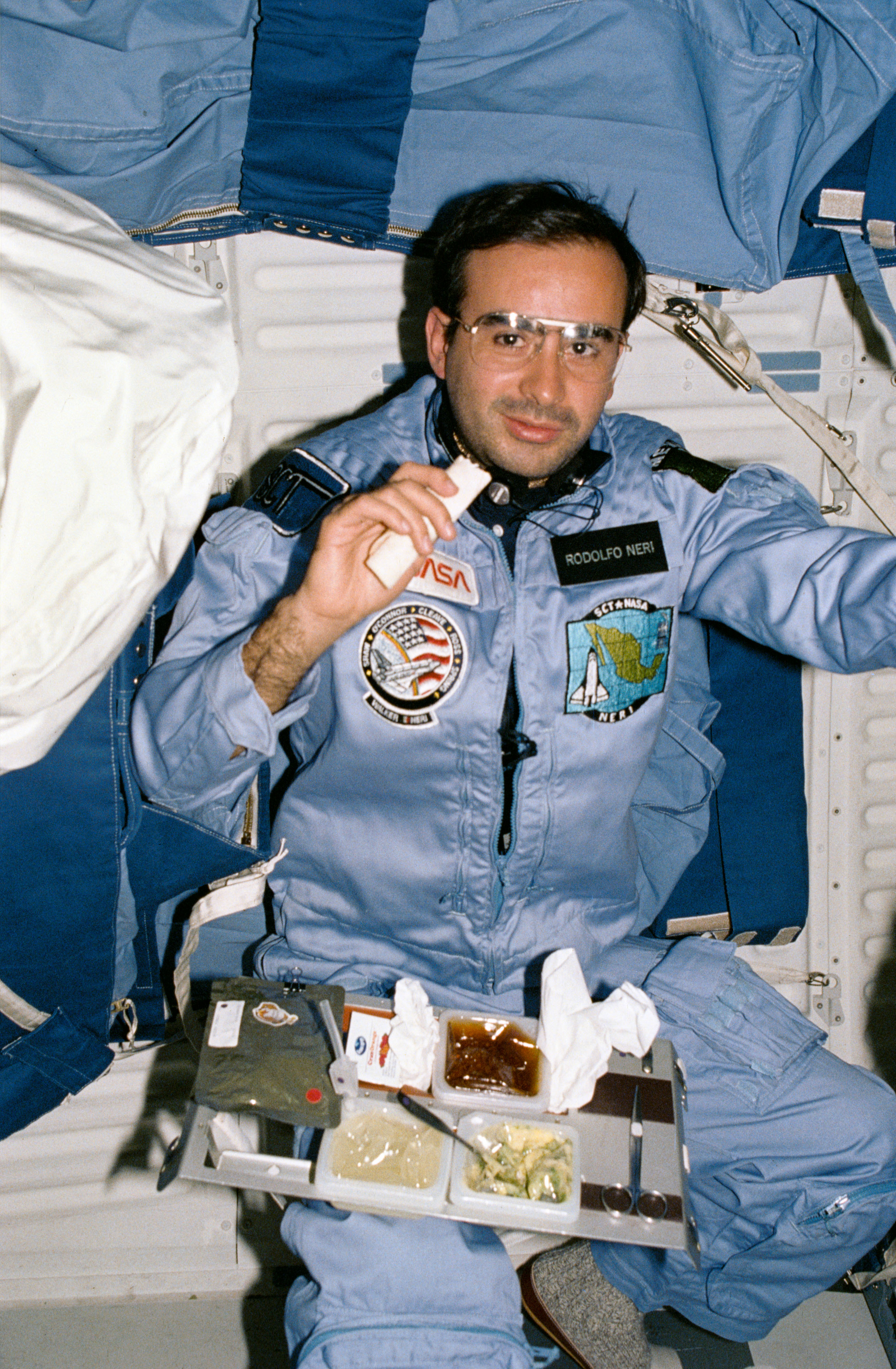
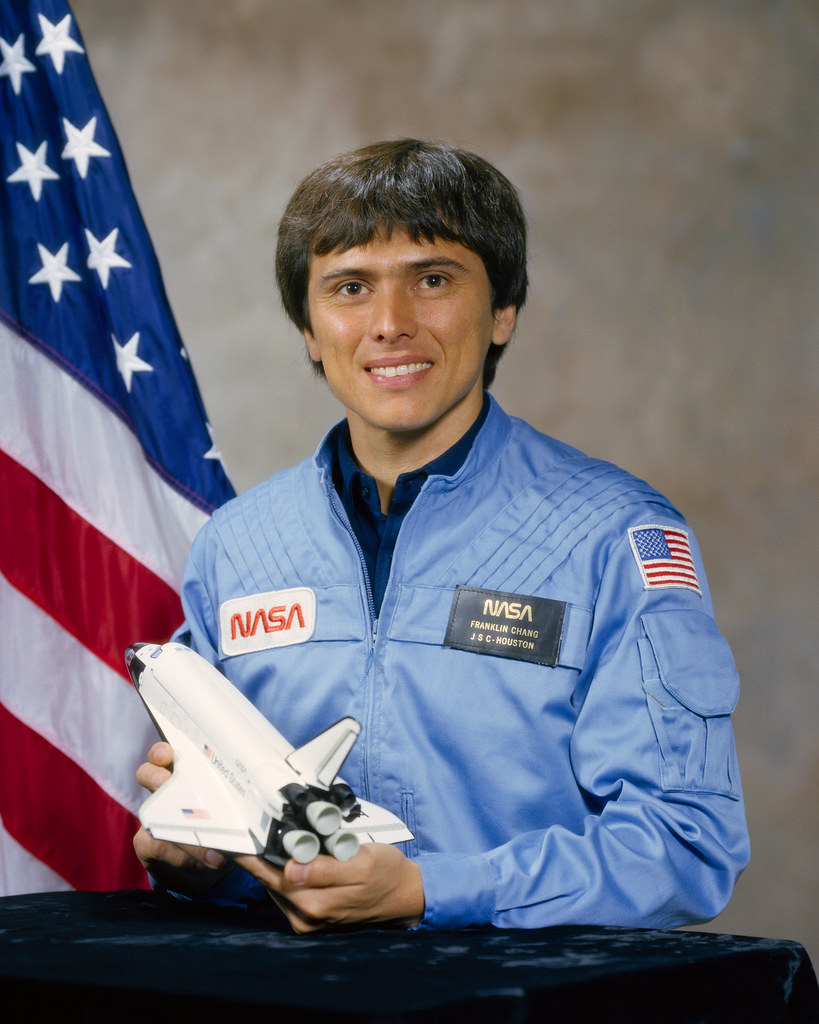



Left: Portrait of Cuban cosmonaut Arnaldo Tamayo Méndez. Middle: Mexican payload specialist Rodolfo Neri Vela enjoys a trend-setting tortilla during the STS-61B mission. Right: Portrait of NASA astronaut Franklin R. Chang-Díaz.
Franklin R. Chang-Díaz
Chang-Díaz’s first flight, STS-61C aboard space shuttle Columbia, took place in January 1986, a six-day flight to deploy a communications satellite and to remotely observe Halley’s comet. The crew included two future NASA administrators, NASA astronauts Charles F. Bolden and U.S. Senator (D-FL) C. William “Bill” Nelson. The flight landed just 10 days before the tragic loss of space shuttle Challenger. His next mission, STS 34 aboard Atlantis, in October 1989 saw the deployment of the Galileo spacecraft to explore Jupiter with an orbiter and an atmospheric probe. Chang-Díaz launched on his third mission, STS 46 in July 1992, an eight-day flight aboard Atlantis to test fly the first Tethered Satellite System (TSS-1).
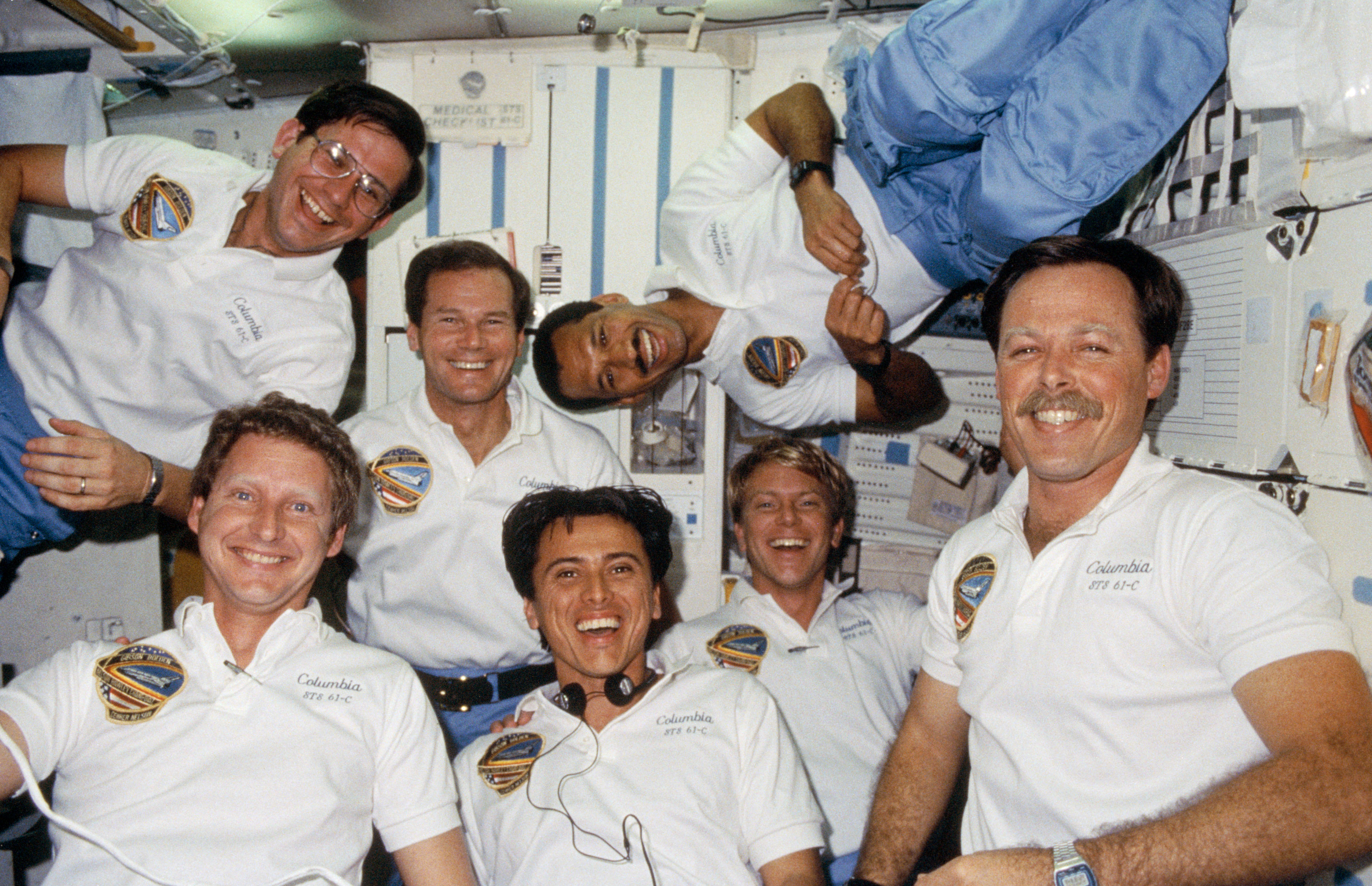
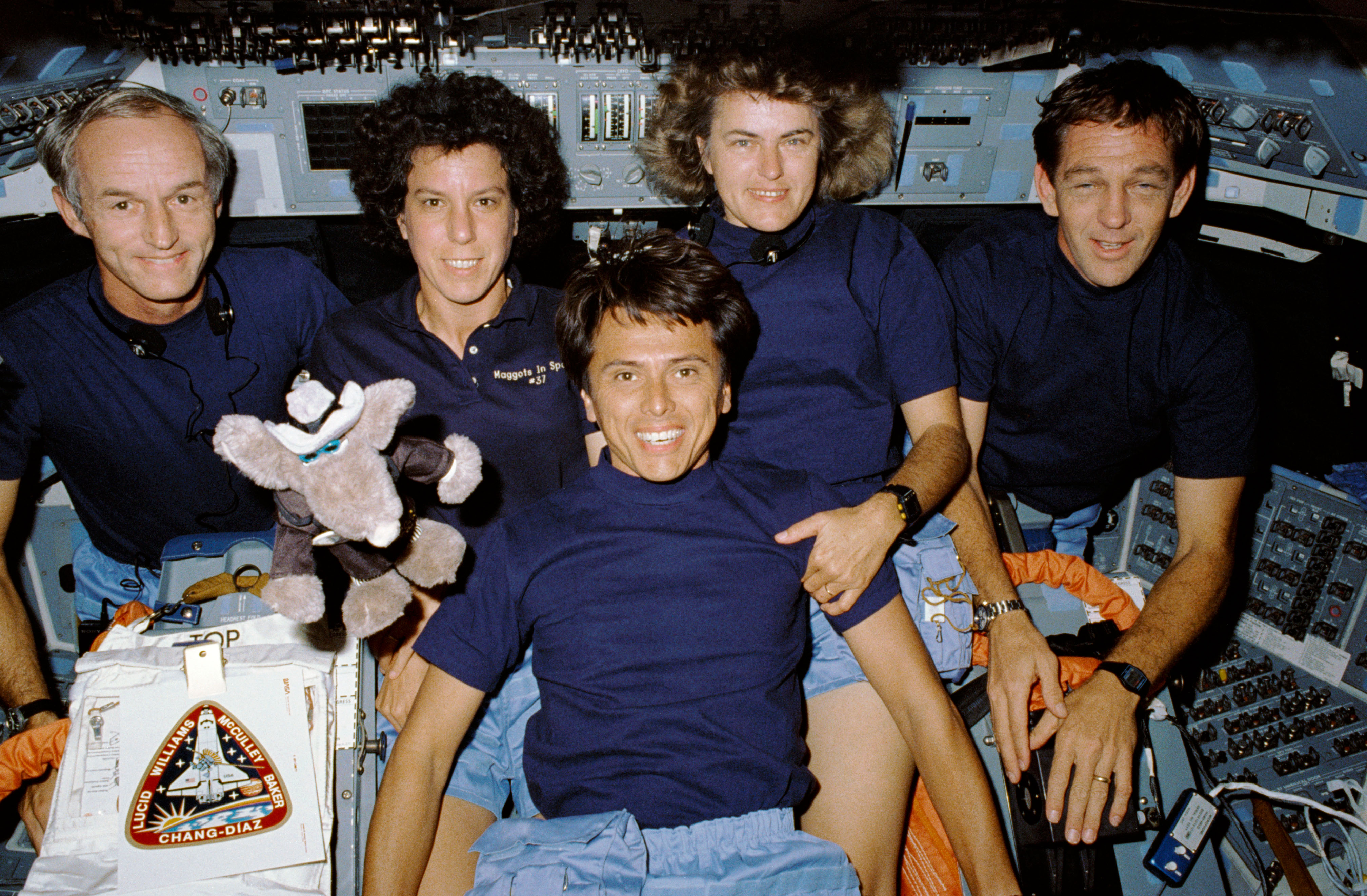
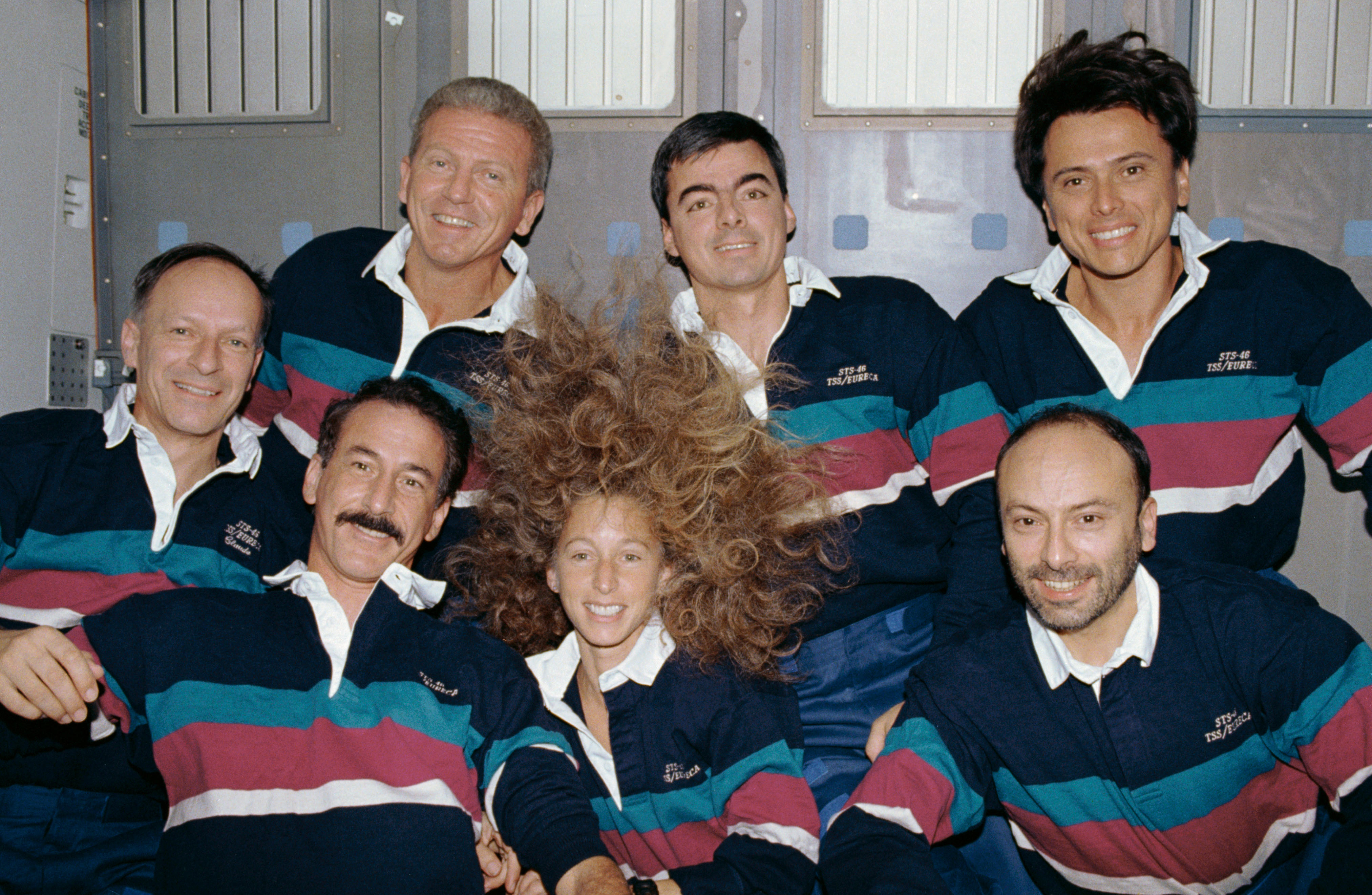



Left: Franklin R. Chang-Díaz, center, the first Hispanic American astronaut, with his fellow STS-61C crew members. Middle: Chang-Díaz, center, and the STS-34 crew. Right: Chang-Díaz, upper right, with the STS-46 crew.
Chang-Díaz returned to space for his fourth mission in January 1994 aboard Discovery. The eight-day STS-60 flight comprised the first flight in the Shuttle-Mir program, with Russian cosmonaut Sergey K. Krikalev a member of the crew. Chang-Díaz launched on his fifth flight in February 1996, the 16-day STS-75 mission aboard Columbia to refly the TSS. On his sixth mission in June 1998, the STS-91 crew docked Discovery with the Russian space station Mir and returned astronaut Andrew S.W. Thomas to earth, the final Shuttle-Mir mission.
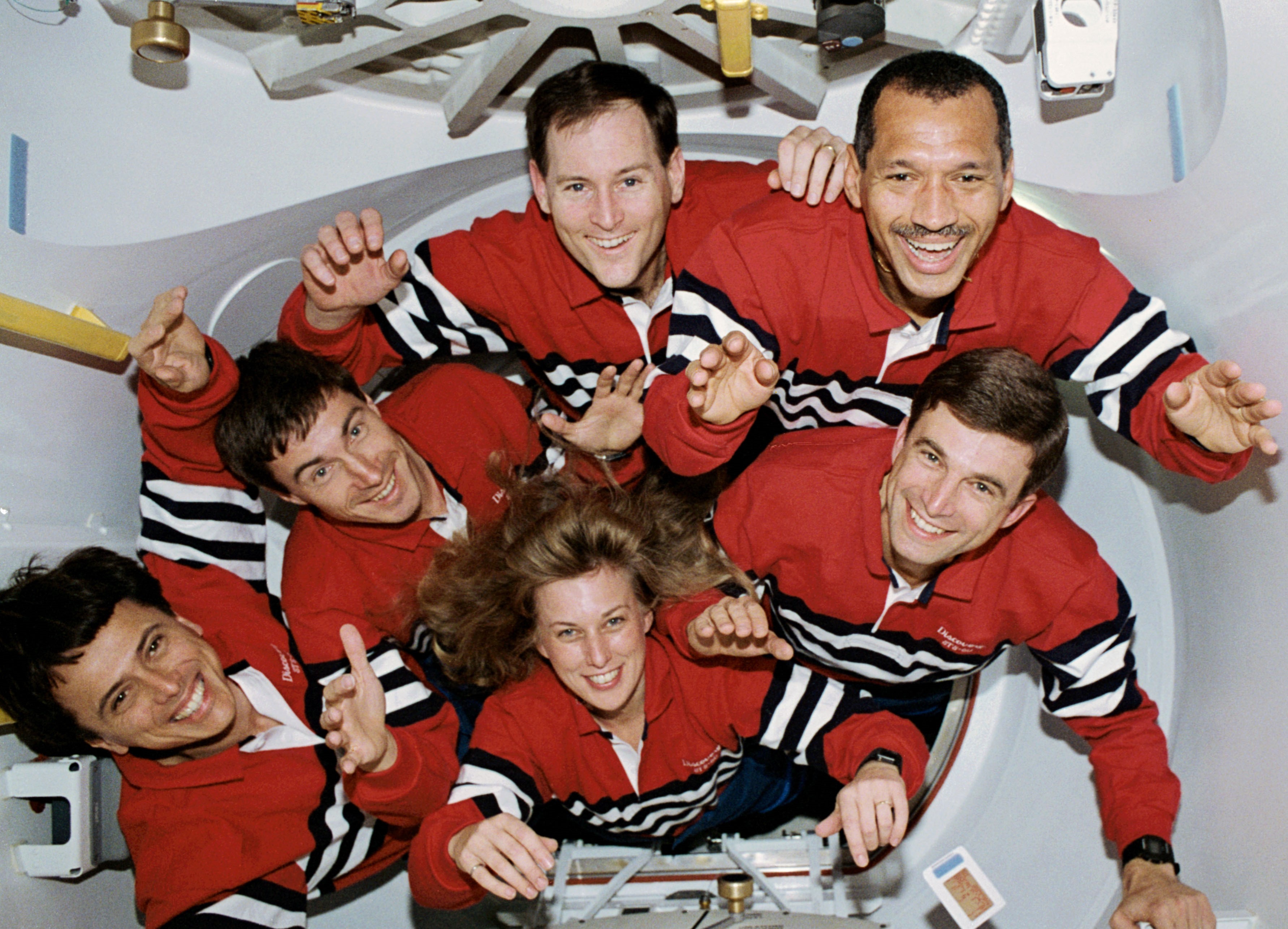
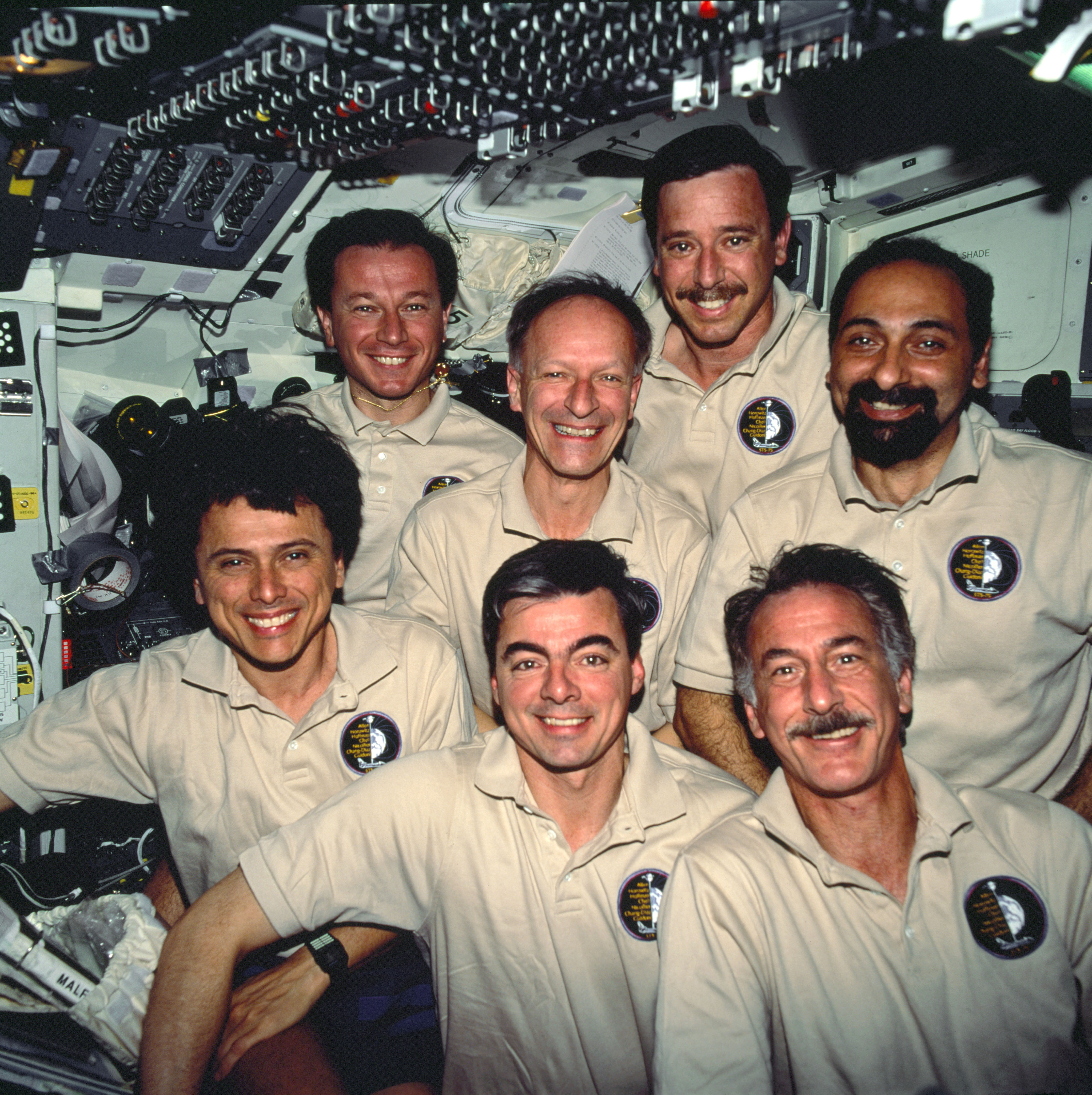



Left: Franklin R. Chang-Díaz, lower left, with the STS-60 crew. Middle: Chang-Díaz, left, with his STS-75 crew mates.
Right: Chang-Díaz, with the STS-91 and Mir 25 crews.
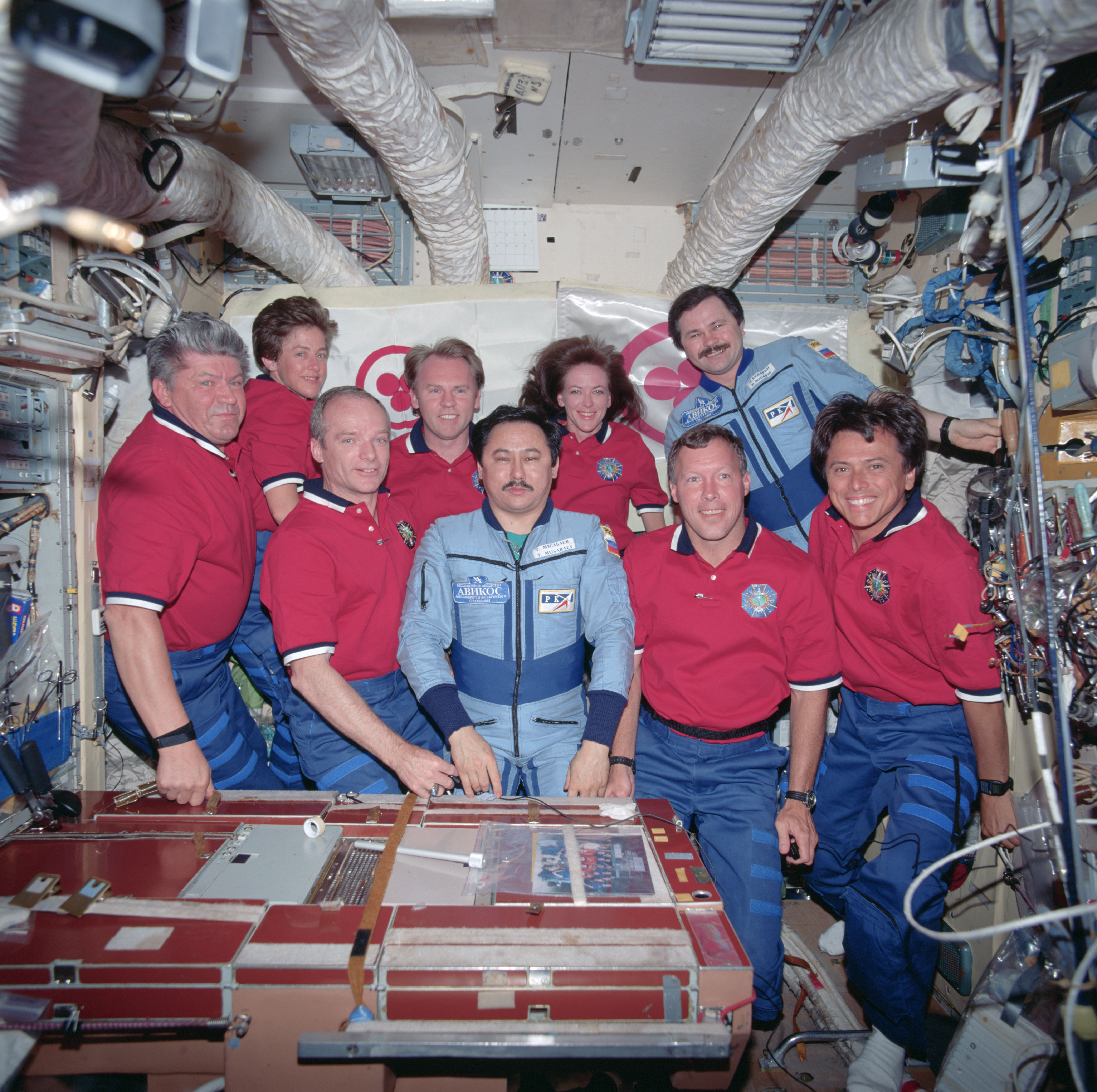
During his record-tying seventh trip into space, Chang-Díaz made his only visit to the space station. The main goals of Endeavour’s STS-111 mission in June 2002, included the exchange of the Expedition 4 and 5 crews and the resupply of the station using the Leonardo Multi-Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM). Two new research facilities rode in the MPLM, the fifth Expedite the Processing of Experiments to the Space Station (EXPRESS) rack and the Microgravity Sciences Glovebox. Chang-Díaz completed three spacewalks with his fellow mission specialist, French astronaut Philippe Perrin, to install the Mobile Base System portion of the Canadarm2’s remote manipulator system and perform maintenance tasks on the station.
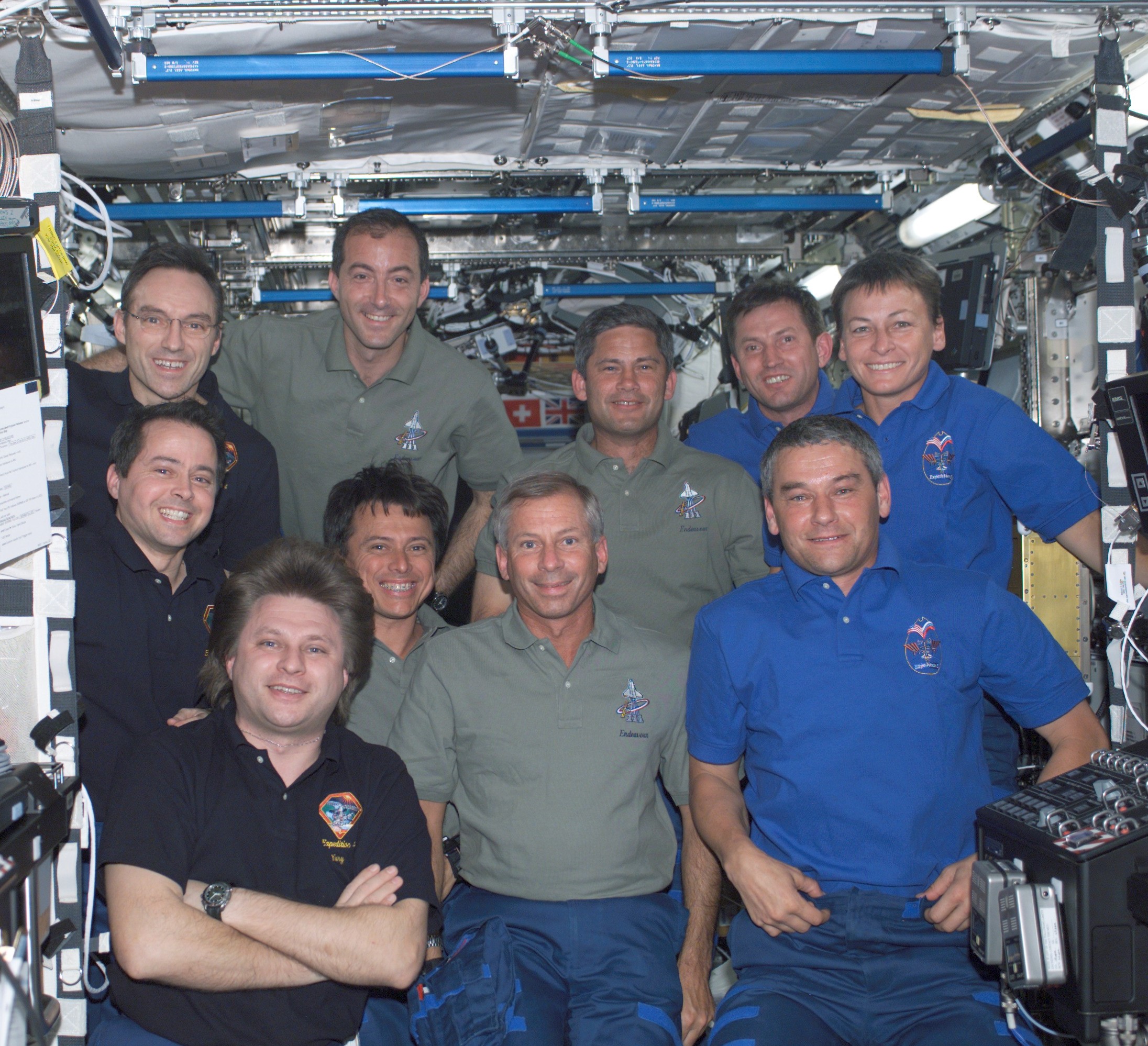
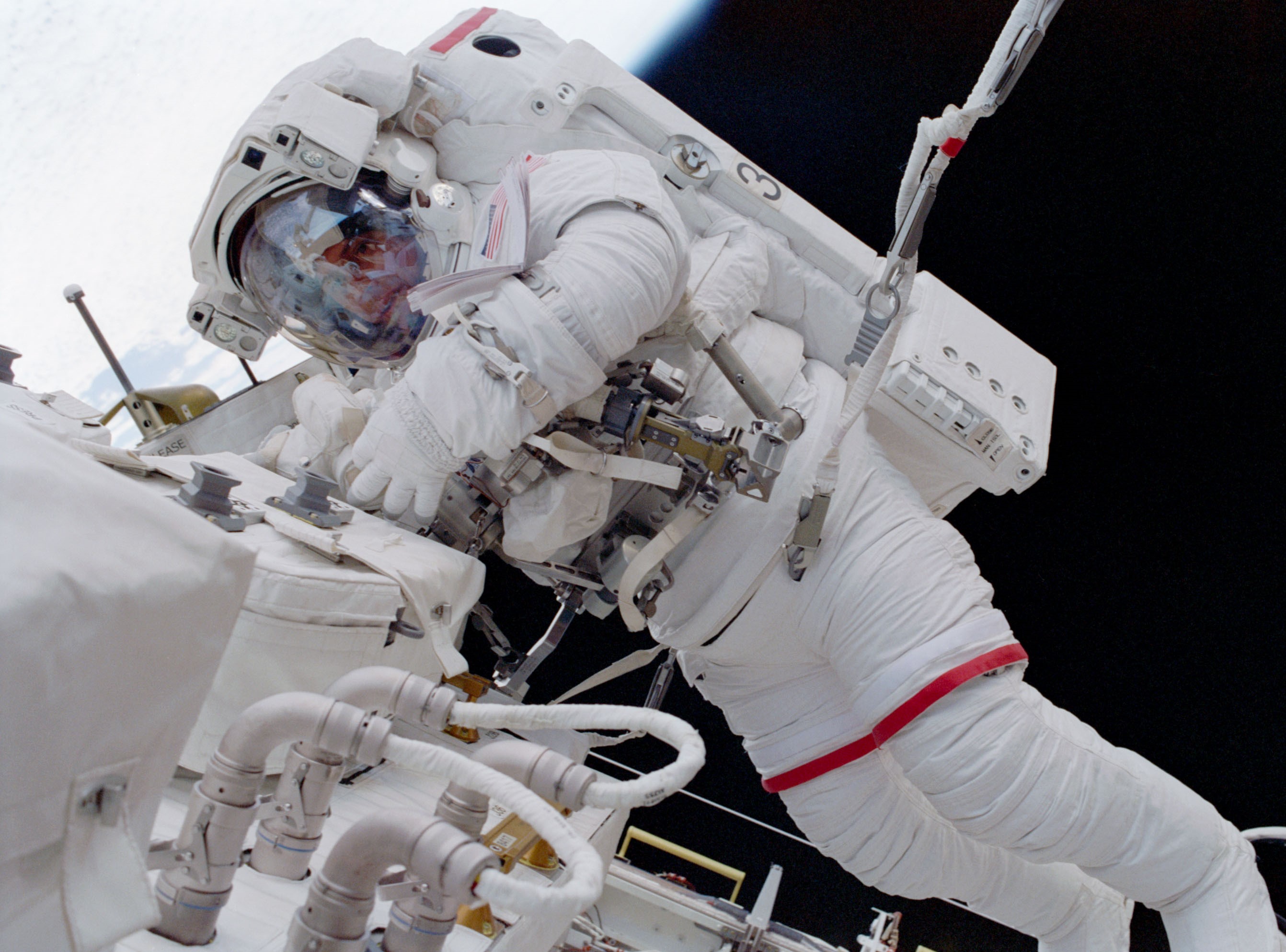
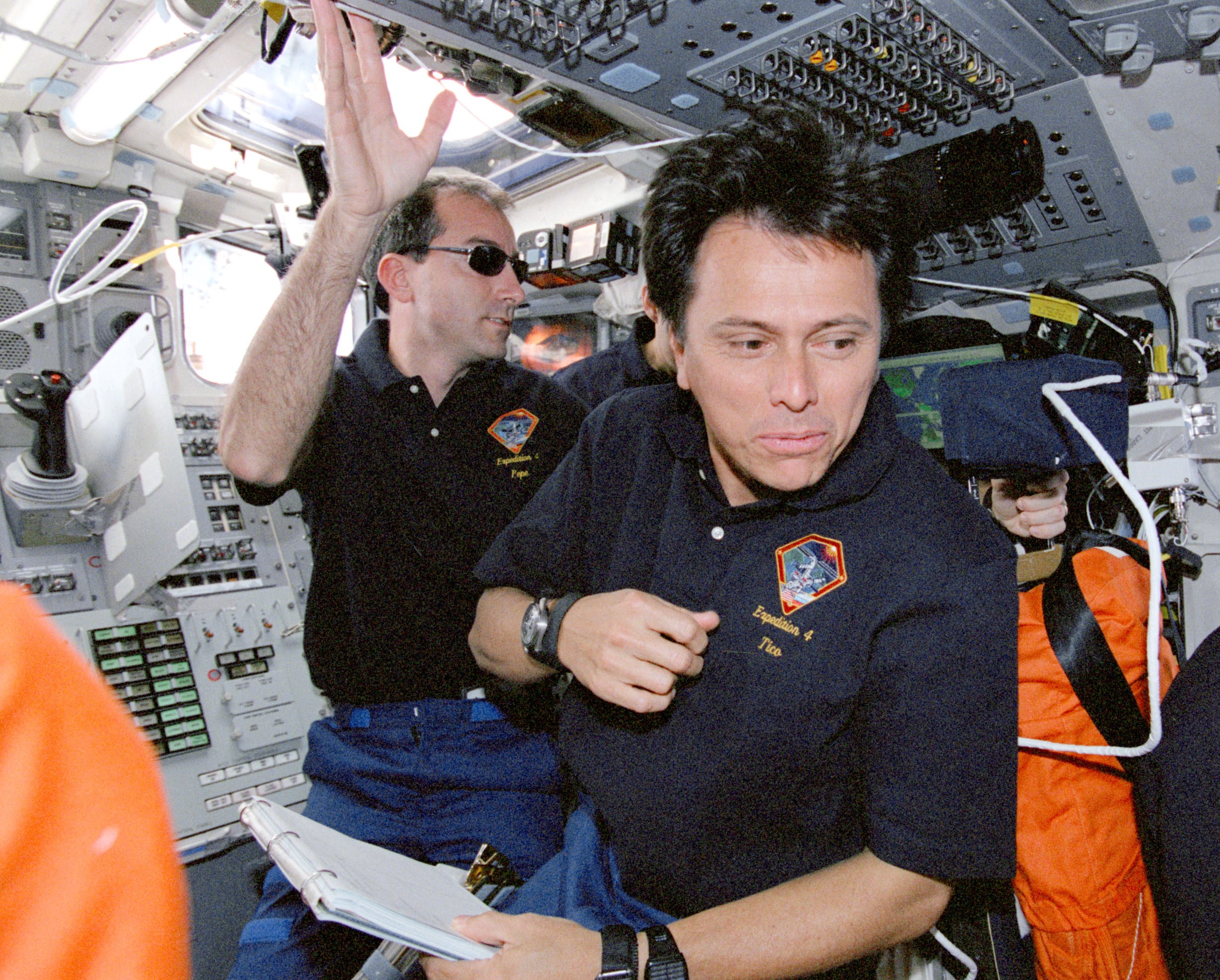



Left: NASA astronaut Franklin R. Chang-Díaz, left of center, with his STS-111 crewmates and the Expedition 4 and 5 crews. Middle: Chang-Díaz during the first STS-111 spacewalk. Right: Chang-Díaz in Endeavour’s middeck following undocking from the space station.
Sidney M. Gutierrez
NASA selected New Mexico native Sidney M. Gutierrez as an astronaut in 1984. On his first mission in June 1991, he served as the pilot of Columbia on the STS-40 Spacelab Life Sciences-1 mission, a nine-day flight dedicated to investigating the responses of the human body to weightlessness. He also served as a test subject for several of the experiments. During his second mission in April 1994, Gutierrez served as the commander of STS-59, the Space Radar Laboratory-1 flight, an 11-day mission aboard Endeavour. The payload included a synthetic aperture imaging radar.
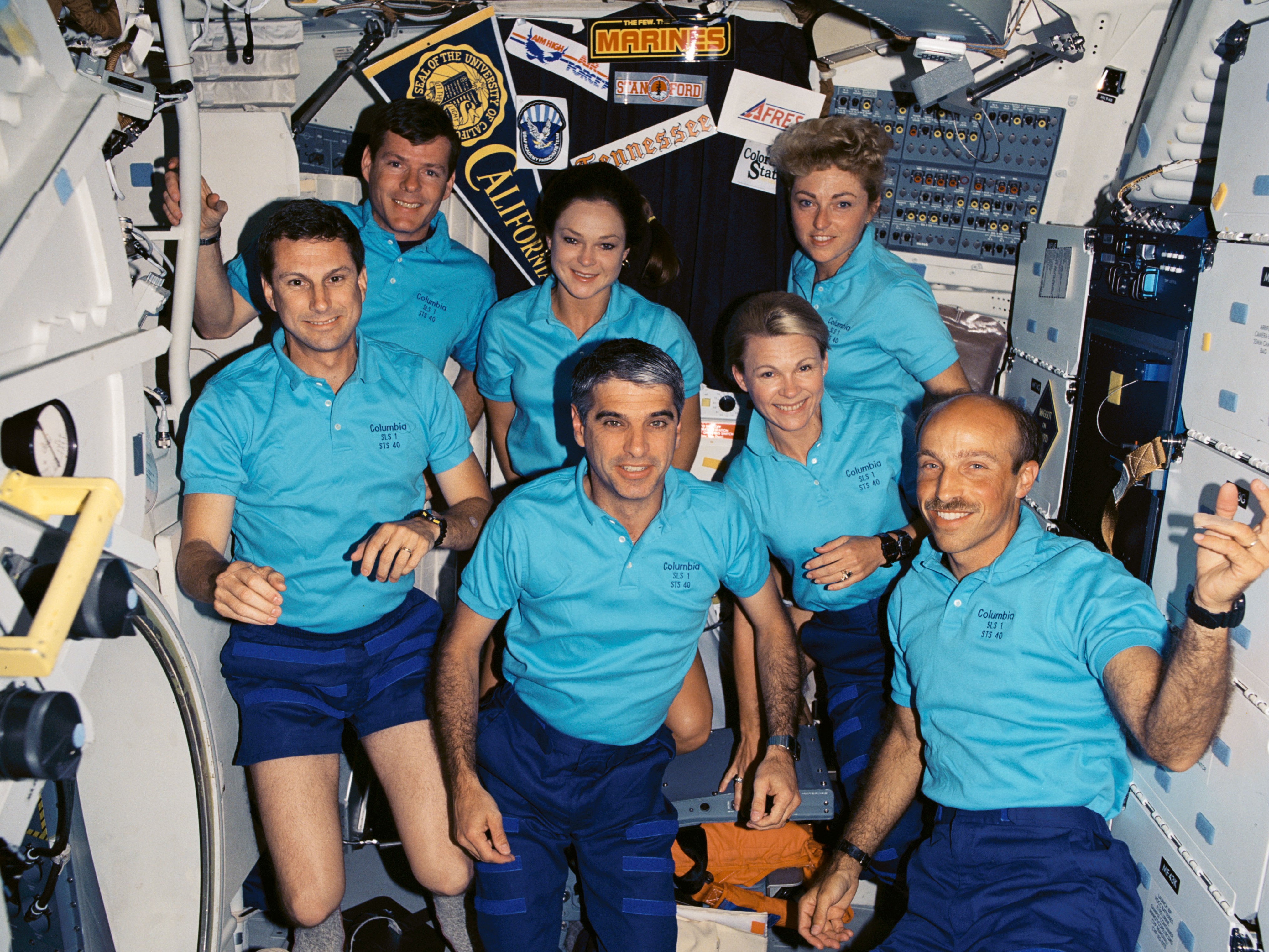
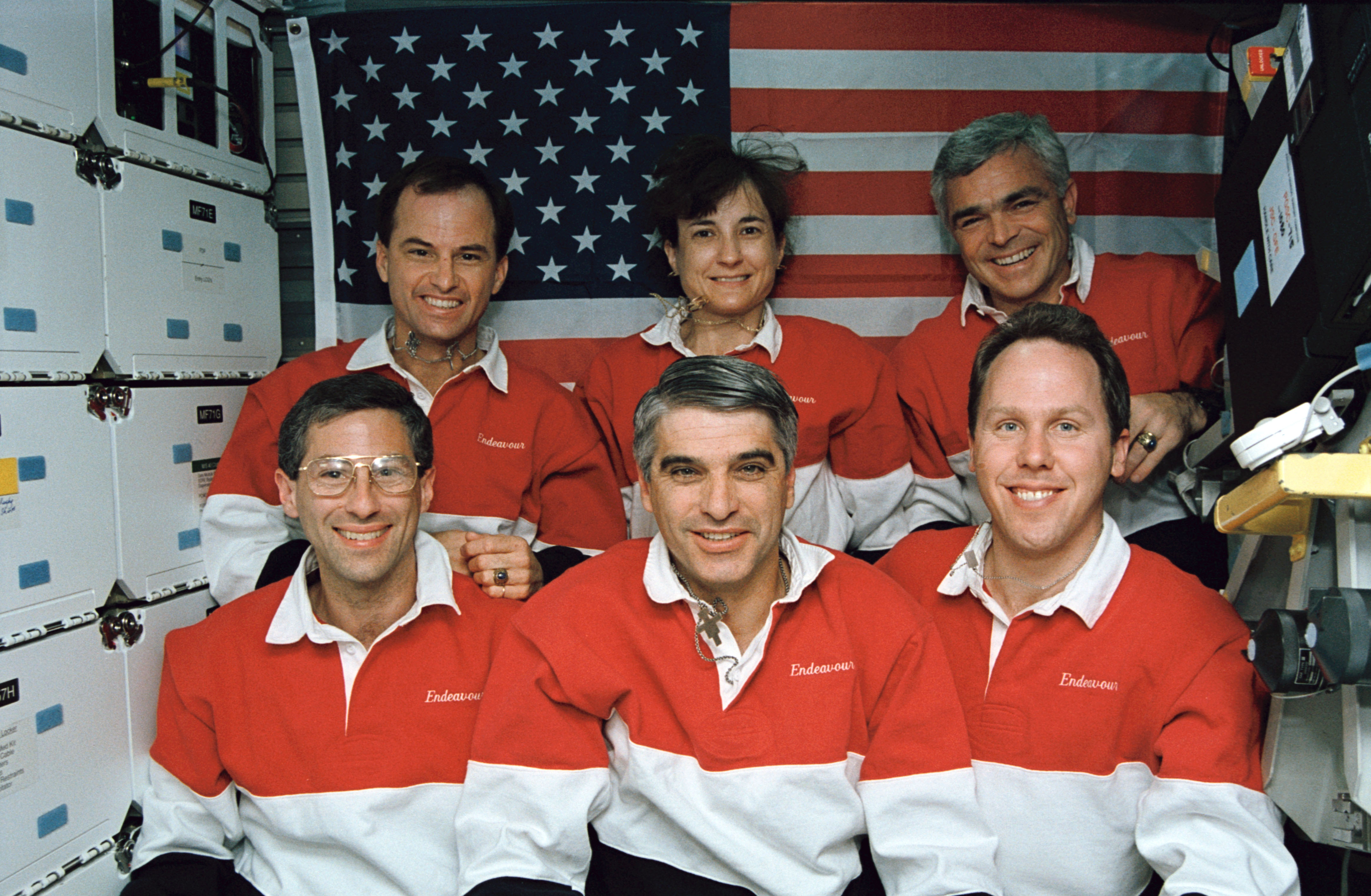


Left: NASA astronaut Sidney M. Gutierrez, center, with his STS-40 crew mates. Right: Gutierrez, center, with the STS-59 crew.
Ellen Ochoa
Selected as the first female Hispanic astronaut in 1990, Ellen Ochoa completed four spaceflights and then served as the first Hispanic director of NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston. On her first mission in April 1993, she served as a mission specialist on the nine-day STS-56 flight, the second Atmospheric Laboratory for Applications and Science (ATLAS) mission aboard Discovery. An accomplished flautist, she played her flute during the flight. On her second flight, STS-66 in March 1994, Ochoa flew aboard Atlantis and operated the experiments of the ATLAS-3 payload during the 11-day mission.
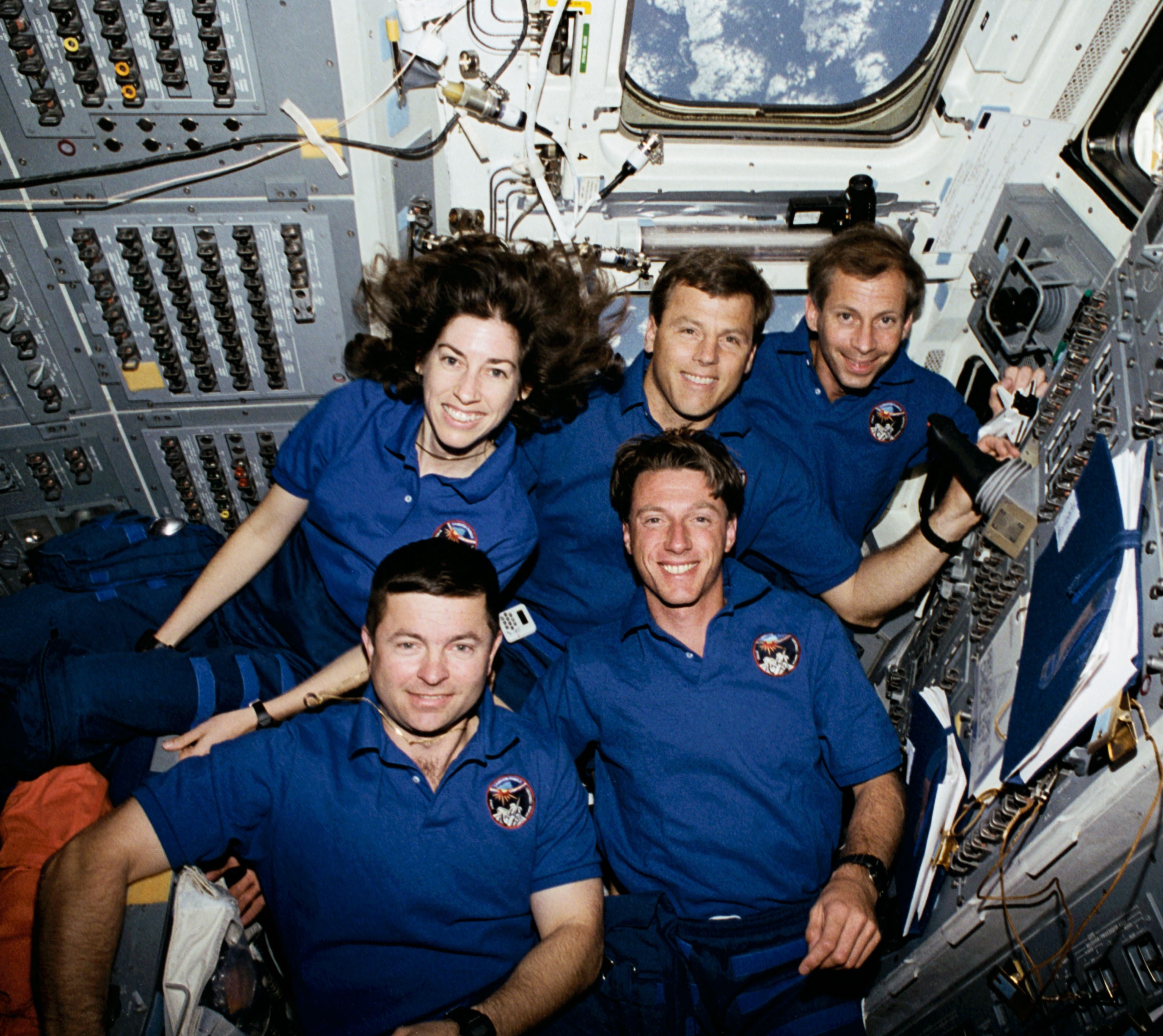
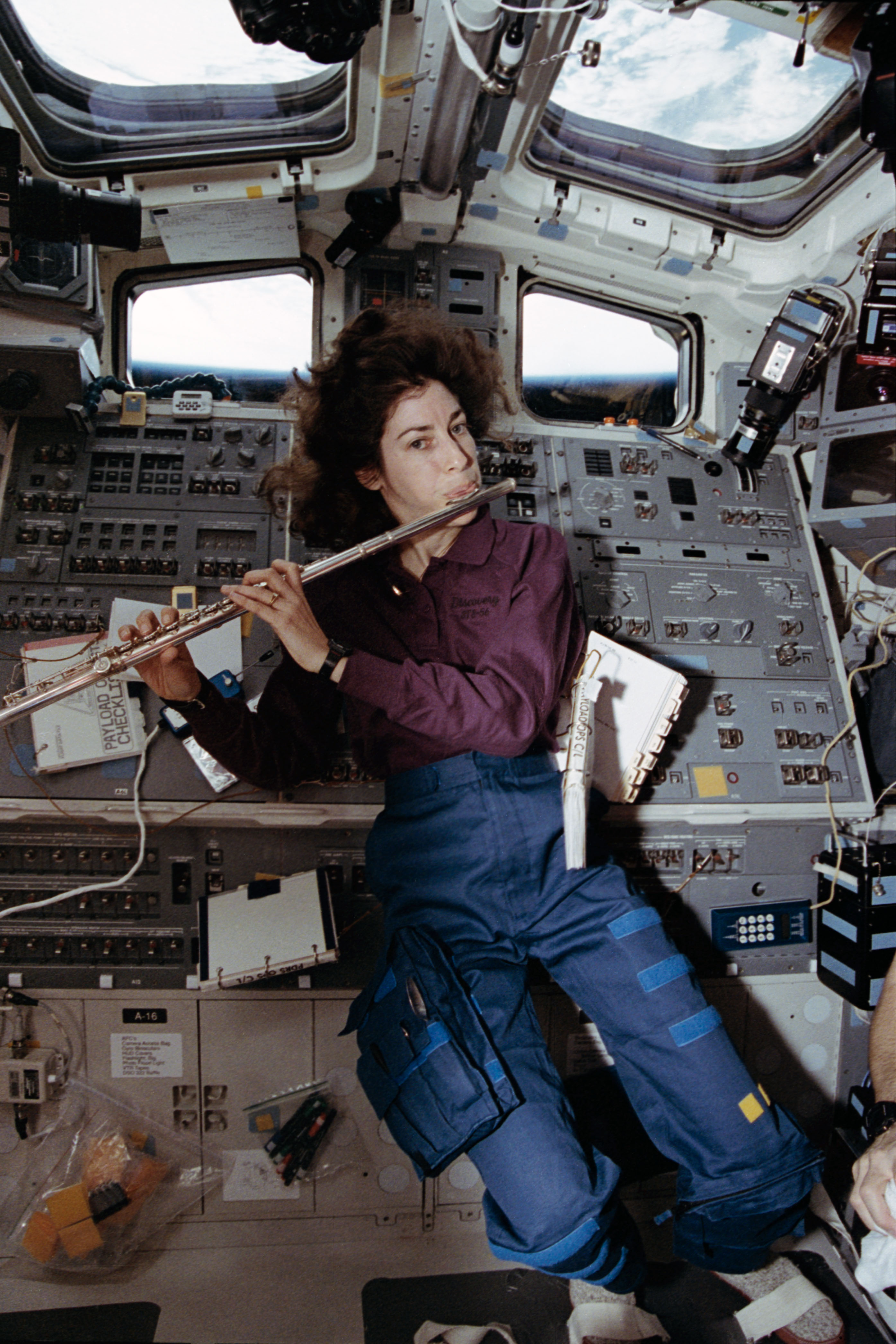
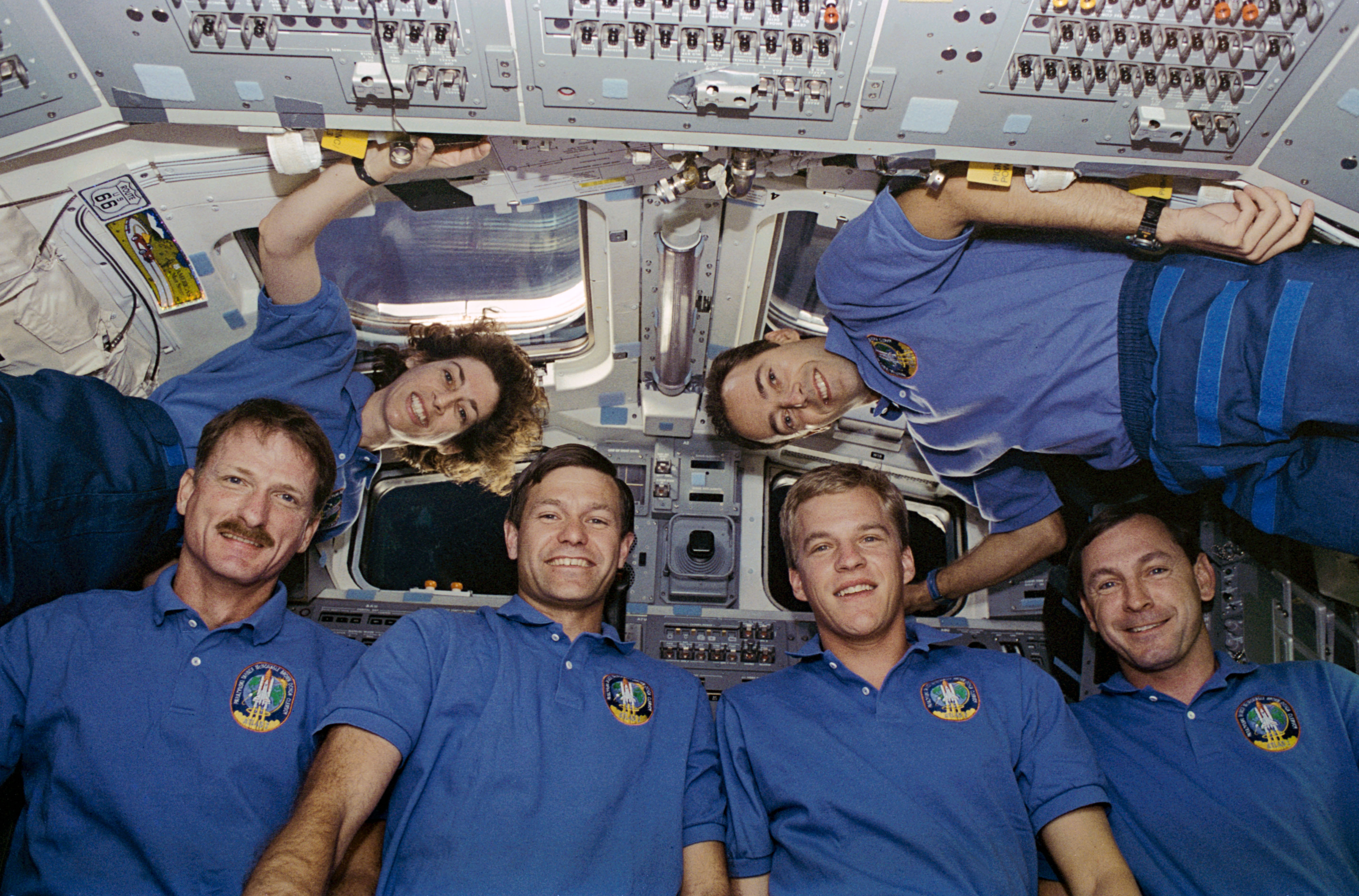



Left: Ellen Ochoa, top left, and the rest of the STS-56 crew. Middle: Ochoa plays the flute on Discovery’s flight deck. Right: Ochoa, top left, and the rest of the STS-66 crew.
Ochoa holds the distinction as the first Hispanic astronaut to visit the space station, making her first visit in May 1999 as a mission specialist aboard Discovery’s 10-day STS-96 mission. The goals of the mission – only the second shuttle flight to the station that, at the time, comprised only two modules – included the transfer of two tons of logistics to the station, launched inside a Spacehab double module, and the delivery of the Russian Strela cargo crane.
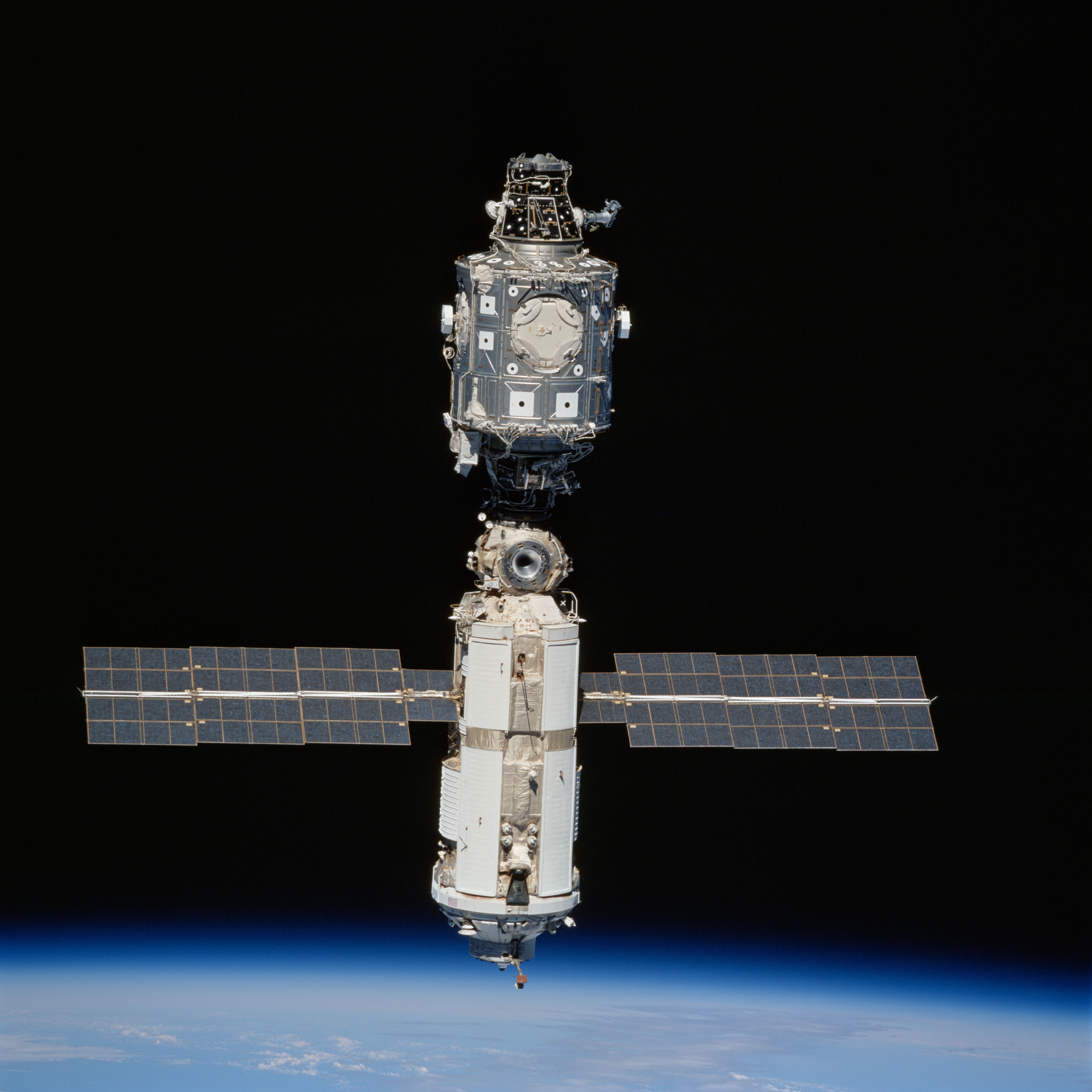
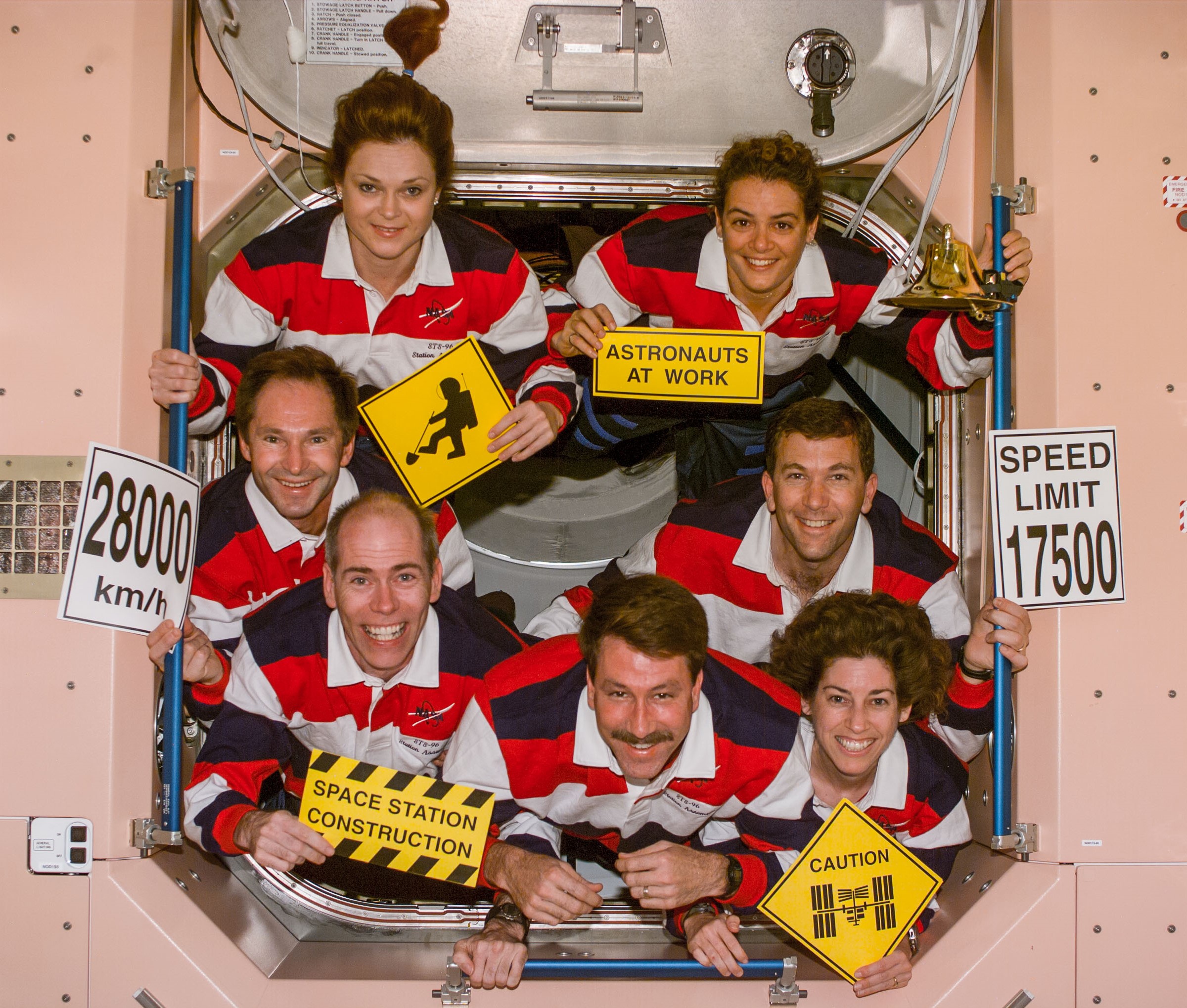
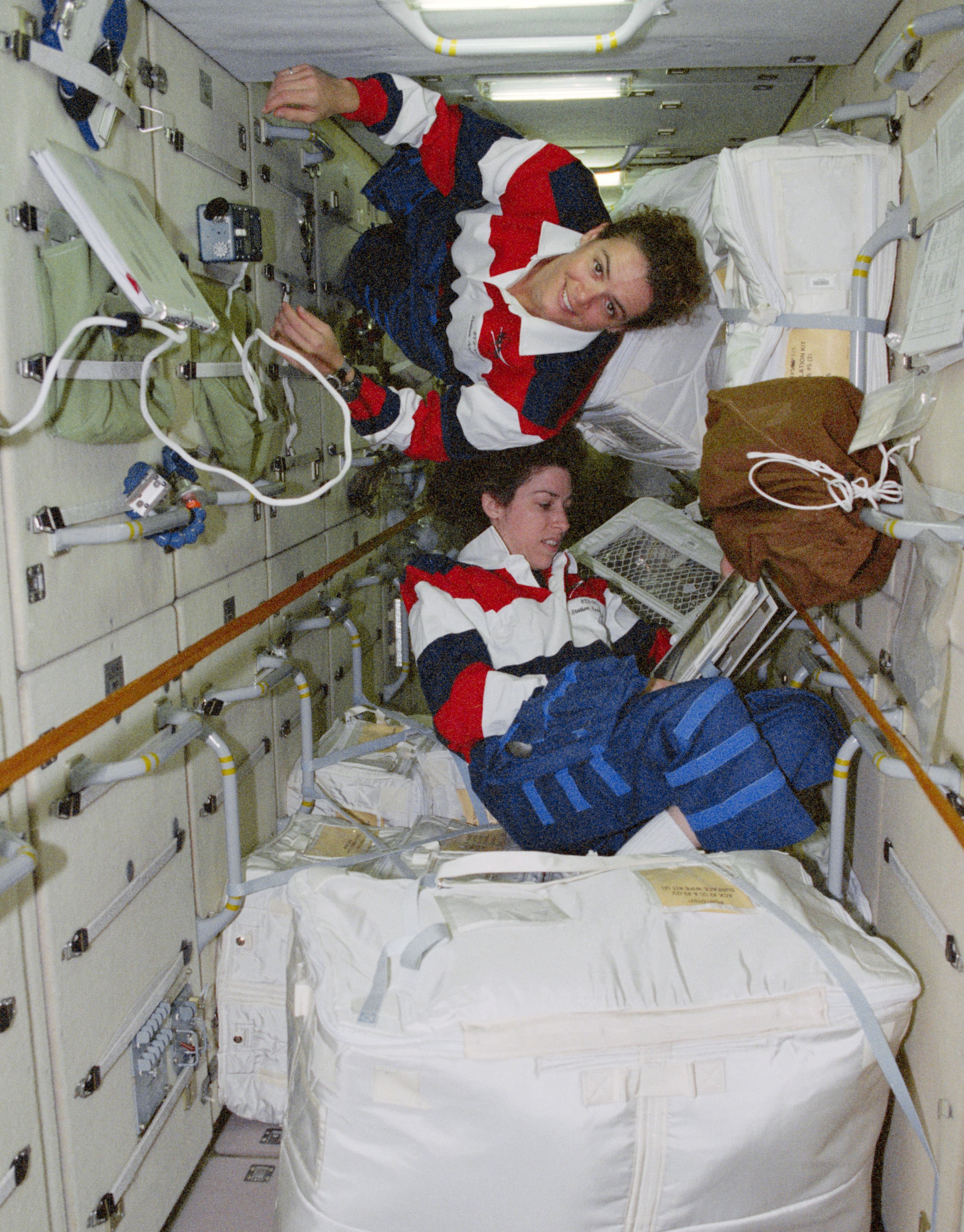



Left: The space station as seen from STS-96. Middle: NASA astronaut Ellen Ochoa, lower right, with the STS-96 crew in the Unity Node 1. Right: Ochoa, bottom, with fellow STS-96 crewmembers Julie Payette of the Canadian Space Agency in the Zarya module.
Ochoa returned to a much-enlarged space station aboard space shuttle Atlantis in April 2002 during the STS-110 mission that delivered the 13-ton S0 truss – the center segment section to which future truss segments were later attached. Ochoa operated the Space Station Remote Manipulator System (SSRMS), also known as Canadarm2, to lift the S0 truss from the shuttle’s payload bay and attach it atop the Destiny module. The S0 truss also contained the Mobile Transporter to allow the SSRMS to translate up and down the trusses. Ochoa was named as JSC’s deputy director in 2007, then as JSC’s first Hispanic director in 2013. She served in that position until her retirement from NASA in 2018.
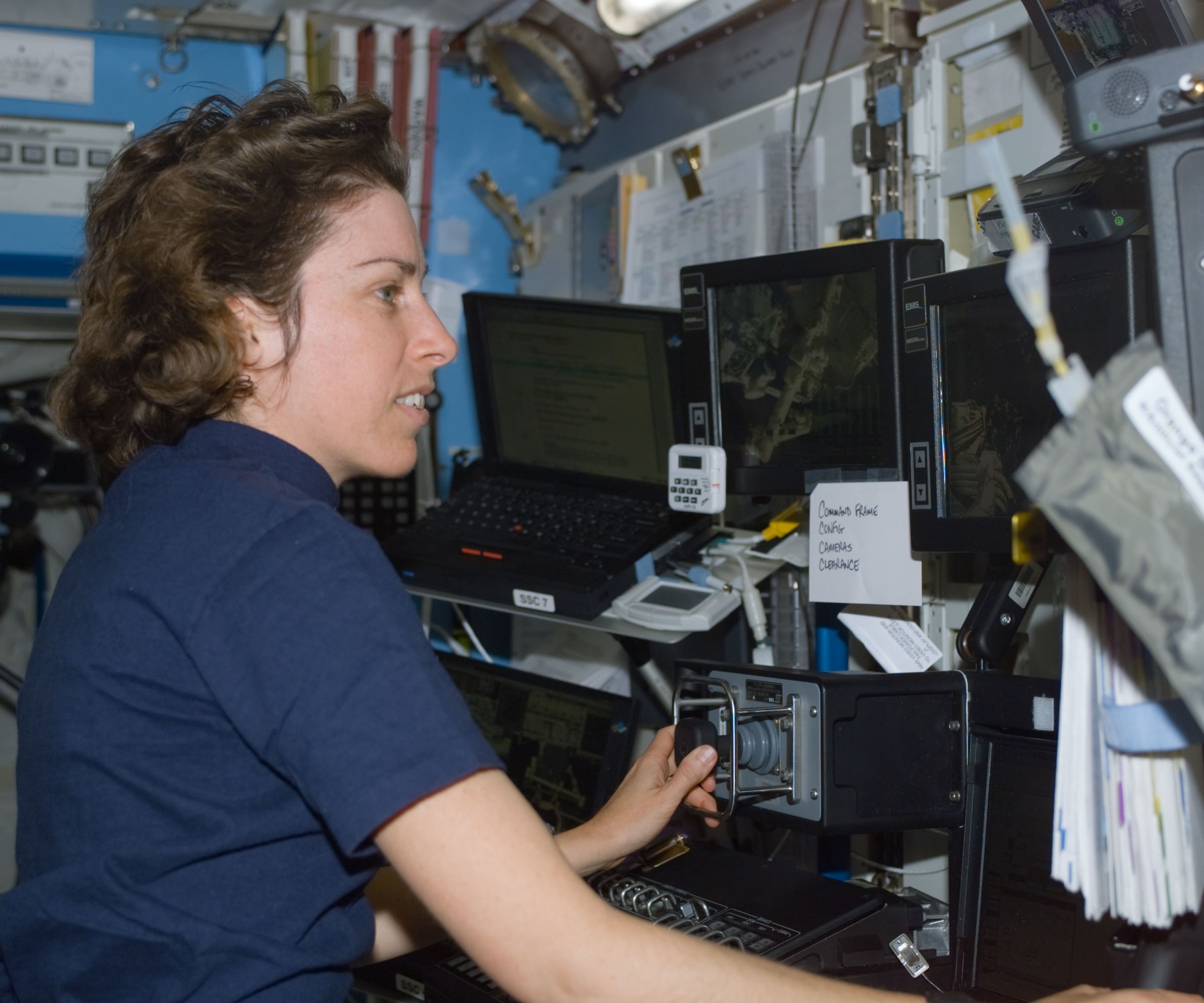
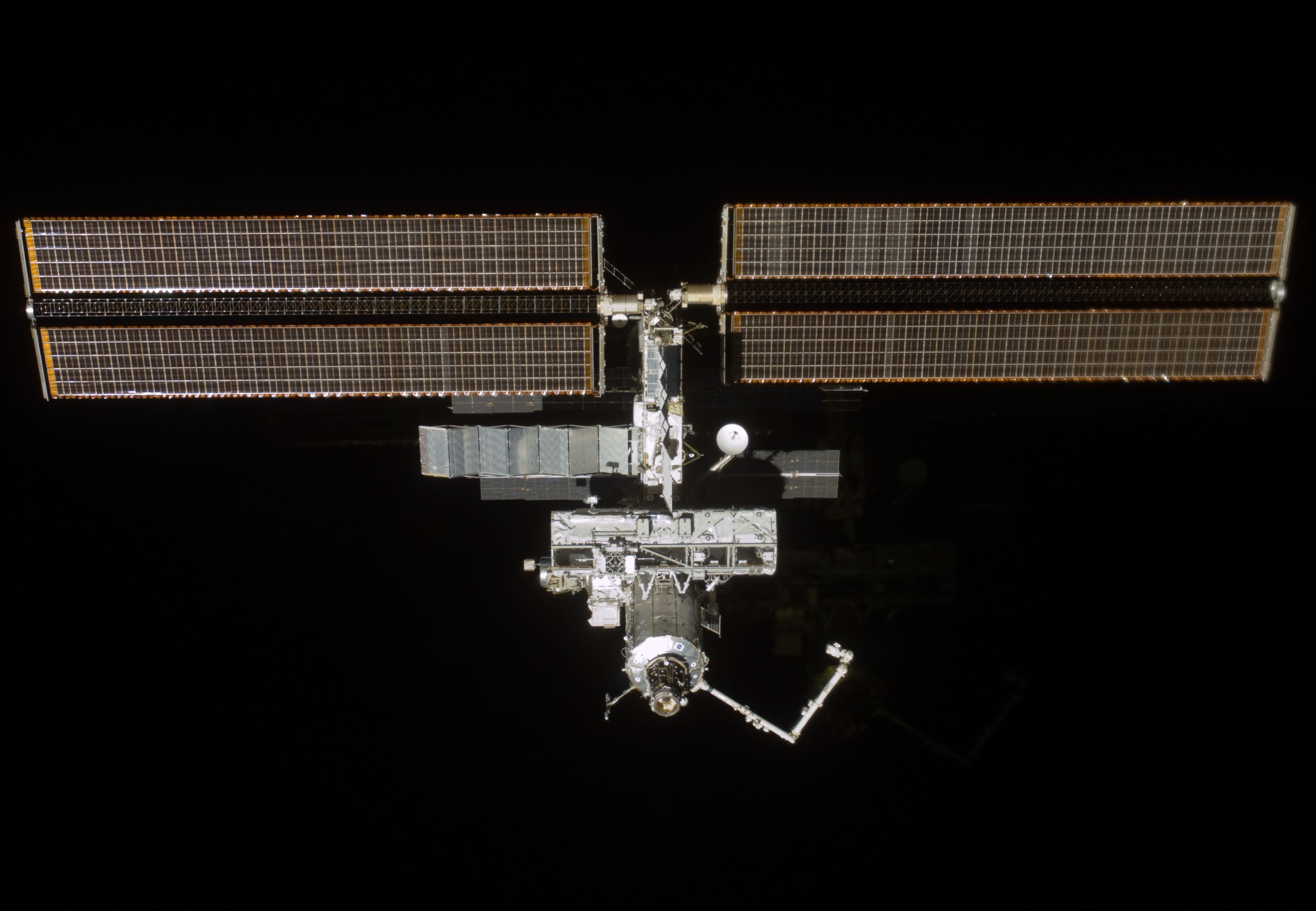
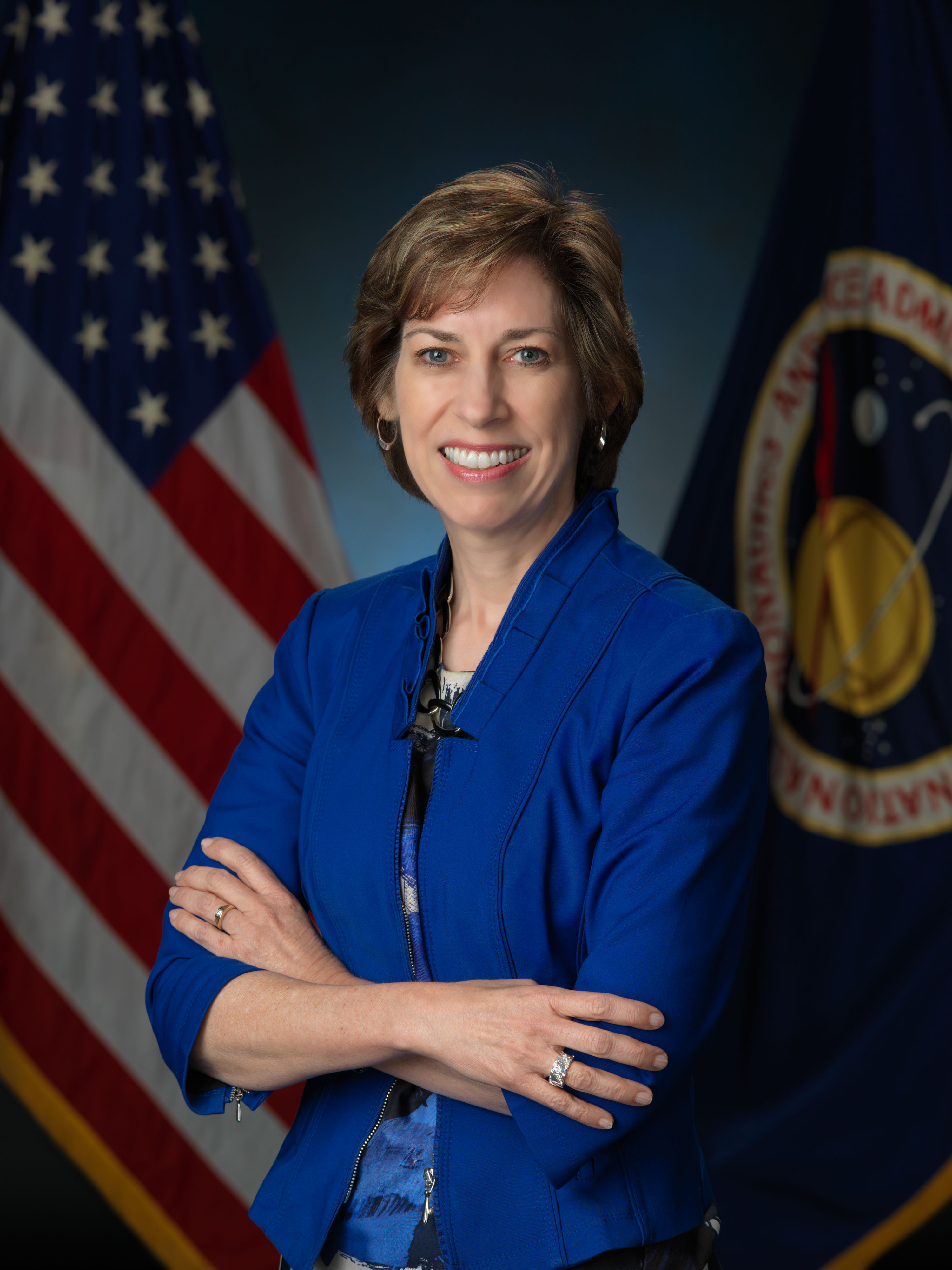



Left: NASA astronaut Ellen Ochoa operating Canadarm2 in the Destiny module. Middle: The space station as seen from the departing STS-110, showing the S0 truss mounted on Destiny. Right: Portrait of Ochoa as director of NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston.
Michael E. Lopez-Alegria
NASA selected Michael E. “LA” Lopez-Alegria, born in Madrid, Spain, as an astronaut in 1992. On his first spaceflight, he served as a mission specialist on STS-73, the second flight of the United States Microgravity Laboratory. The 16-day mission aboard Columbia in October 1995 included 37 investigations supported by 11 facilities, with the seven-member crew working around the clock in two shifts in a Spacelab module.
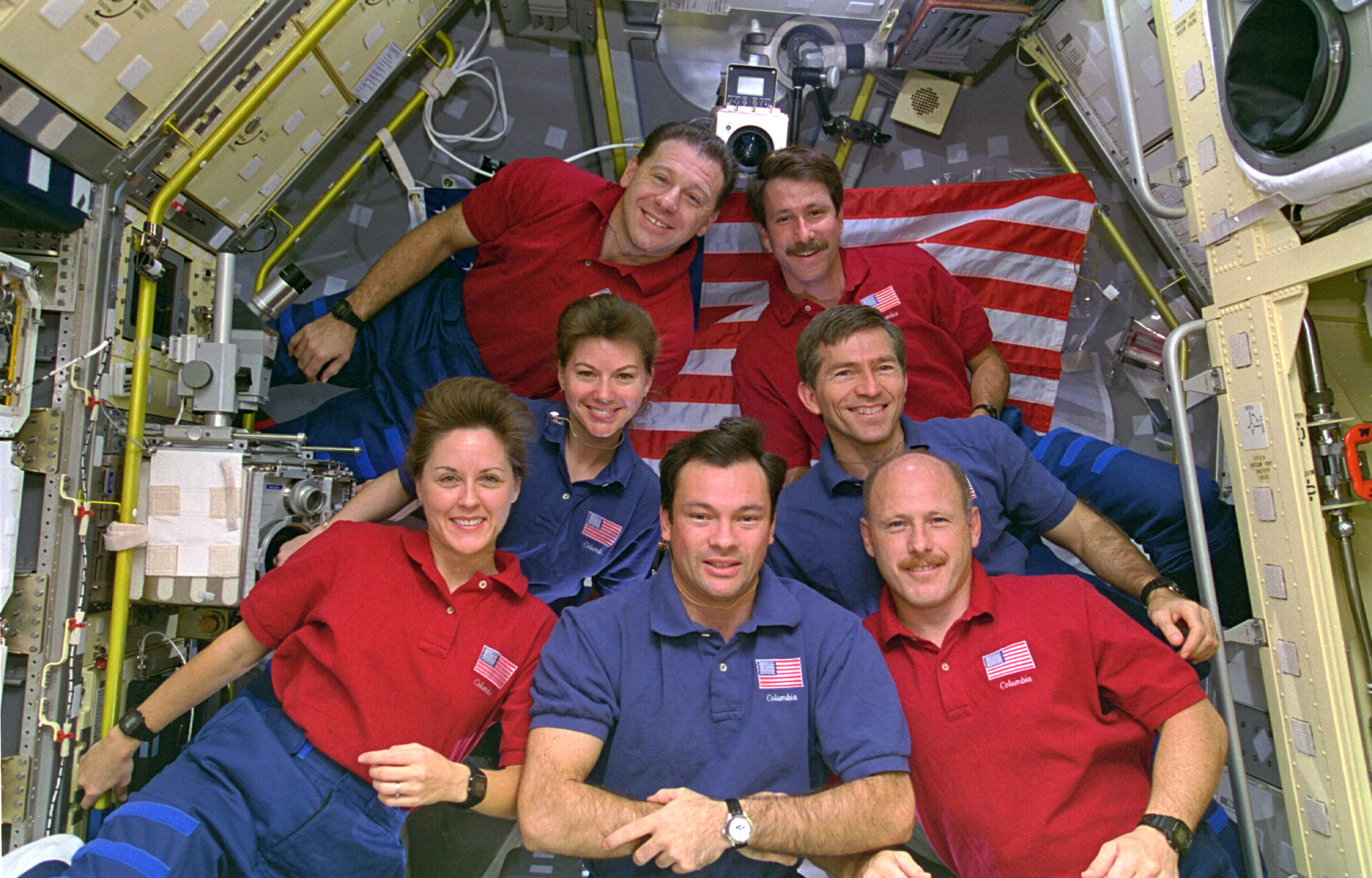


Left: Michael E. Lopez-Alegria, center, with the rest of the STS-73 crew inside the Spacelab module. Right: Lopez-Alegria working on biological experiment in the Spacelab module.
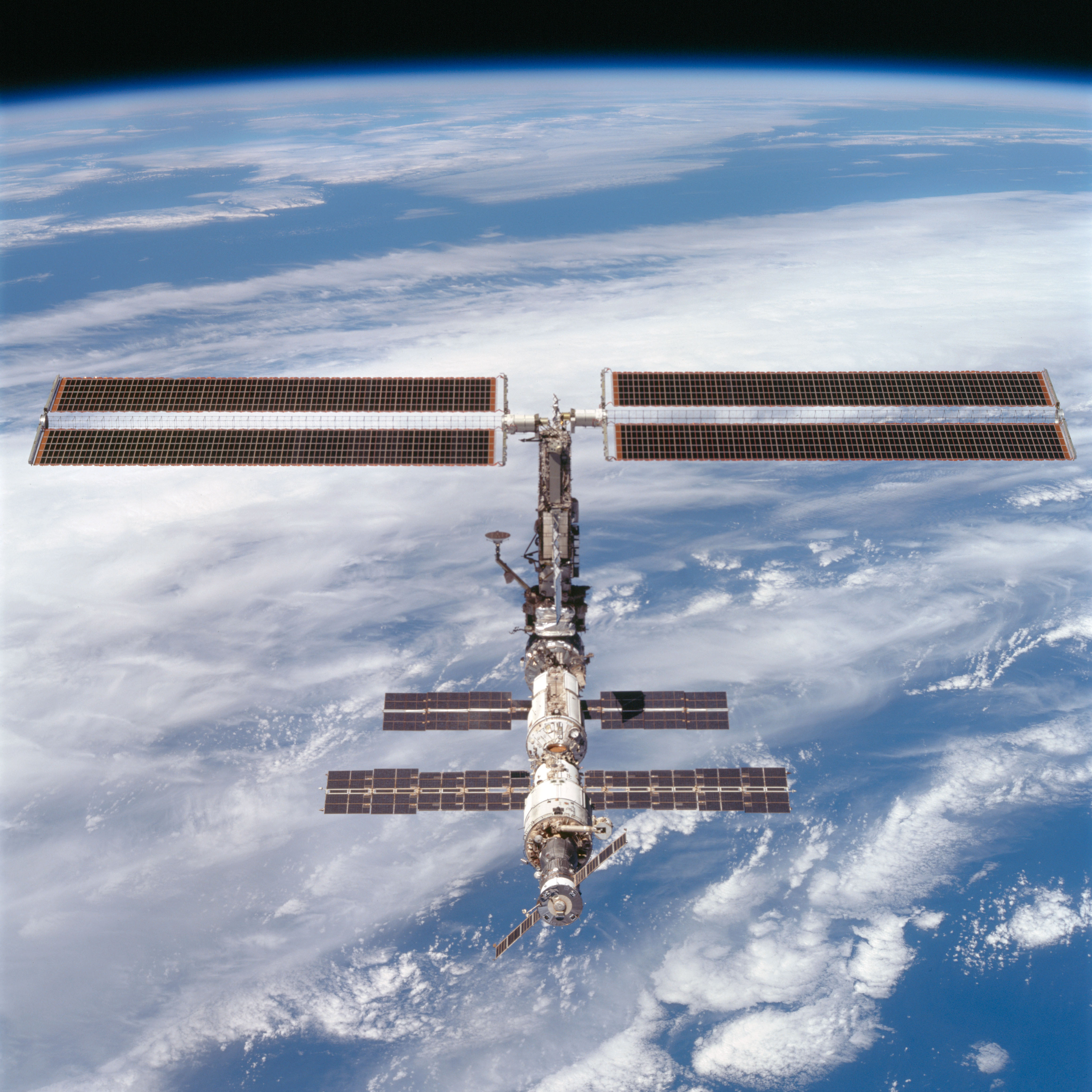
Lopez-Alegria served as a mission specialist on STS-92 during his first visit to the space station. He and his six crewmates launched aboard Discovery in October 2000, the 100th launch of the program and the last to visit an unoccupied station. At the time, the station comprised just three modules. During the mission, the STS-92 crew installed the Z1 truss atop the Unity module, four Control Moment Gyros, and the third Pressurized Mating Adaptor. The Z1 truss enabled the addition of solar arrays and radiators on the subsequent assembly flight and also contained high-rate communications equipment including the first Space-to-Ground antenna. Lopez-Alegria participated in two of the mission’s four spacewalks with Peter J. “Jeff” Wisoff to complete the assembly tasks. During their last spacewalk, the two conducted the first flight evaluation at the station of the Simplified Aid for EVA Rescue (SAFER), a propulsive backpack to be used by astronauts should they become detached from the spacecraft. The STS-92 crew left the station ready for its first inhabitants, and indeed less than two weeks later, the first Expedition crew arrived to begin permanent residency in low Earth orbit.
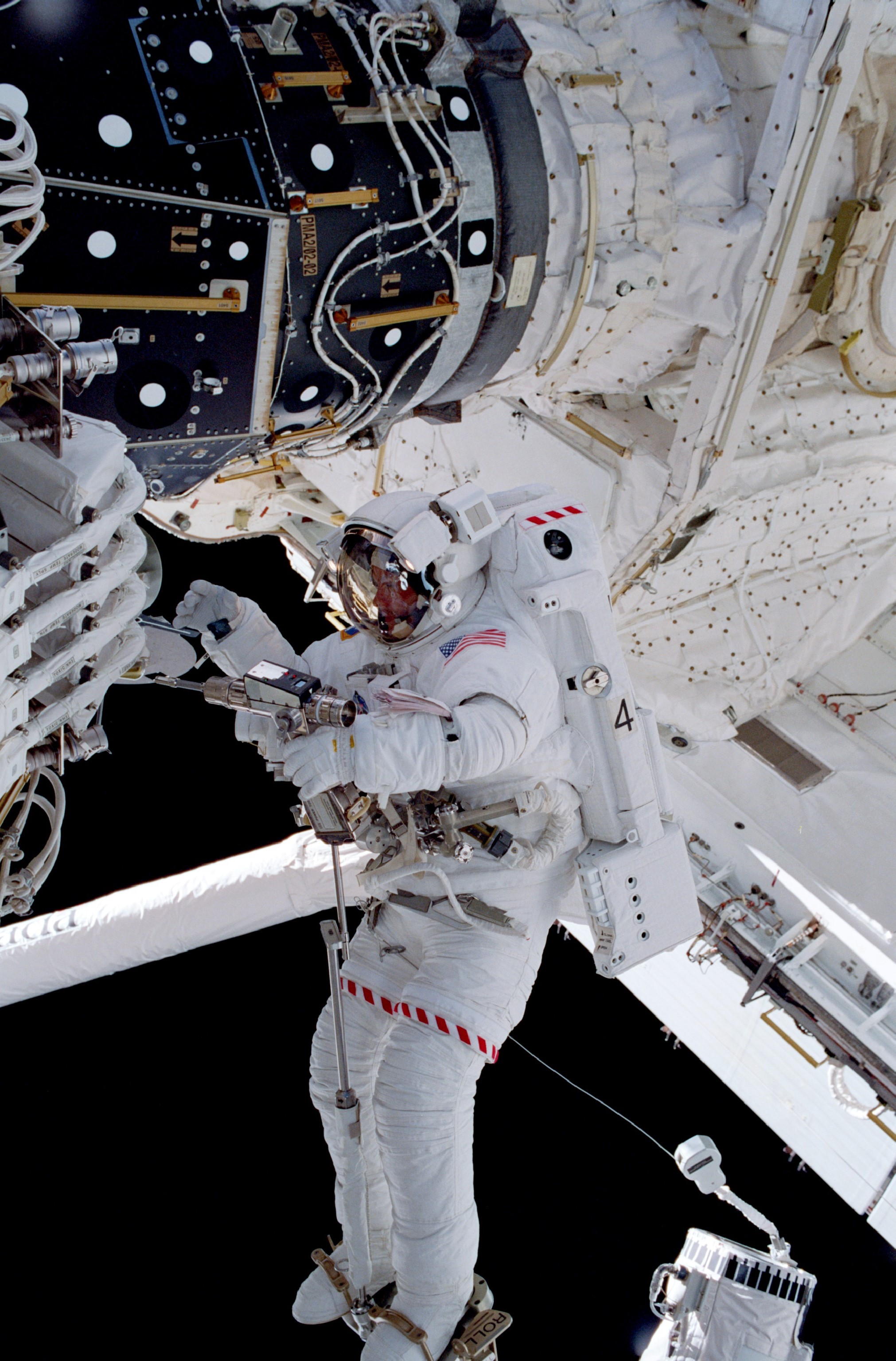
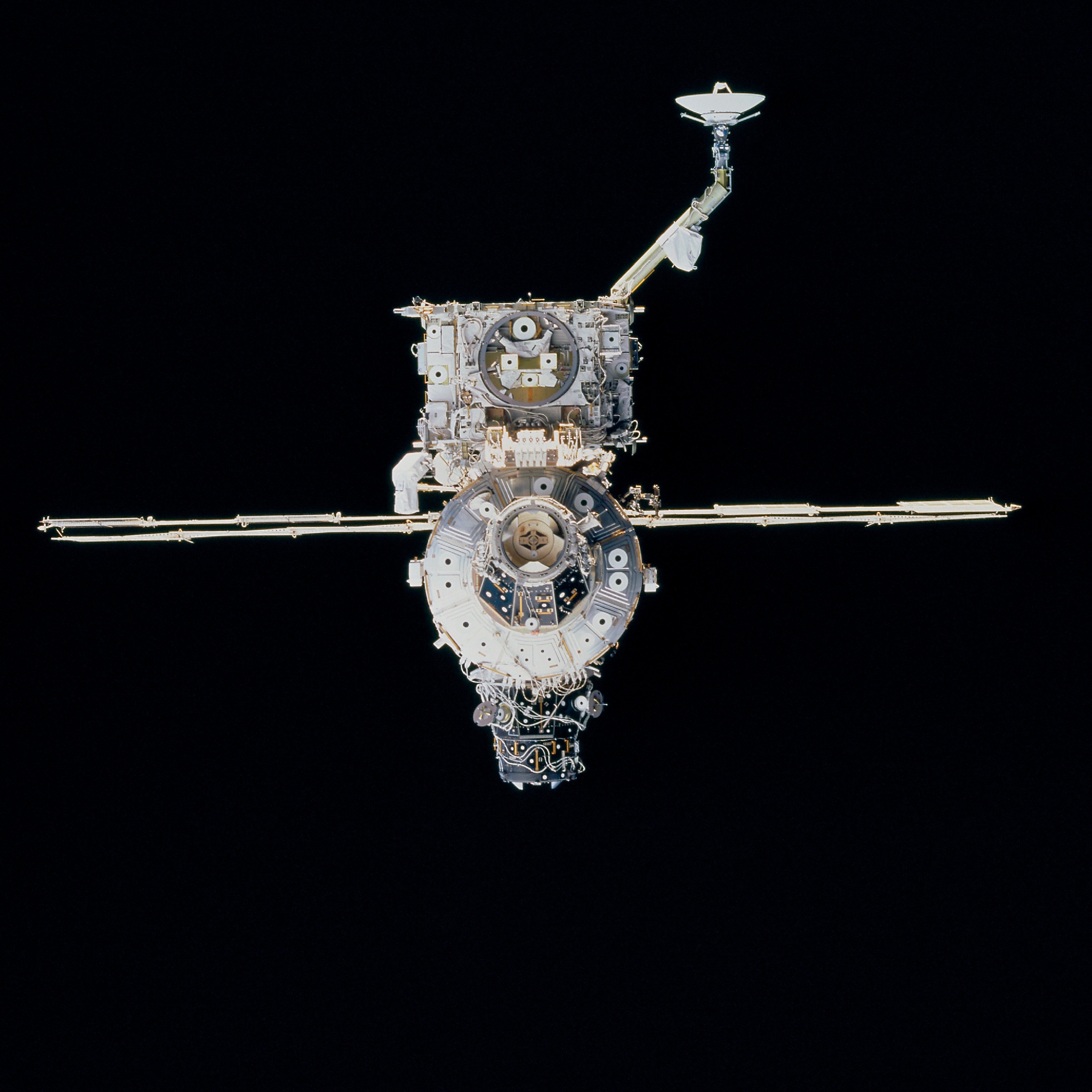

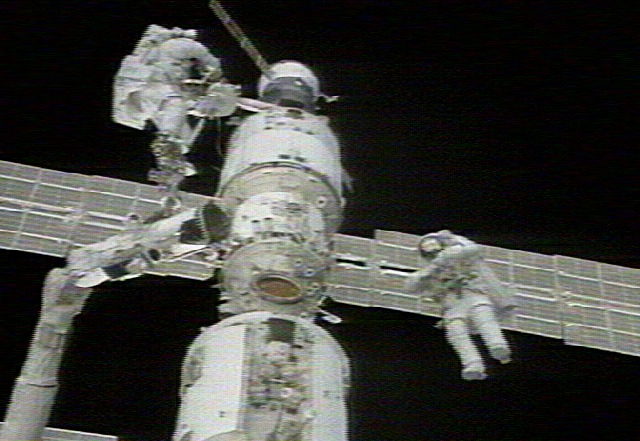

Left: NASA astronaut Michael E. Lopez-Alegria working outside the space station during STS-92. Middle: Lopez-Alegria, left, tests the Simplified Aid for EVA Rescue as fellow NASA astronaut Peter J. “Jeff” Wisoff looks on. Right: The space station as seen from Discovery shortly after undocking, showing the Z1 Truss with the Space-to-Ground
Antenna at top and the third Pressurized Mating Adaptor at bottom.
For his third flight into space, Lopez-Alegria returned to the station in November 2002 during the STS-113 mission, the facility now permanently occupied and having grown significantly in the intervening two years. The primary tasks for the STS-113 crew included adding the P1 truss on the station’s port side, installing the Crew Equipment Translation Aid (CETA) cart, and assisting in the exchange between the Expedition 5 and 6 crews. Lopez-Alegria and fellow STS-113 mission specialist John B. Harrington conducted three spacewalks to complete the installation of the P1 truss and the CETA cart. After STS-113, assembly of the station came to a temporary halt following the Feb. 1, 2003, Columbia accident, and the subsequent grounding of the space shuttle fleet. Flights did not resume until September 2006.
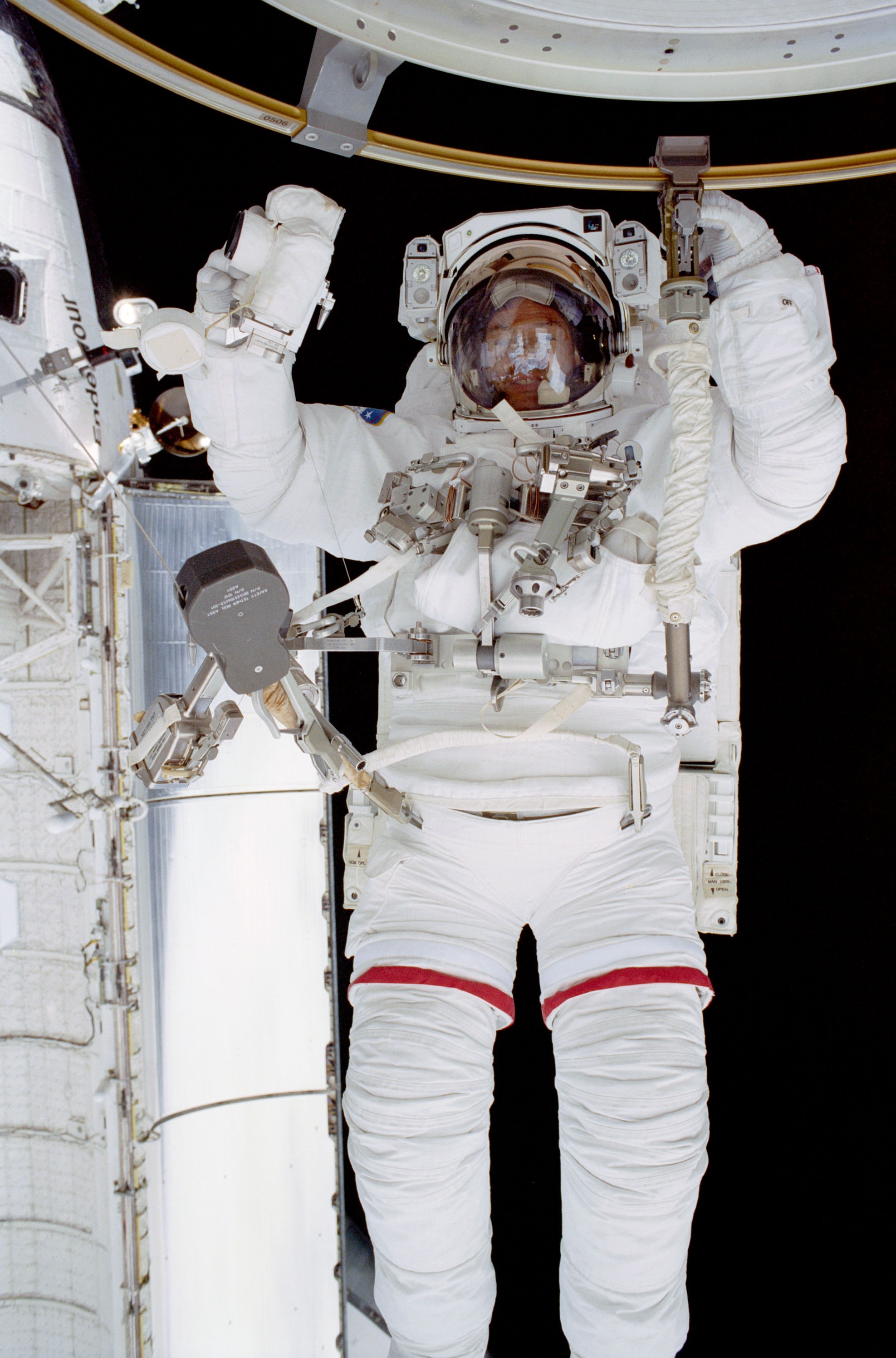
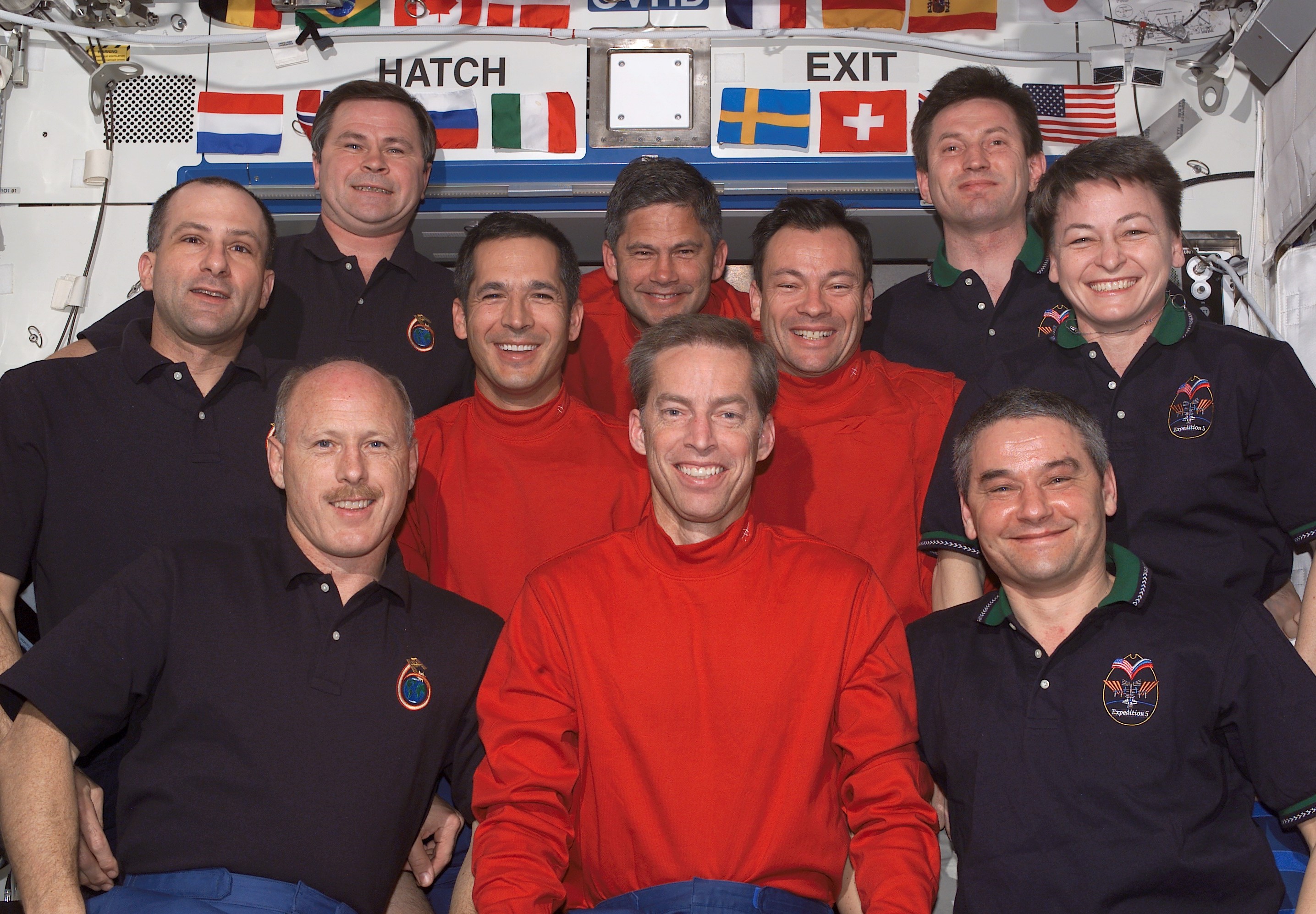



Left: NASA astronaut Michael E. Lopez-Alegria during the first STS-113 spacewalk. Middle: Lopez-Alegria, second from right in the middle row, posing in the Destiny module with his STS-113 crewmates, as well as the Expedition 5 and 6 crews. Right: The space station as seen by the departing STS-113 crew, with the newly installed P1 truss visible at right.
Lopez-Alegria returned to the space station again shortly after assembly resumed. For his fourth spaceflight, he launched aboard Soyuz TMA9 in September 2006, from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Mikhail V. Tyurin of Roscosmos accompanied him during the 215-day mission, to that time the longest space station expedition, was Mikhail V. Tyurin of Roscosmos. European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Thomas A. Reiter, onboard the station since July 2006, became part of the Expedition 14 crew. As Commander of Expedition 14, Lopez-Alegria oversaw one of the most complex set of activities in the assembly of the station – the reconfiguration of its power and cooling systems. A week before his arrival, the STS-115 mission had delivered the second set of solar arrays to the station as part of the P3/P4 truss segment, positioning them outboard of the P1 segment. As part of the reconfiguration, the port side P6 array mounted atop the Z1 truss needed to be retracted to prevent interference with the rotation of the new arrays, a task that was completed during the visiting STS-116 mission in December that also added the P5 short spacer to the port side truss. That mission brought NASA astronaut Sunita L. “Suni” Williams to the station as a new addition to Expedition 14 and returned Reiter back to Earth. During Expedition 14, Lopez-Alegria took part in five spacewalks, two in Orlan spacesuits with Tyurin to conduct work on the outside of the Russian segment and three in American spacesuits, with Williams to reconfigure the cooling system of the U.S. segment. He accumulated a total of 67 hours and 40 minutes over 10 spacewalks – still the record among American astronauts. Lopez-Alegria also conducted a variety of scientific experiments.
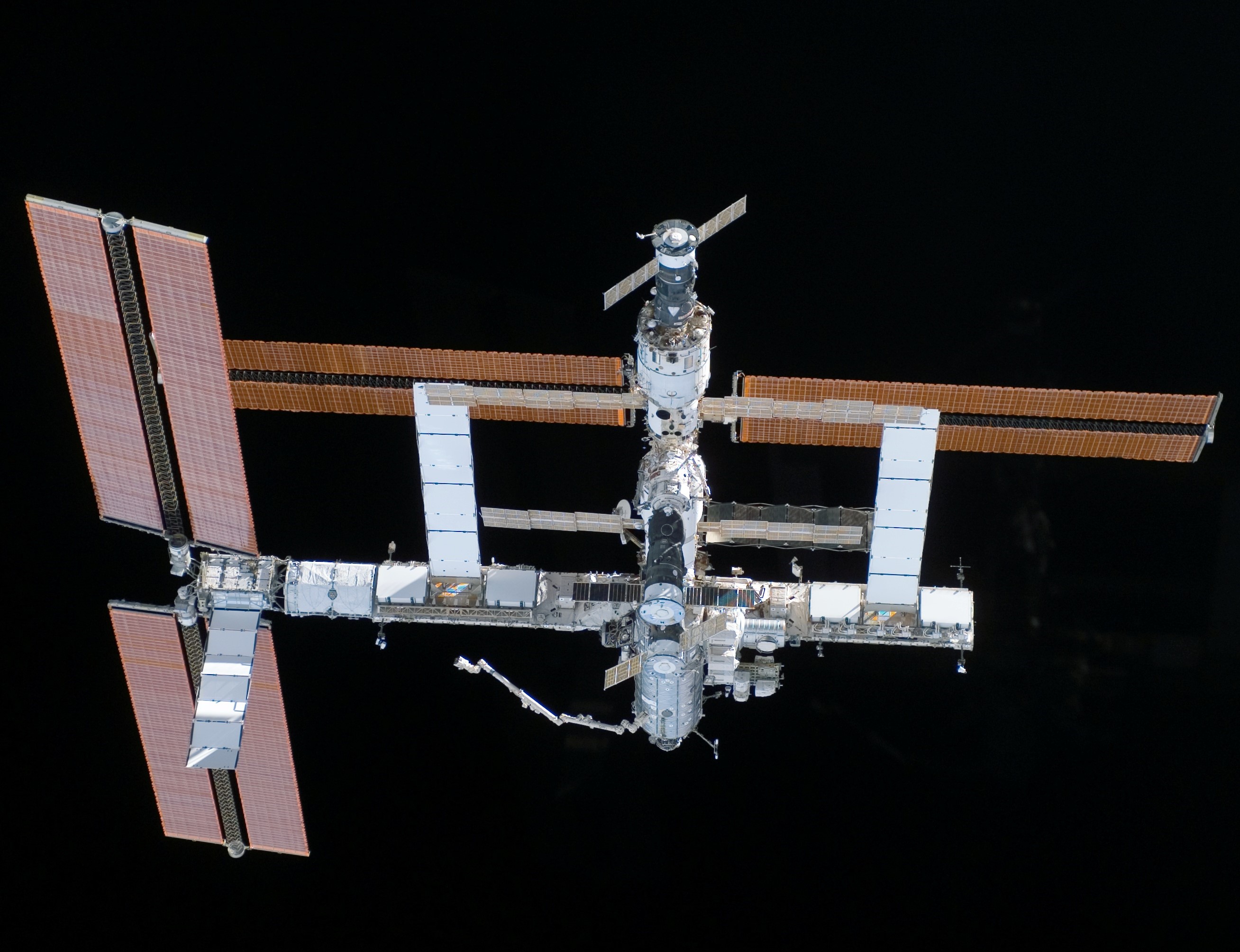
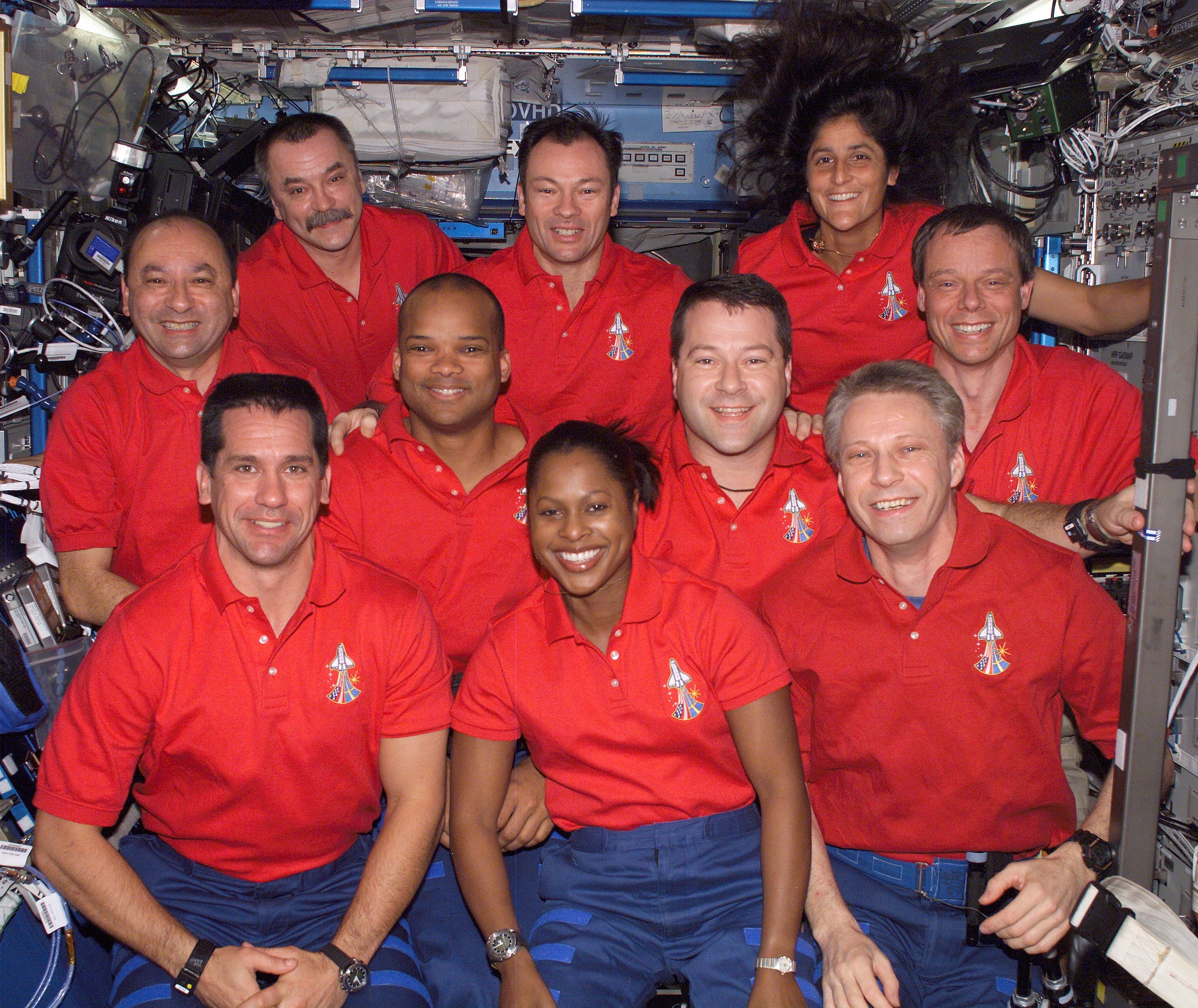
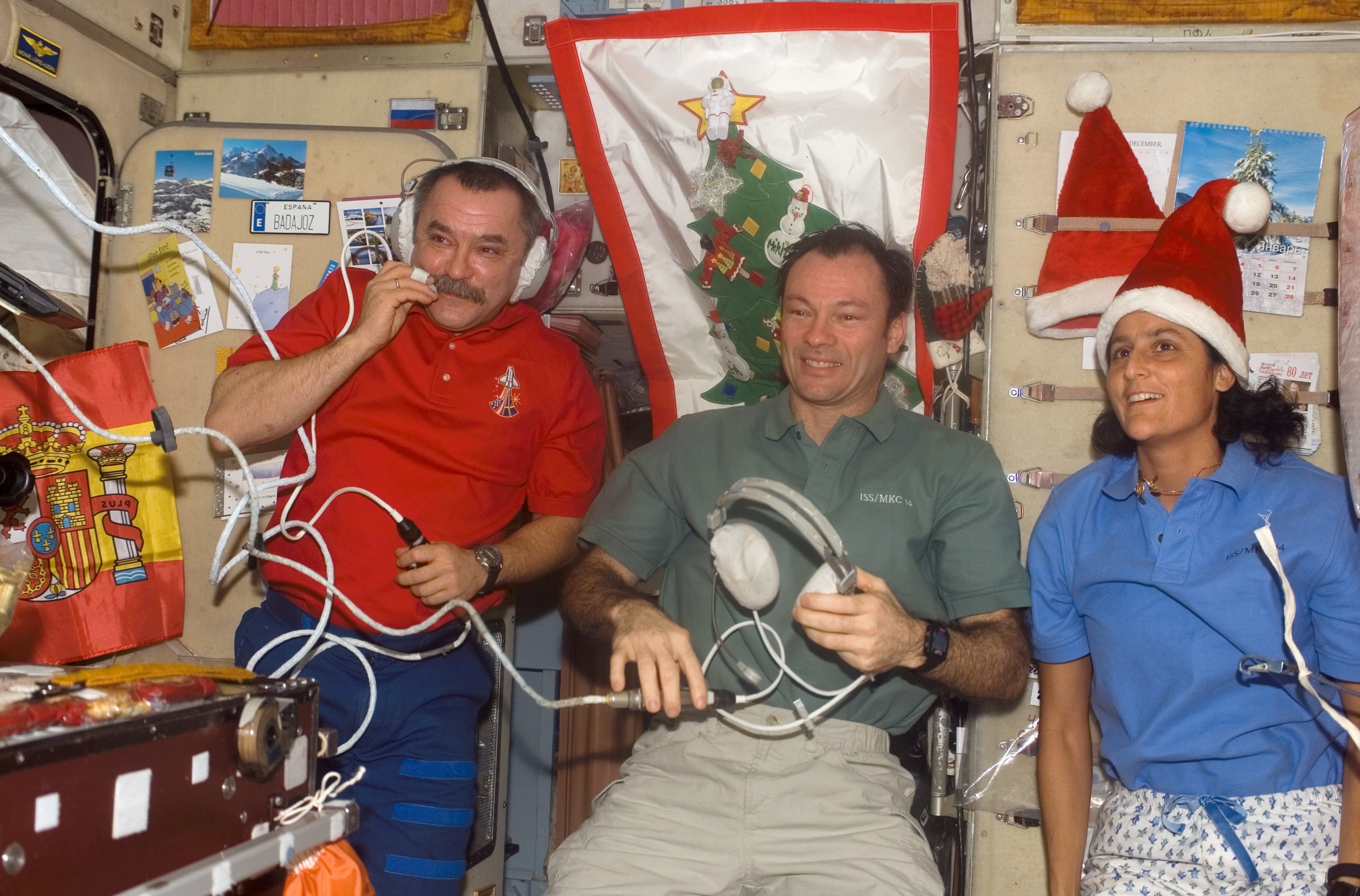



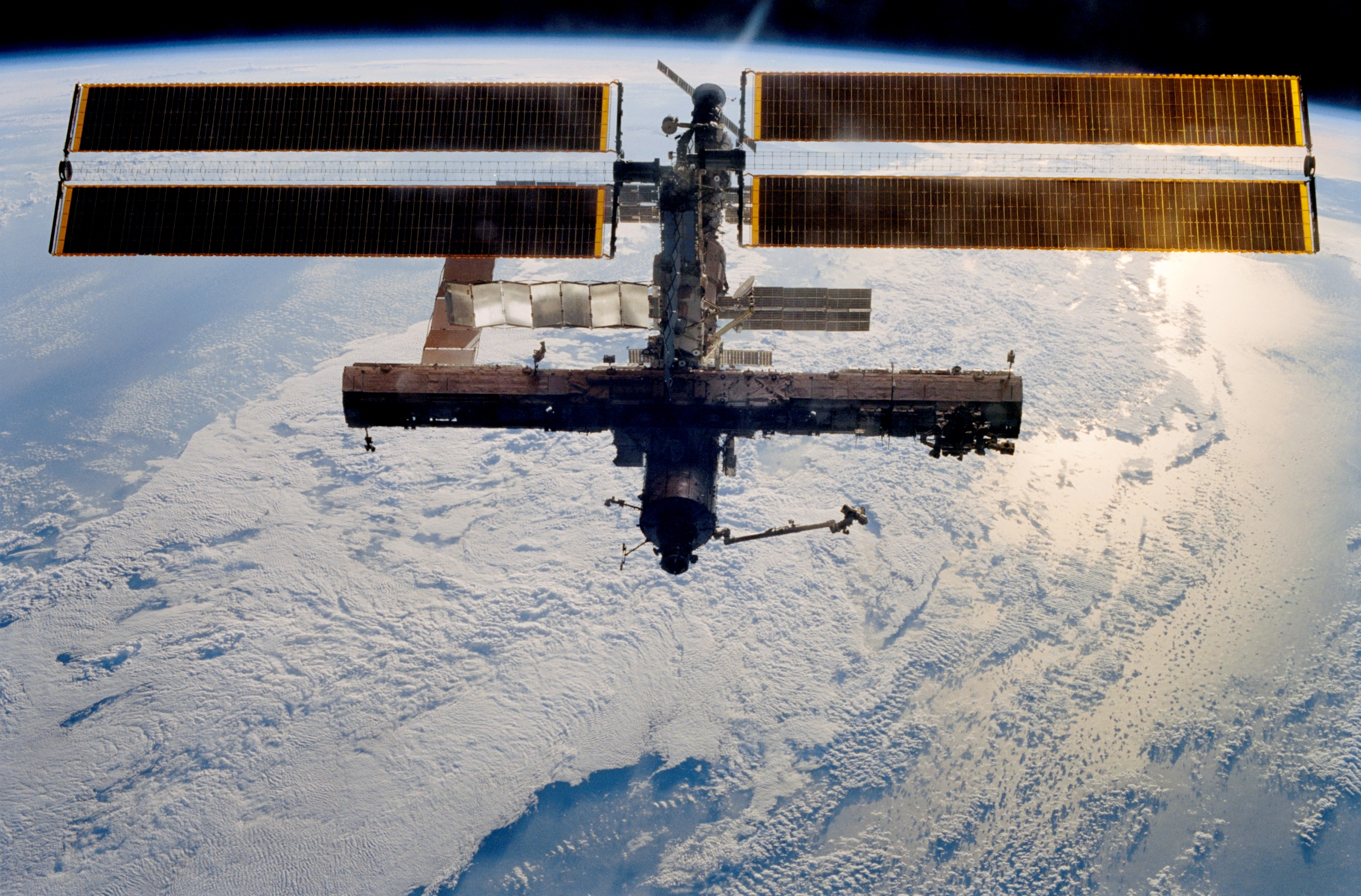
Left: Space station configuration when NASA astronaut Michael E. Lopez-Alegria arrived in September 2006. Middle: Lopez-Alegria, back row middle, with STS-116 and Expedition 14 crew members. Right: Celebrating the holidays aboard the space station.
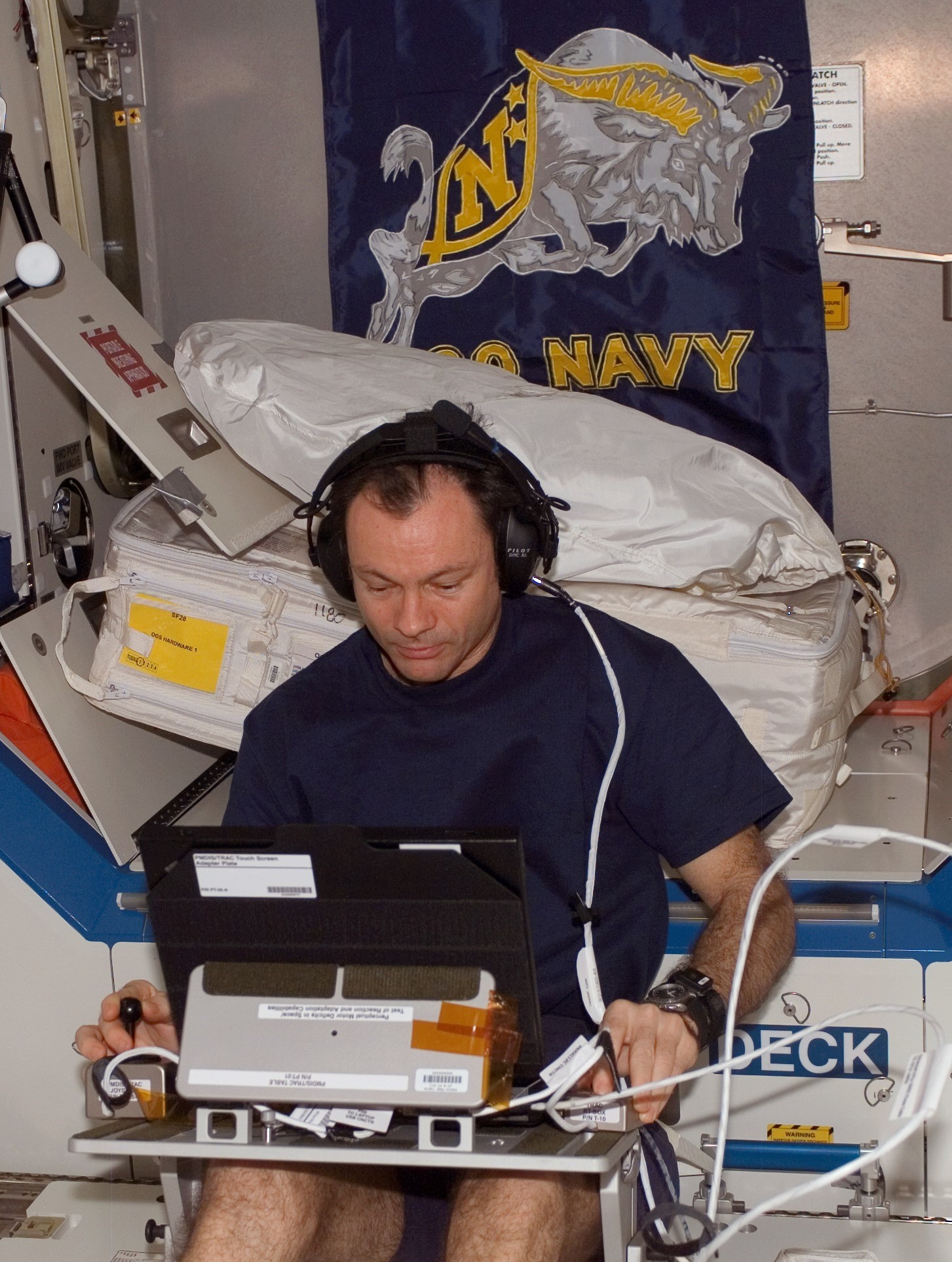
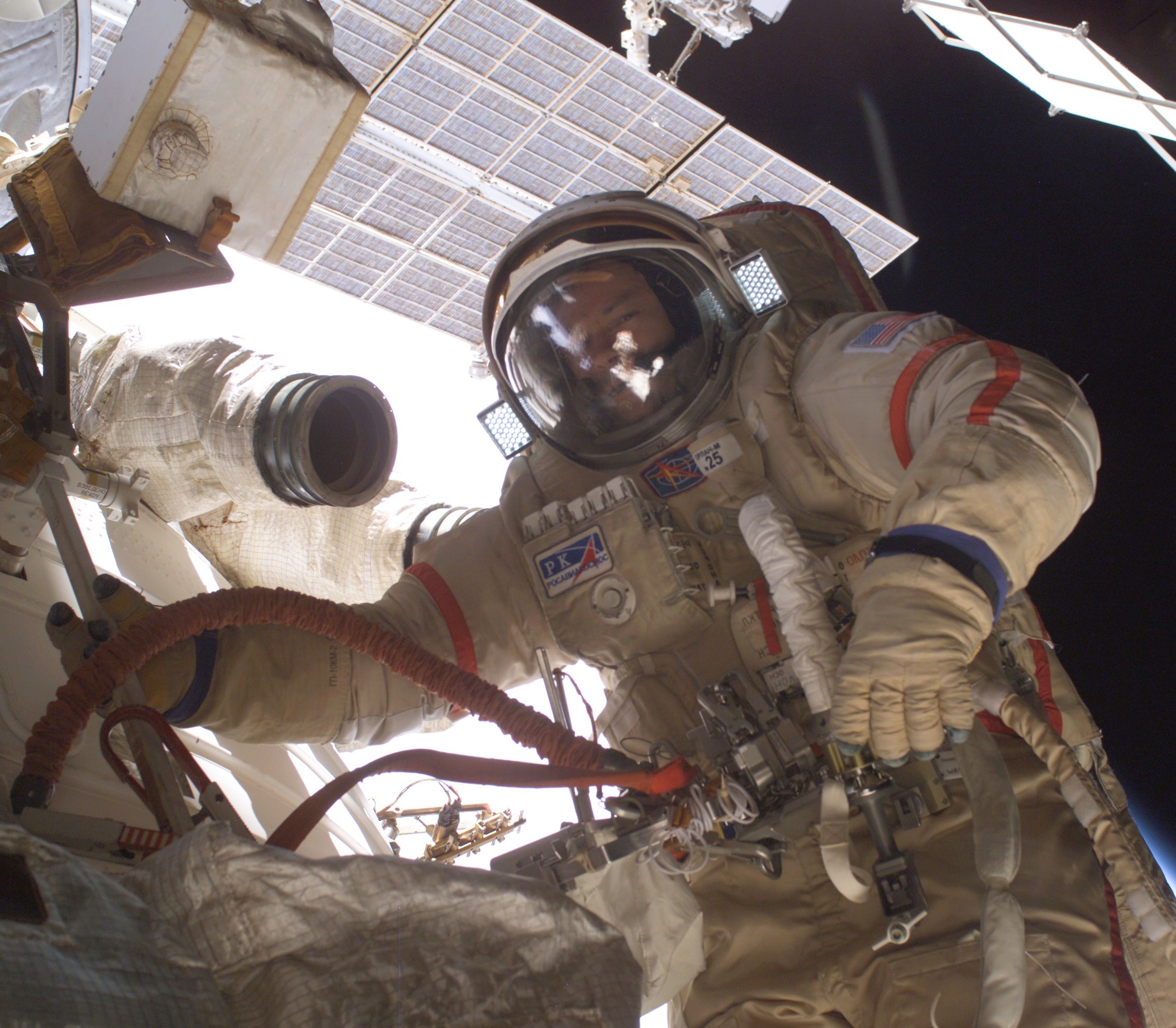


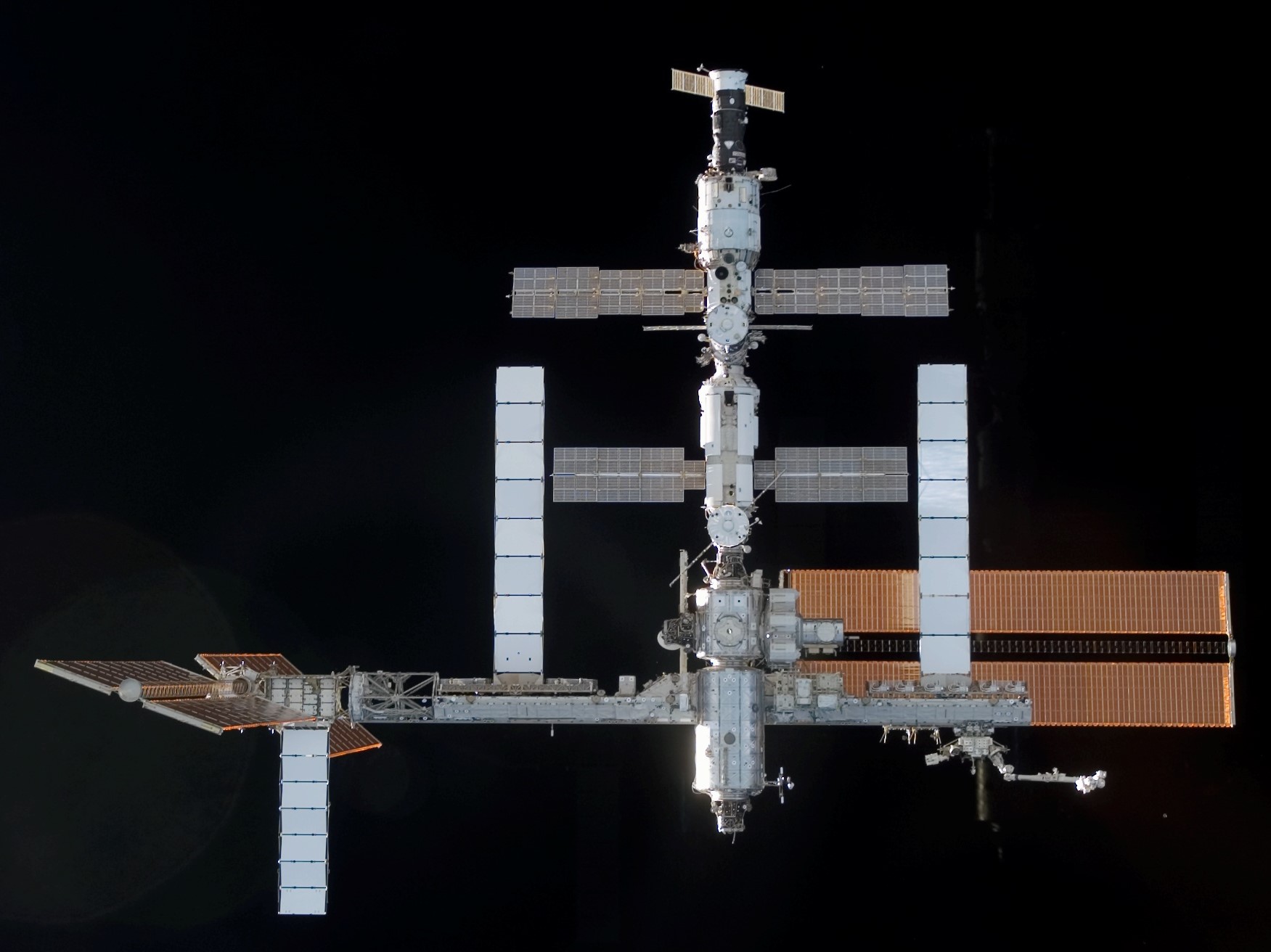
Left: NASA astronaut Michael E. Lopez-Alegria conducting a session of the Canadian TRAC experiment in the Destiny module. Middle: In an Orlan suit, Lopez-Alegria conducts maintenance on the exterior of the Russian segment. Right: The space station’s configuration at the end of Lopez-Alegria’s mission – note the retracted P6 solar array.
Lopez-Alegria retired from NASA in 2012, joining Axiom Space shortly thereafter. In April 2022, he commanded the Ax-1 mission, the first commercial astronaut mission to the space station. He and his three crewmates spent 17 days aboard, conducting a variety of experiments. Across his five missions, Lopez-Alegria accumulated a total of 275 days in space.
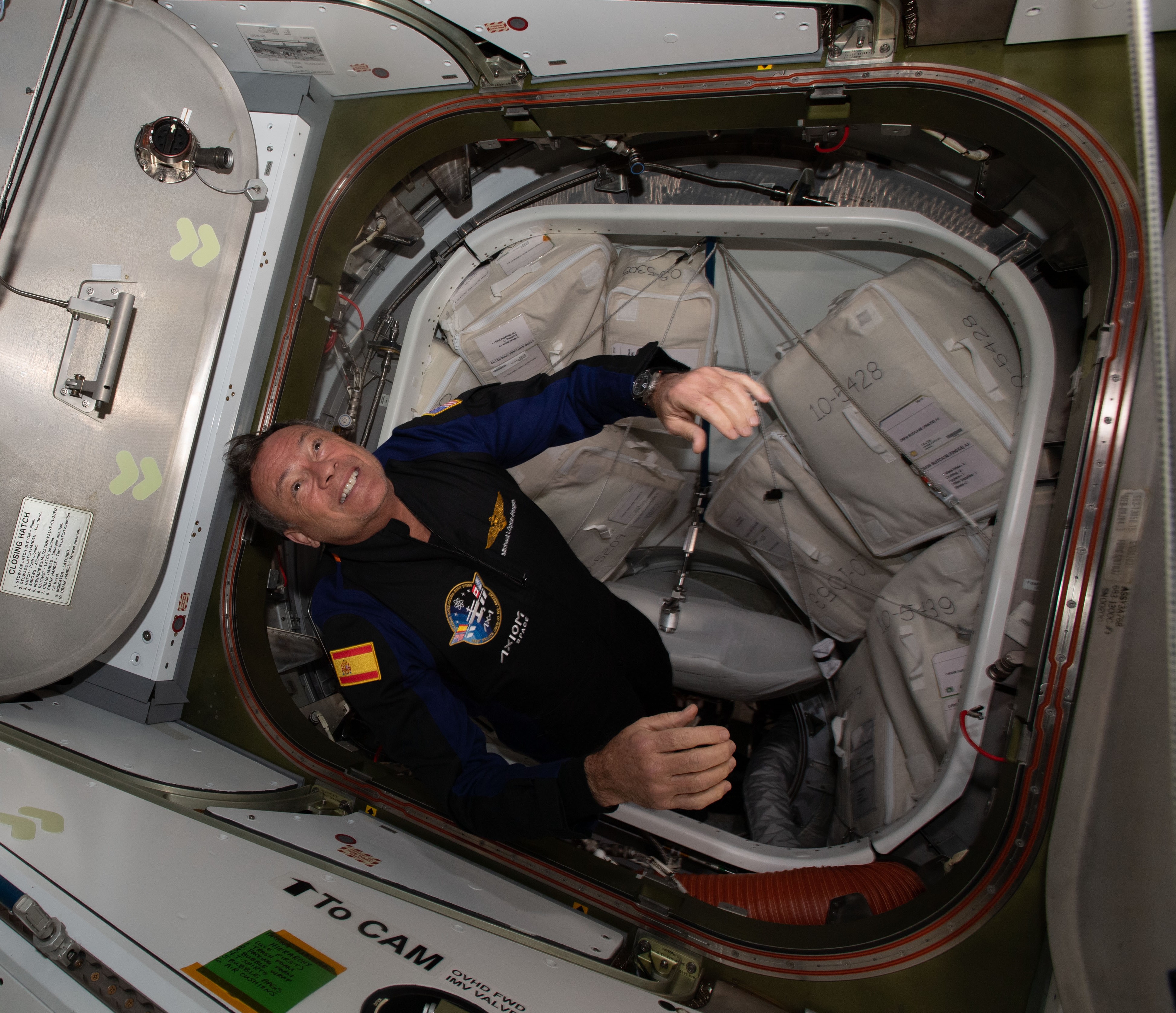
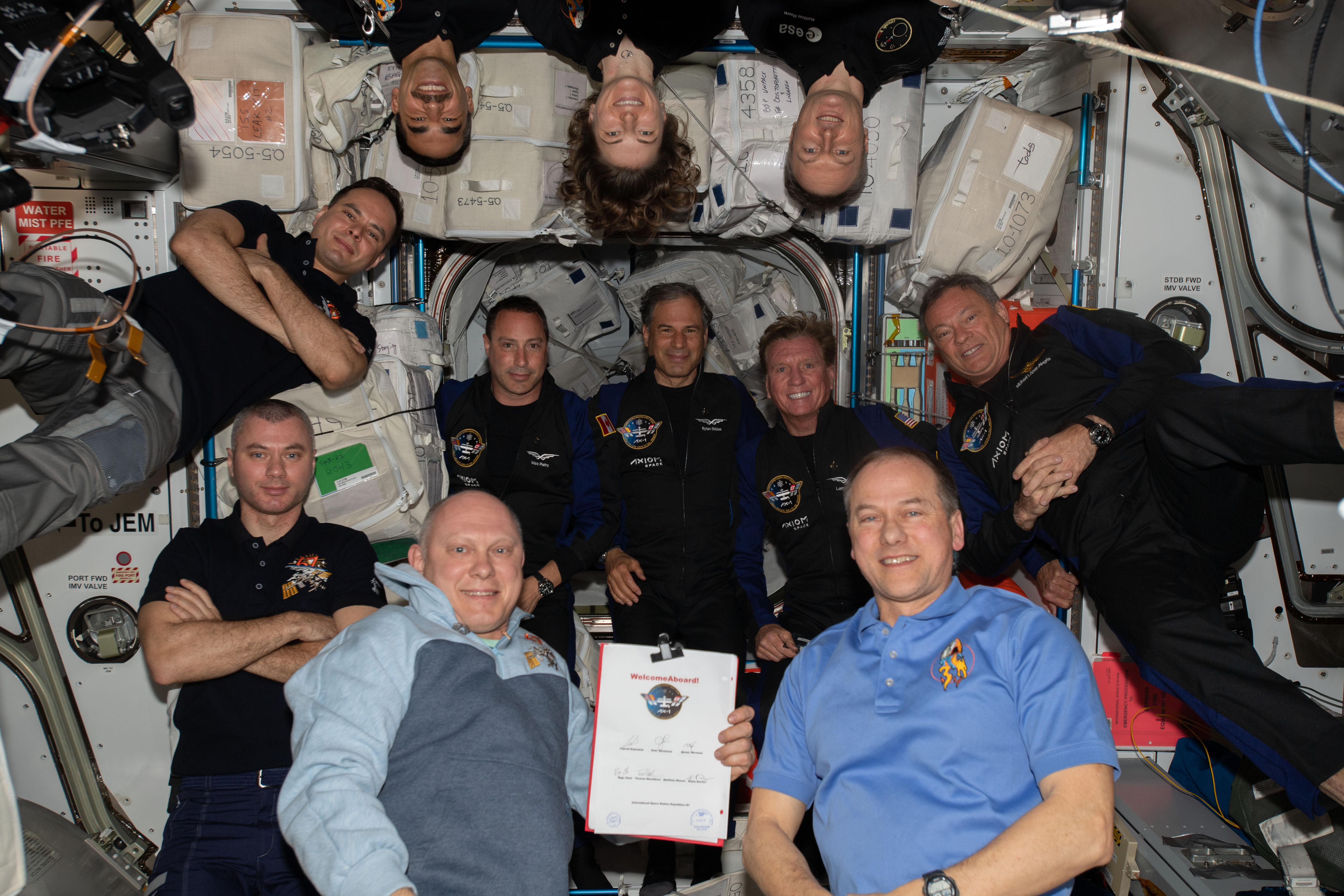



Left: Axiom astronaut Michael E. Lopez-Alegria floats into the space station during the Ax-1 mission.
Middle: Lopez-Alegria, second from right, and the rest of the Ax-1 crew. Right: The 11 crew members
aboard the space station during the Ax-1 mission, with Lopez-Alegria at far right.
Carlos I. Noriega
In 1994, NASA selected Carlos I. Noriega as the first Peruvian-born astronaut. On his first spaceflight in May 1997, he served as a mission specialist aboard STS-84, the sixth Shuttle-Mir docking mission. During the nine-day flight, the crew resupplied the Mir space station, brought NASA astronaut C. Michael Foale to the Russian outpost, and returned Jerry M. Linenger to Earth.
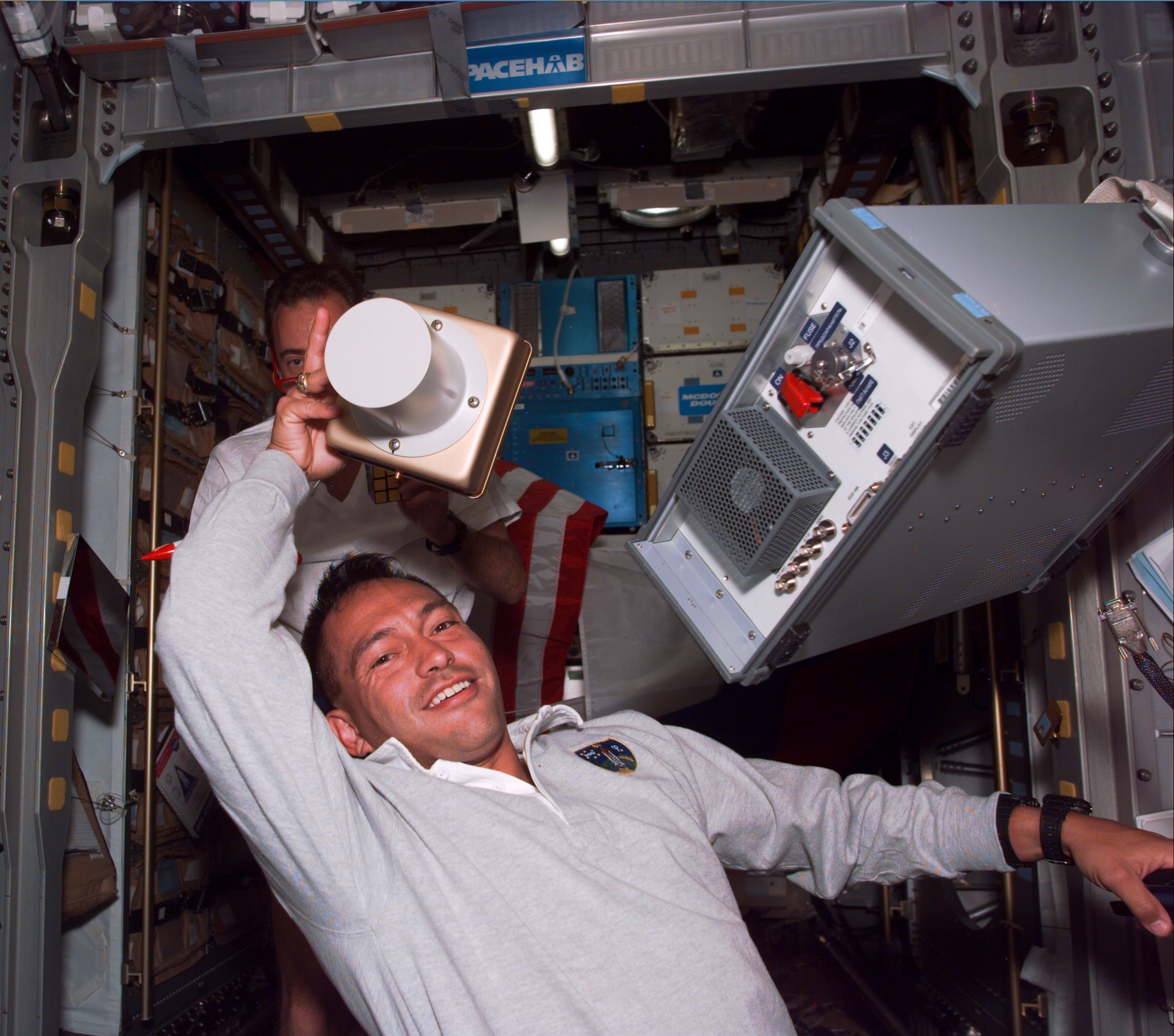
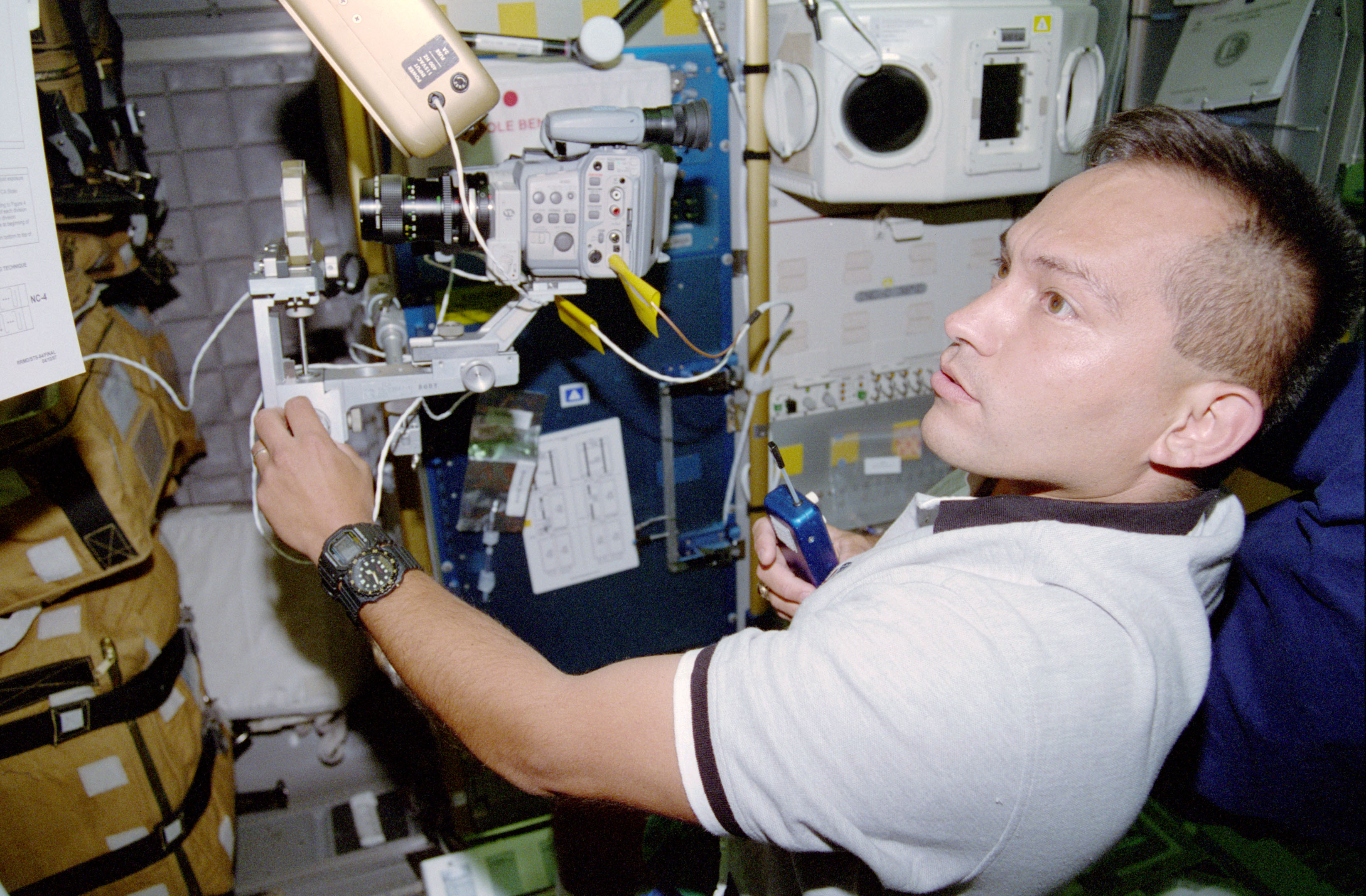
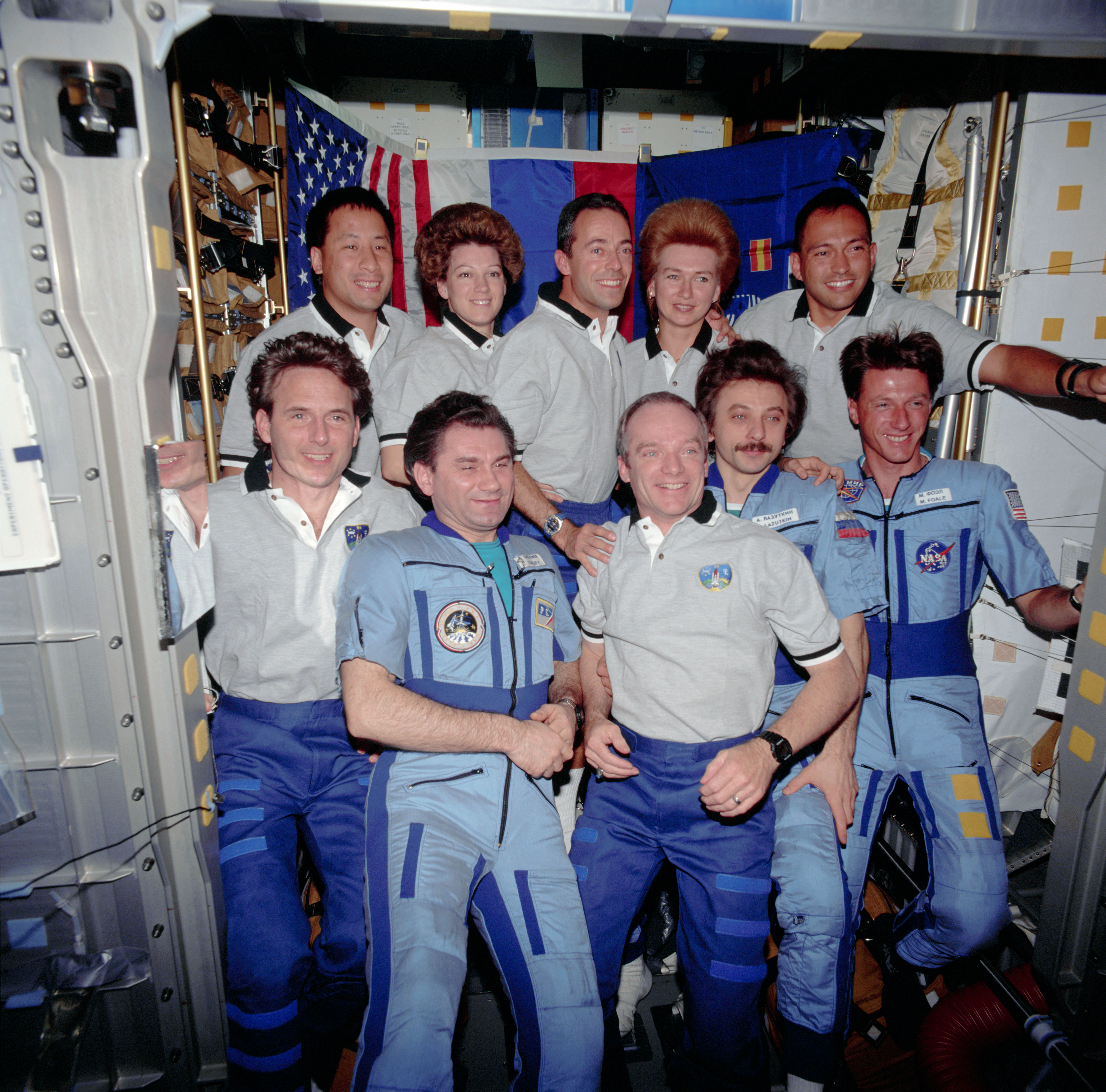



Left: Carlos I. Noriega sets up an experiment during the STS-84 mission. Middle: Noriega working
on an experiment in the Spacehab module. Right: The 10 members of the STS-84 and Mir resident crew, with Noriega at upper right.
In December 2000, Noriega launched on his second mission, aboard Endeavour with his four crewmates on STS-97, their primary goal to install the P6 truss segment with the first set of solar arrays and radiators atop the Z1 truss. STS-97 marked the first time a shuttle visited the station after its occupancy began, but given the busy spacewalk schedule, the hatches between the two vehicles were only open for 24 hours. Noriega and fellow mission specialist Joseph R. Tanner conducted three spacewalks to complete the P6 installation and other assembly tasks. The new solar arrays generated enough power for the arrival of the U.S. laboratory module Destiny early in 2001 and the start of intensive research aboard the space station.
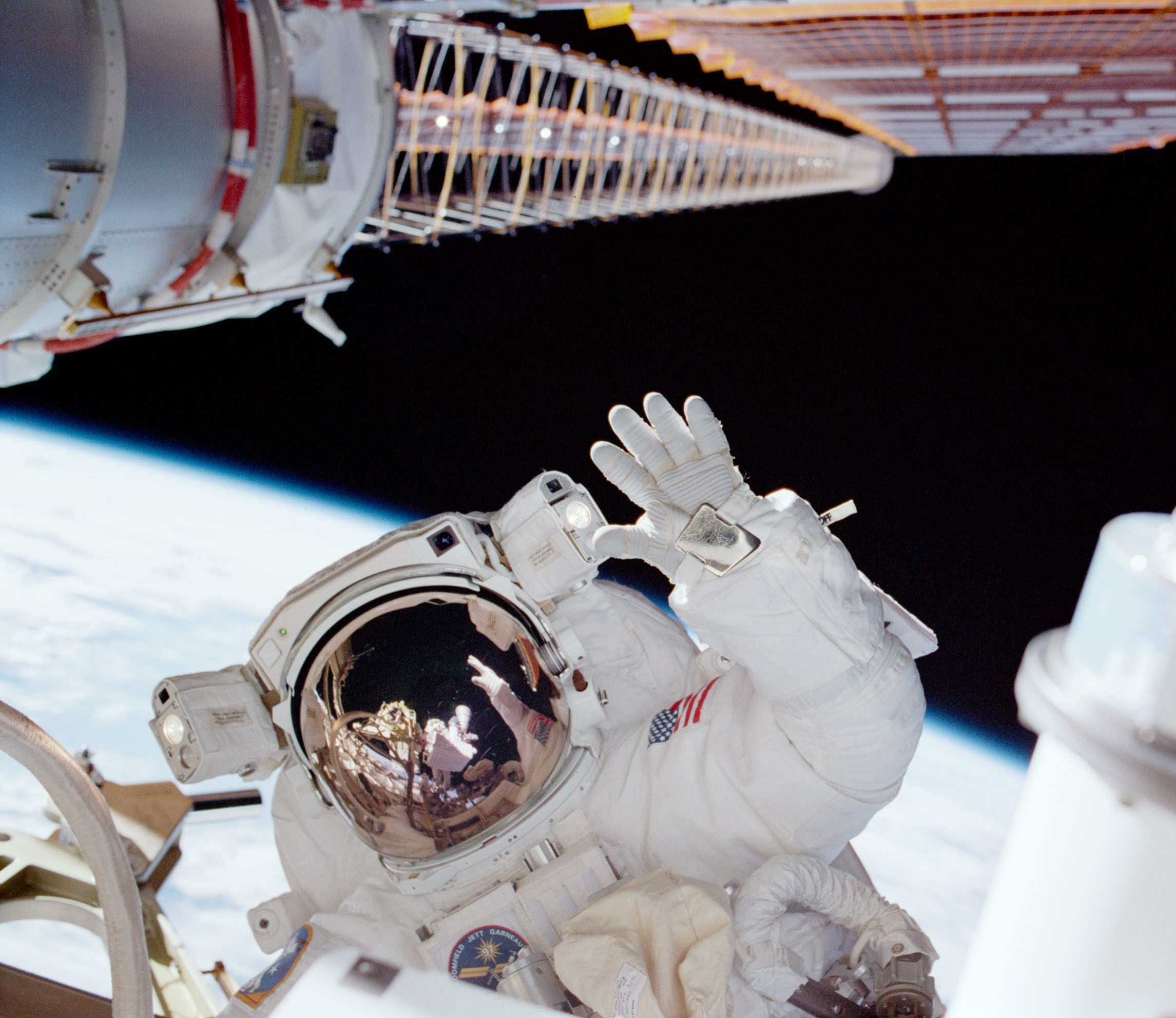



Left: NASA astronaut Carlos I. Noriega waves to the camera as he installs the P6 truss and solar arrays. Middle: Noriega, center, with the STS-97 and Expedition 1 crews in the Zarya Service Module. Right: The space station as seen from the departing STS-97 showing the newly deployed P6 solar arrays.
Pedro Duque
The European Space Agency (ESA) selected Pedro Duque, born in Madrid, Spain, as an astronaut in 1992. Four years later, he joined NASA’s astronaut class of 1996 in training and two years later certified as a mission specialist. His first launch into space took place in October 1998 on Discovery’s STS-95 mission, the nine-day flight that saw astronaut John H. Glenn’s return to space. Duque returned to space in October 2003 aboard Soyuz TMA3, conducting experiments aboard the space station as part of his Cervantes visiting mission. He returned to Earth 10 days later aboard Soyuz TMA2.
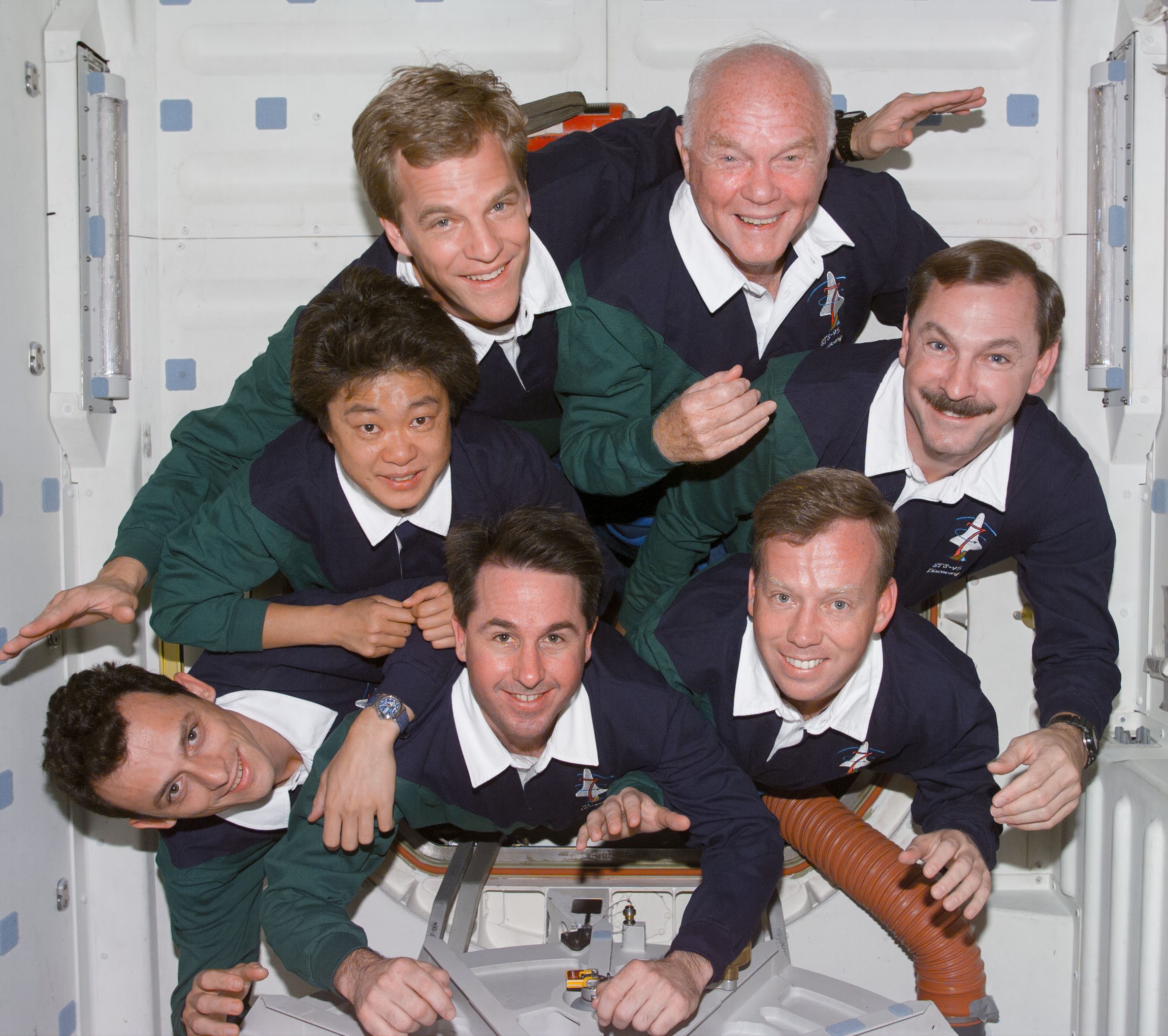
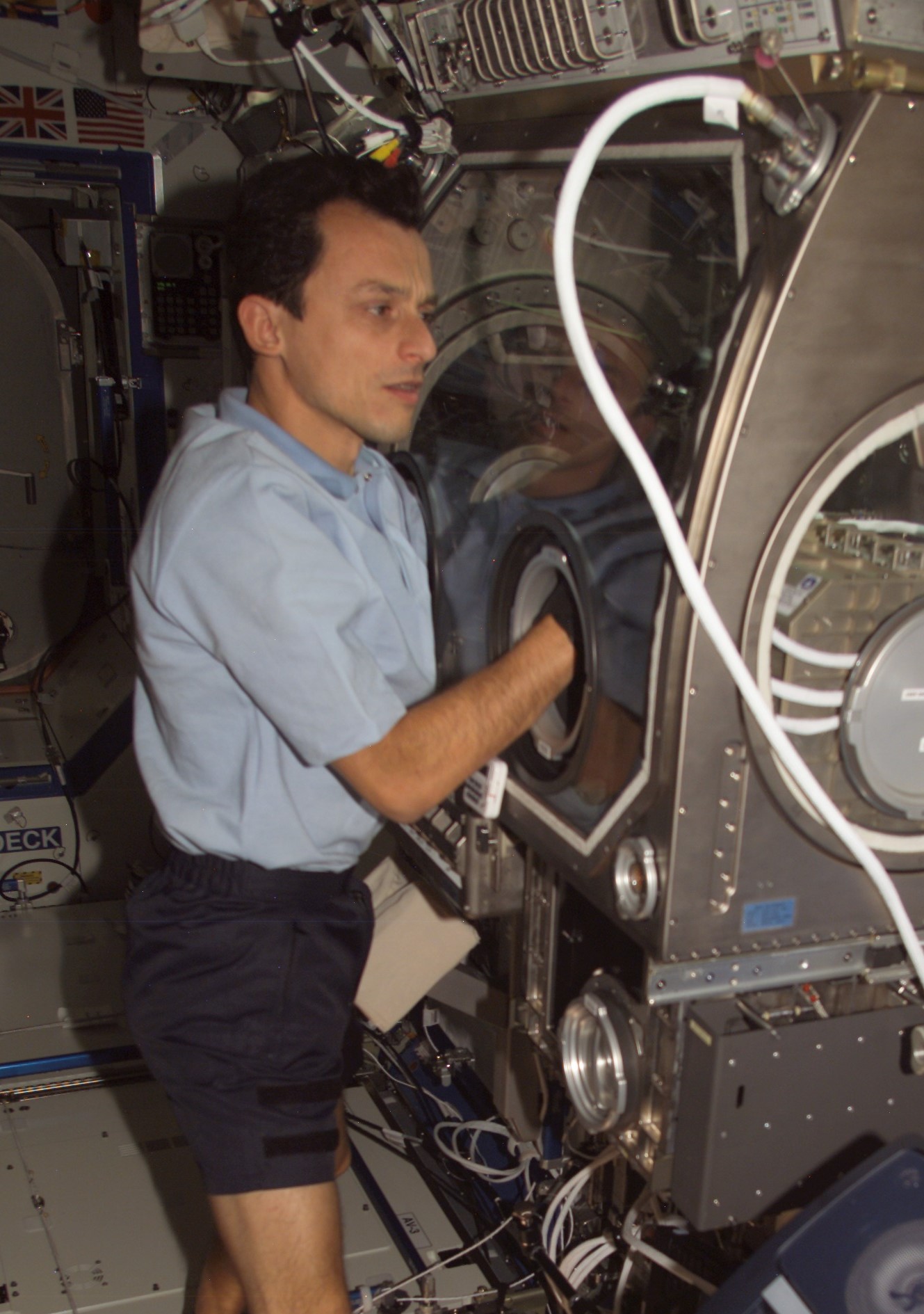
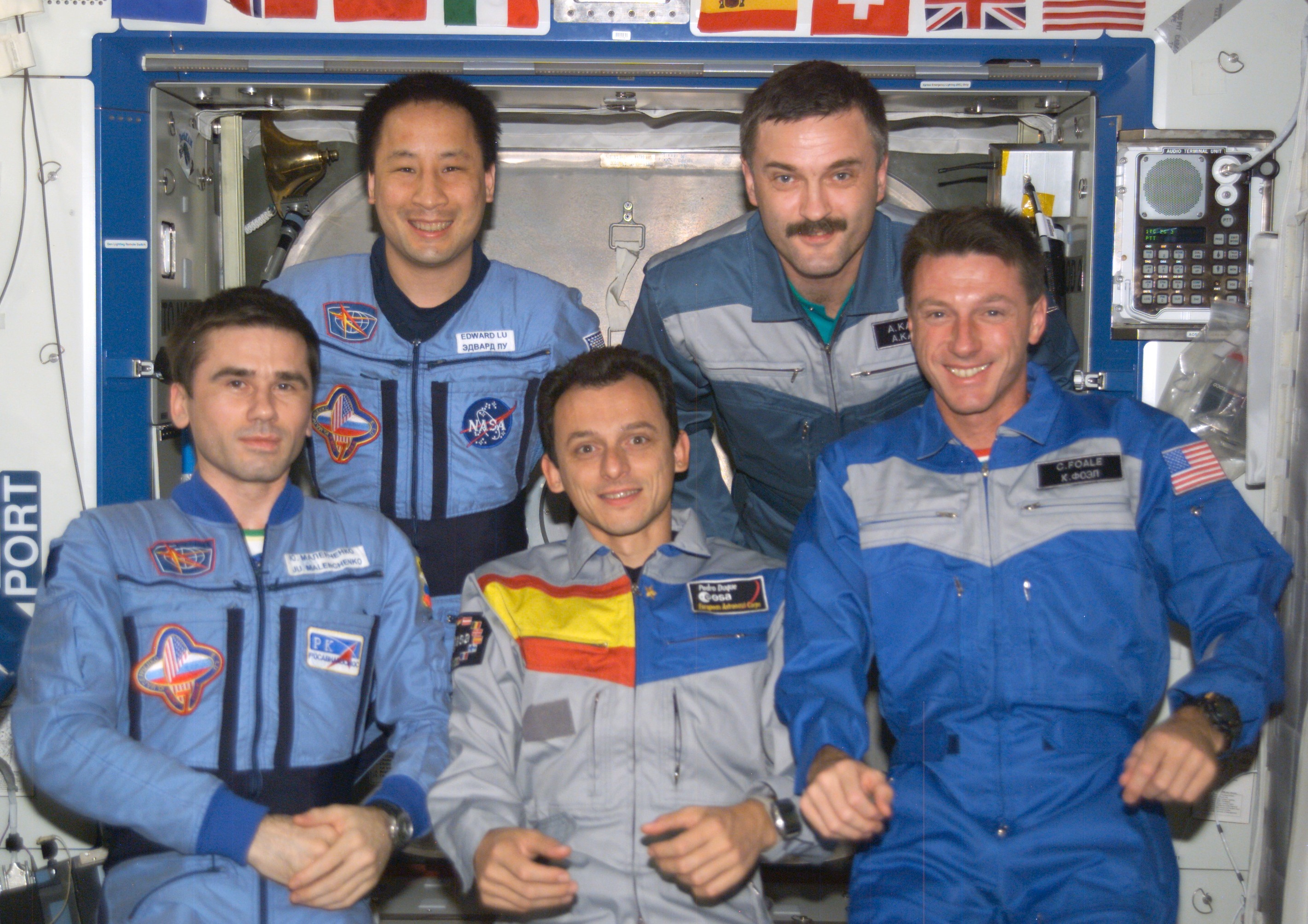



Left: Spanish astronaut Pedro Duque, lower left, representing the European Space Agency, with his STS-95 crewmates. Middle: Duque conducting an experiment in the Microgravity Science Glovebox aboard the space station. Right: Duque, center, with his Expedition 7 and 8 crewmates.
Marcos C. Pontes
The Brazilian Space Agency selected Marcos C. Pontes as an astronaut in 1998. He trained with NASA’s astronaut class of 1998 and certified as a mission specialist two years later. Pontes made his one and only spaceflight in March 2006 aboard Soyuz TMA8, carrying out eight experiments. He returned to Earth 10 days later aboard Soyuz TMA7.
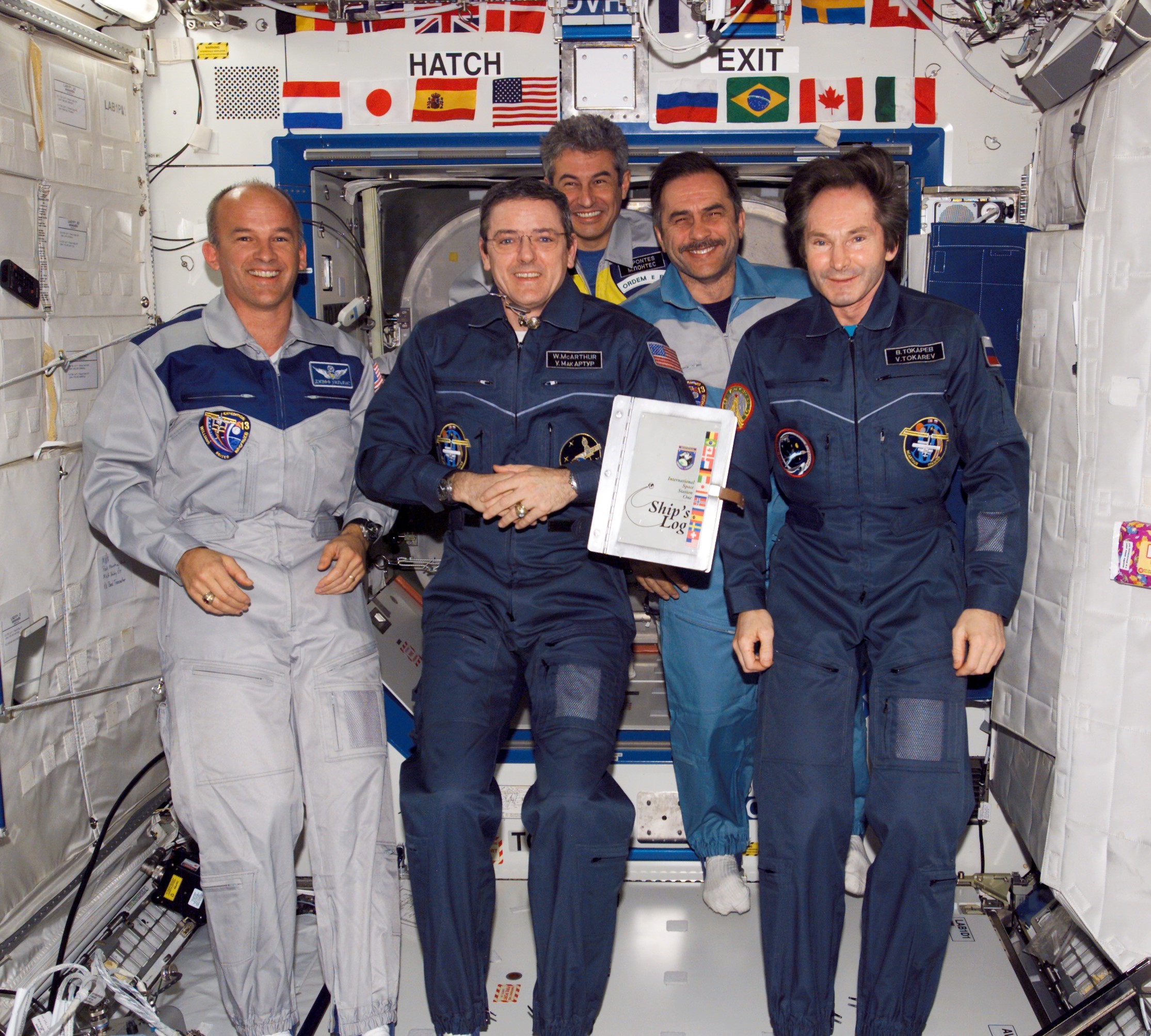
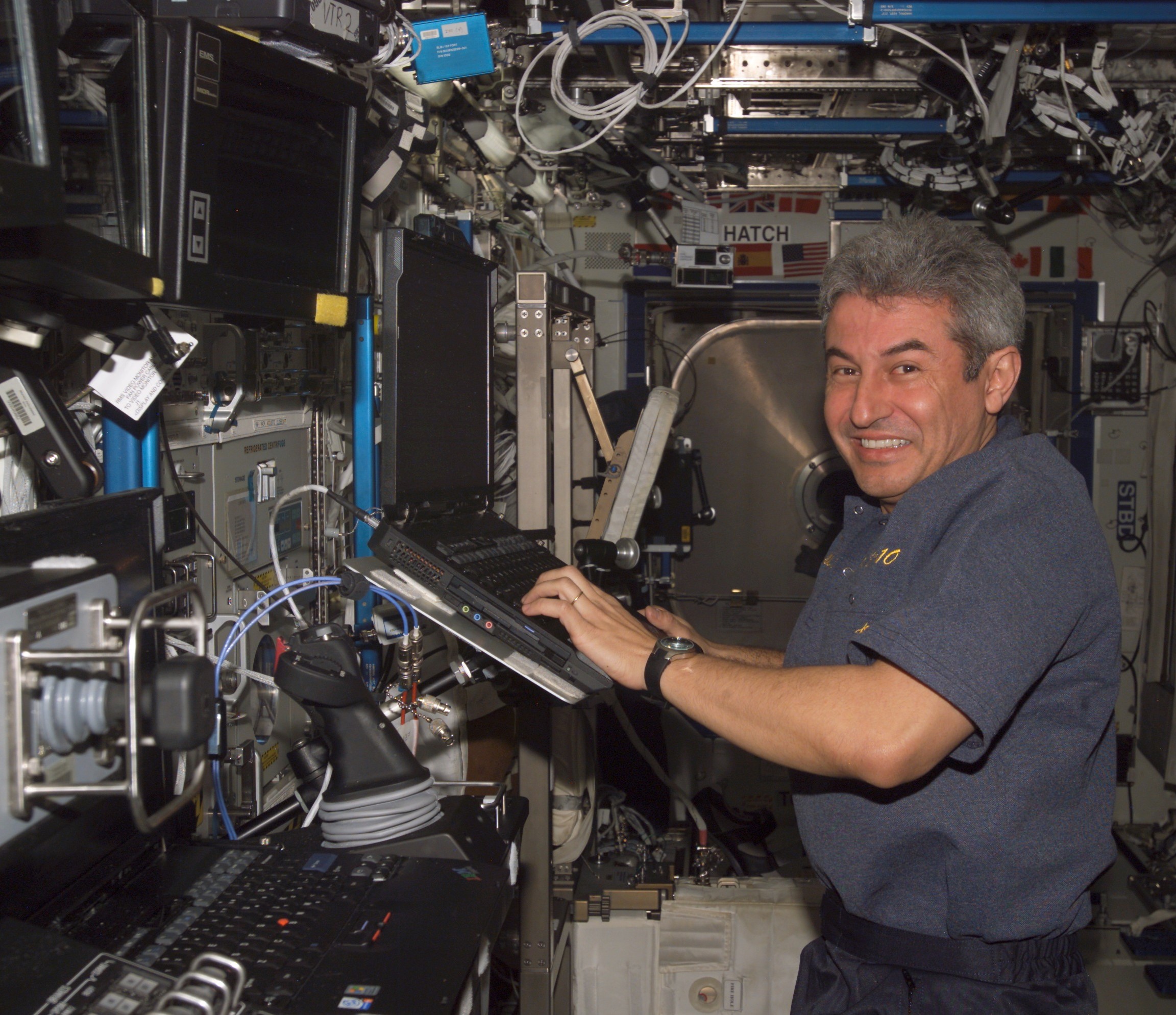
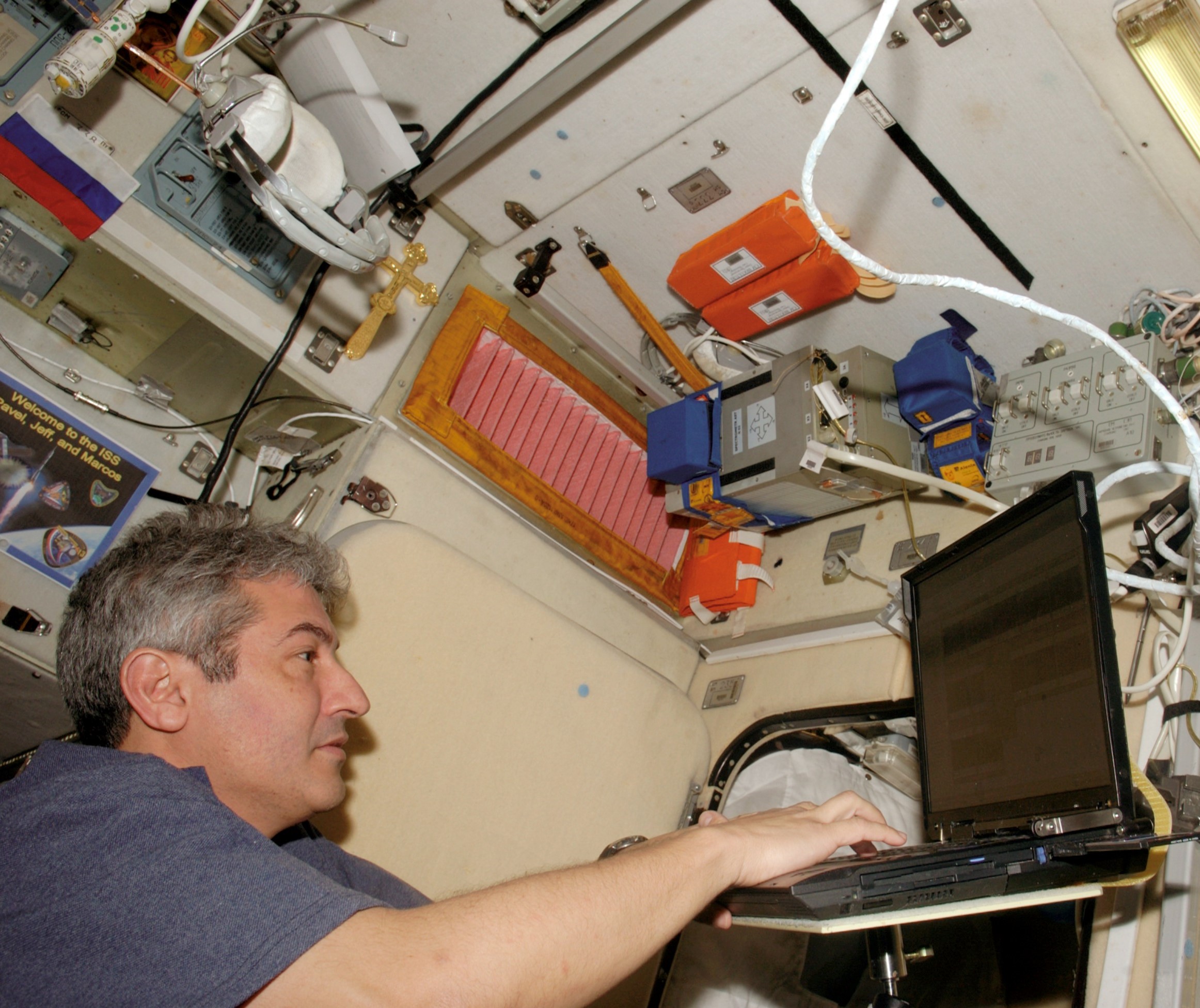



Left: Brazilian astronaut Marcos Pontes, center at rear, with his Expedition 12 and 13 crewmates. Middle: Pontes works on an experiment in the Destiny Laboratory Module. Right: Pontes at work on an experiment in the Russian Zvezda module.
John D. “Danny” Olivas
Selected as a member of NASA’s Astronaut Class of 1998, John D. “Danny” Olivas visited the space station on two occasions as a shuttle mission specialist. His first visit took place aboard Atlantis during the STS-117 mission in June 2007. During the flight, Olivas and fellow mission specialist James F. Reilly conducted two of the four spacewalks to install the S3/S4 truss segment that included the third set of solar arrays. To prevent interfering with the rotation of the new arrays, the crew retracted the starboard P6 array mounted atop the Z1 truss. The STS-117 mission also served as a crew exchange flight, with NASA astronaut Clayton C. Anderson replacing Suni Williams as a member of Expedition 15.
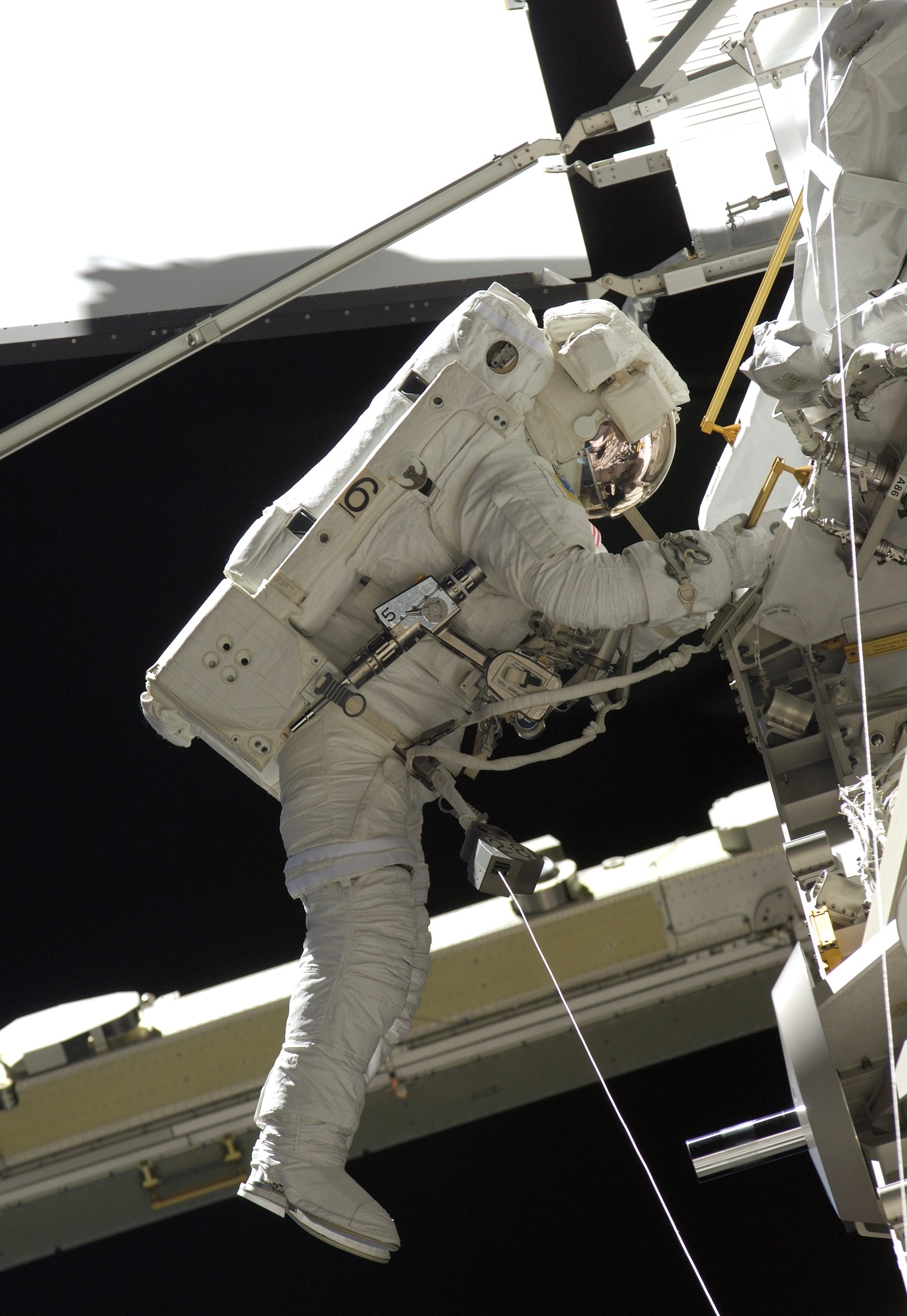
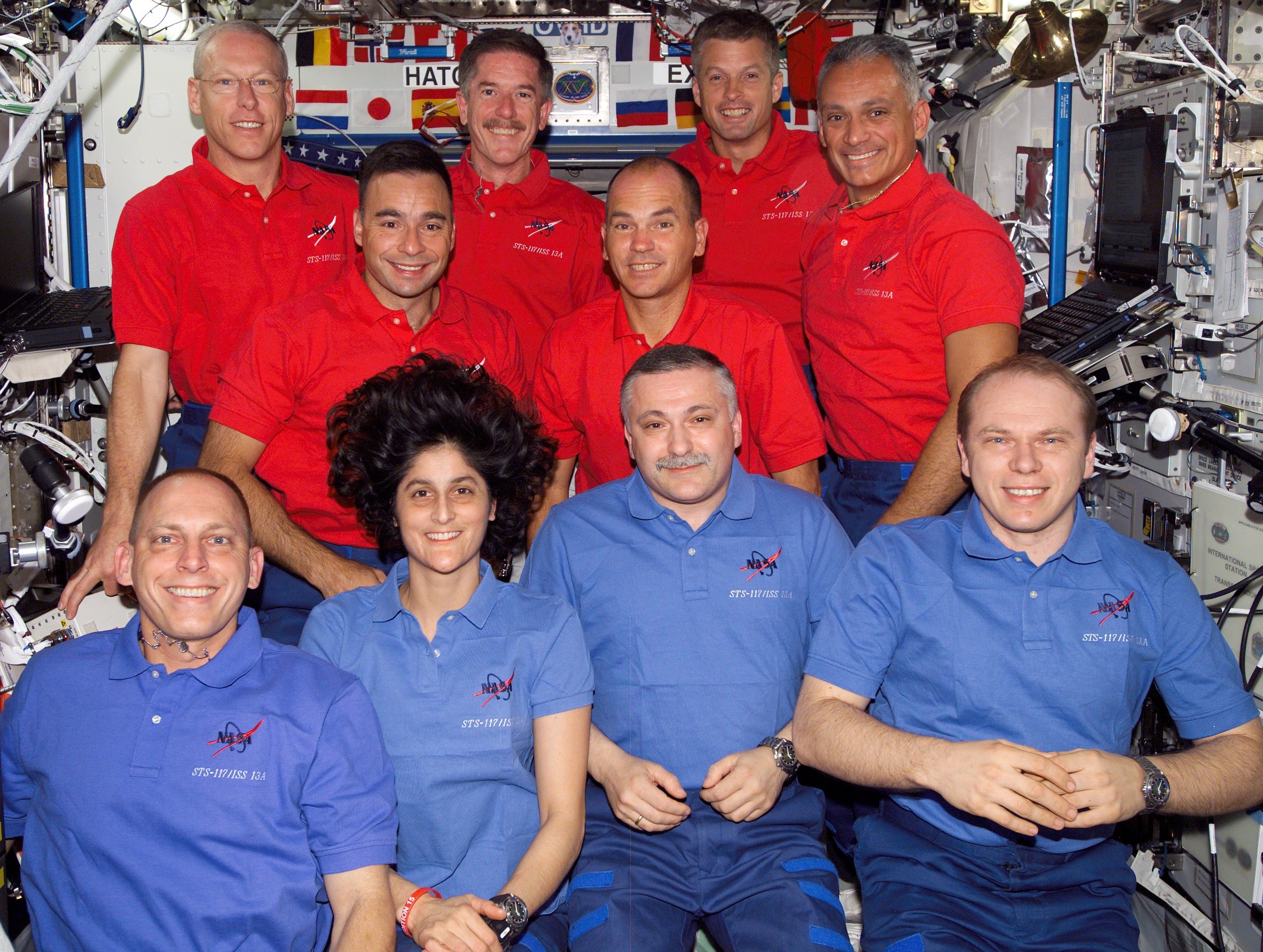


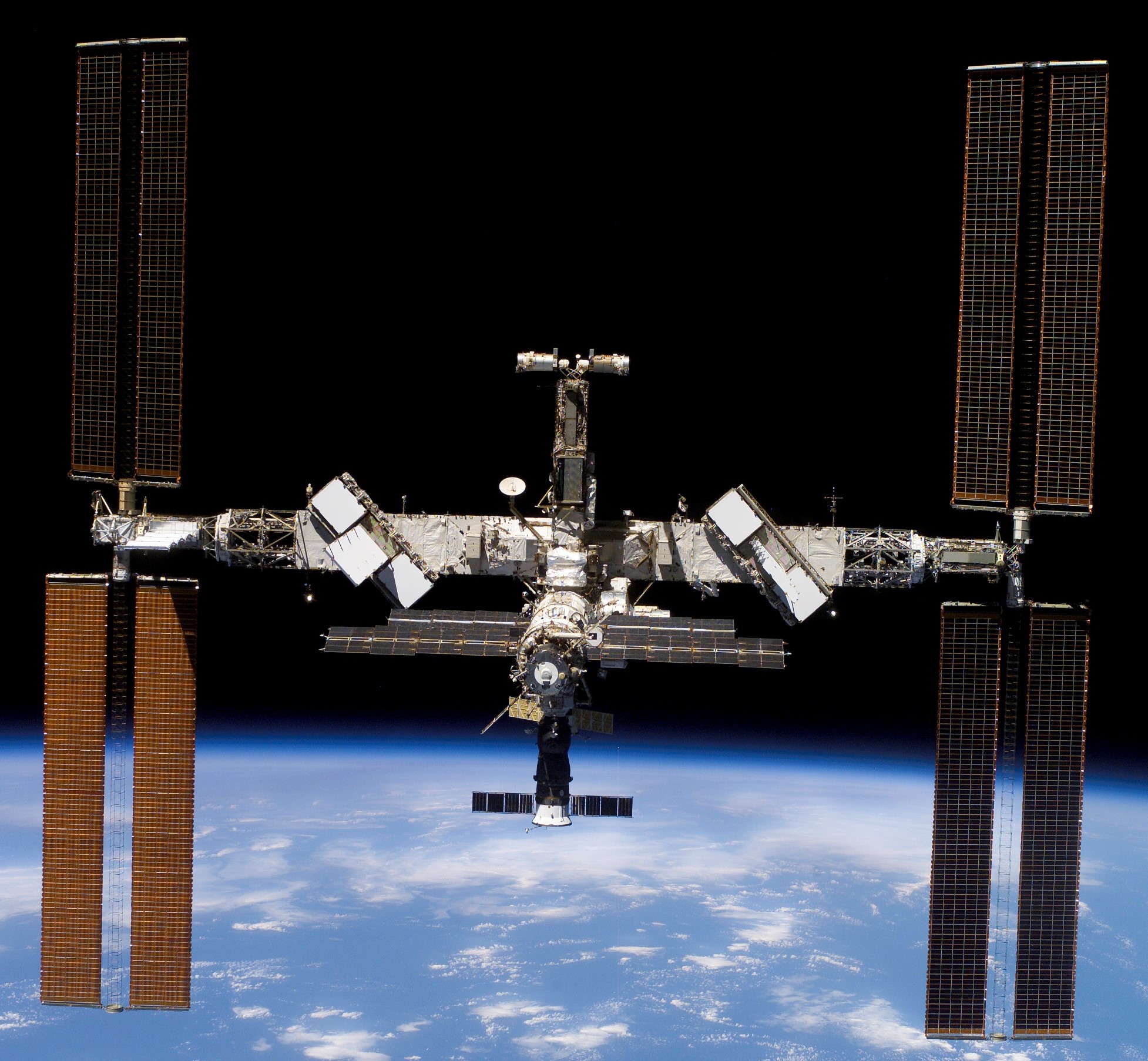
Left: NASA astronaut John D. “Danny” Olivas during an STS-117 spacewalk working on the S3/S4 truss installation. Middle: Olivas, back row at right, with the STS-117 and Expedition 15 crews. Right: The space station as seen by the departing STS-117 crew, showing the new set of starboard solar arrays at right.
On his return to the station, Olivas found it a bit more crowded – three months earlier, the permanent crew aboard the station had expanded from three to six. He and his crewmates launched aboard Discovery on the STS-128 mission in August 2009. The shuttle’s payload bay contained the Leonardo MPLM bringing supplies to help maintain a 6-person crew on the space station, including three systems racks: a crew quarters, an Air Revitalization System rack, and the Combined Operational Load Bearing External Resistance Treadmill (COLBERT) for crew exercise – as well as three research racks – the Fluid Integrated Rack , the Materials Science Research Rack, and the second Minus Eighty-degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI). Olivas participated in three spacewalks to replace the Ammonia Tank Assembly on the P1 truss and to retrieve two experiments from the European Columbus module’s External Payload Facility. STS-128 also completed the final shuttle-based crew exchange, with NASA astronauts Nicole P. Stott and Timothy L. Kopra exchanging places as Expedition 20 crewmembers.
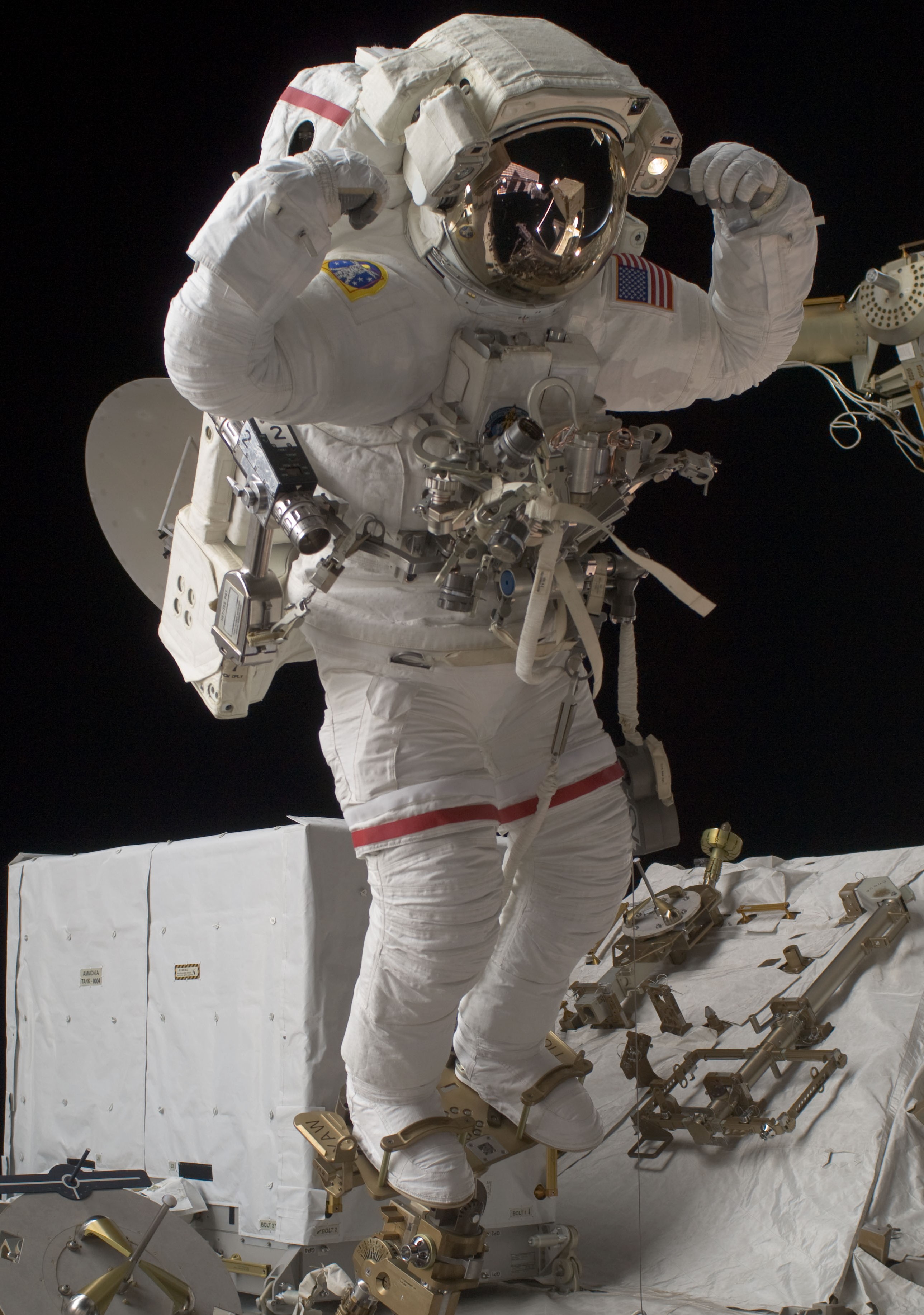
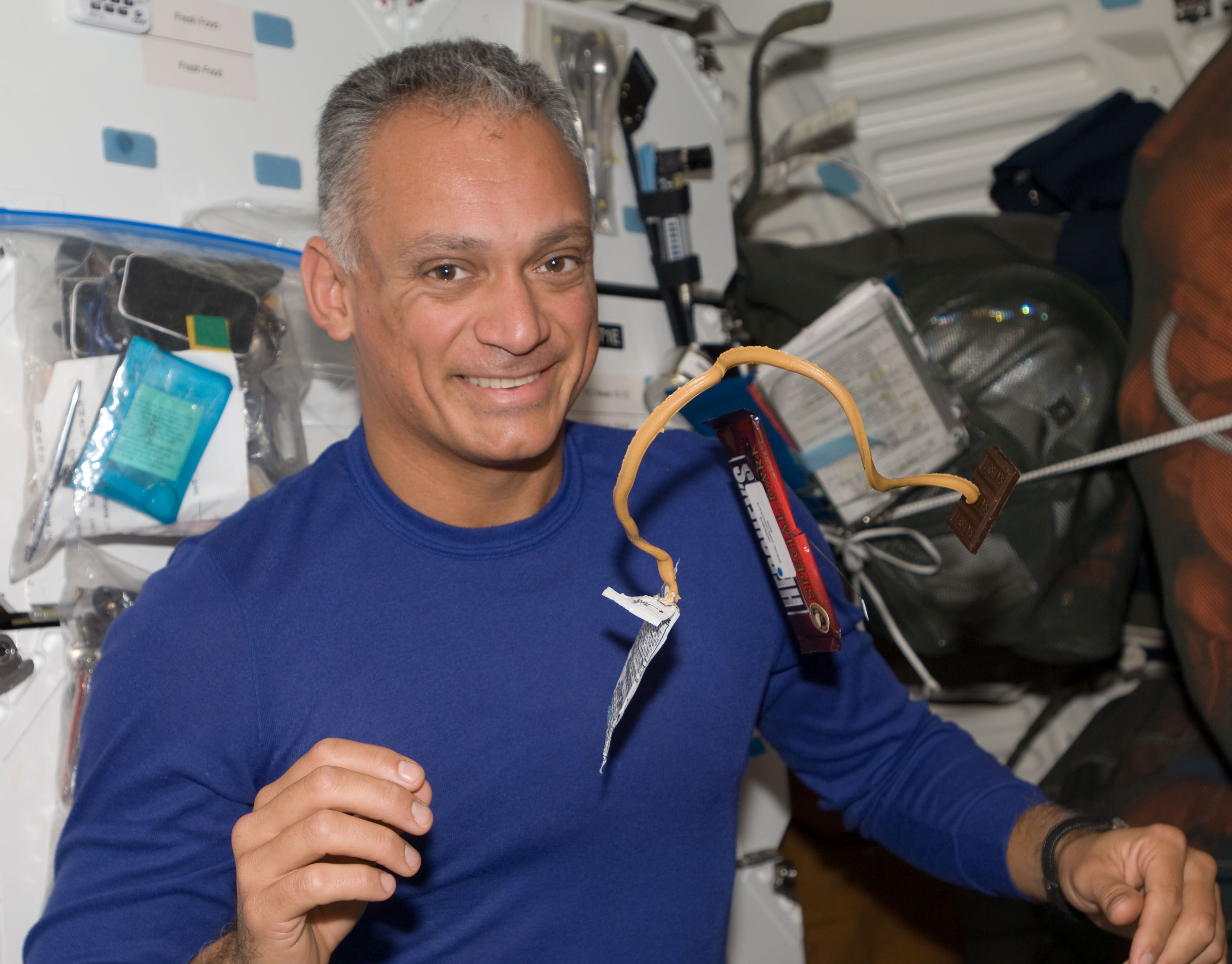
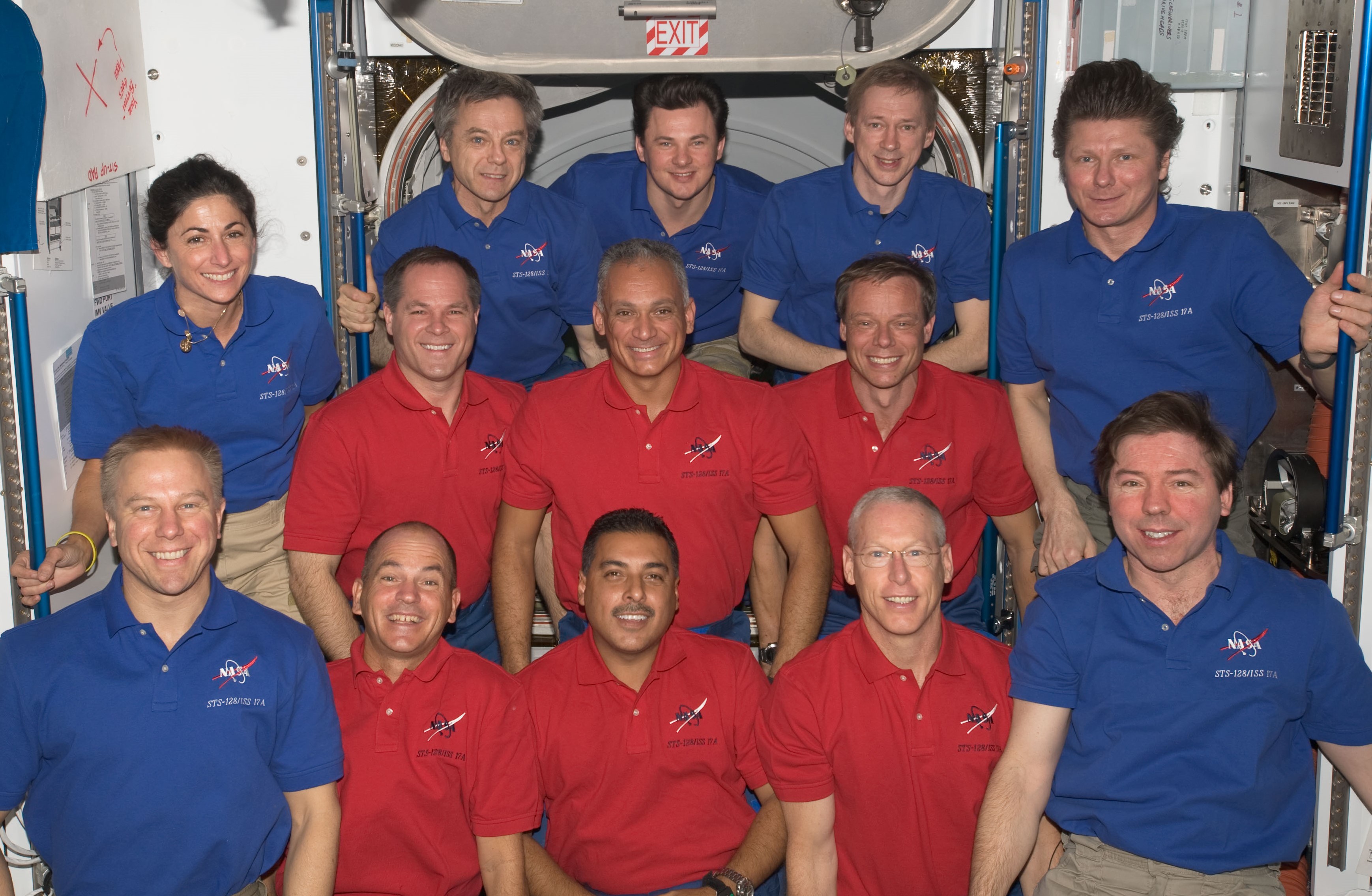



Left: NASA astronaut John D. “Danny” Olivas poses during spacewalk work on the Ammonia
Tank Assembly. Middle: Olivas eating a chocolate and peanut butter snack. Right: Olivas, at center, with the STS-128 and Expedition 20 crews.
George D. Zamka
Selected as a NASA astronaut in 1998, George D. Zamka completed his first space flight as pilot on Discovery’s STS-120 mission. Launching in October 2007, Zamka and his crewmates brought the Harmony Node 2 module to the station, temporarily berthing it on the Unity Node 1’s port side until the Expedition 16 crew relocated it to Destiny’s forward hatch. In its final location, Harmony enabled the later installation of the European and Japanese elements. The crew also relocated the P6 truss segment from atop Z1 to the outboard port truss. During the redeployment of the P6 solar arrays, one of the arrays developed a tear that required repair using a cufflink-like device to sew up the gap in the panel. STS-120 also conducted a crew exchange, with NASA astronauts Daniel M. Tani and Clay Anderson exchanging places as members of Expedition 16. As the STS-120 pilot, Zamka completed the undocking from the station and the departure fly-around maneuver.
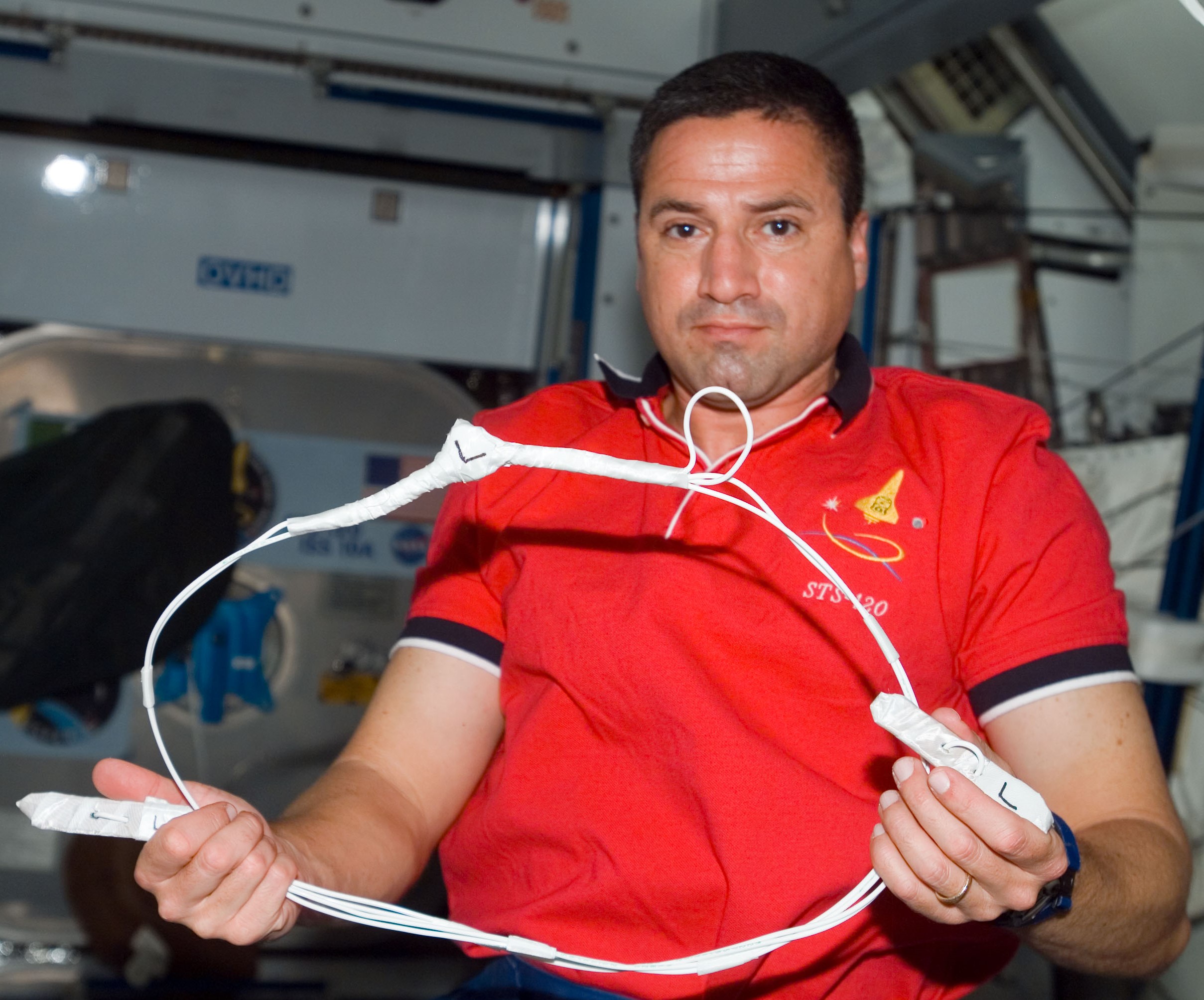
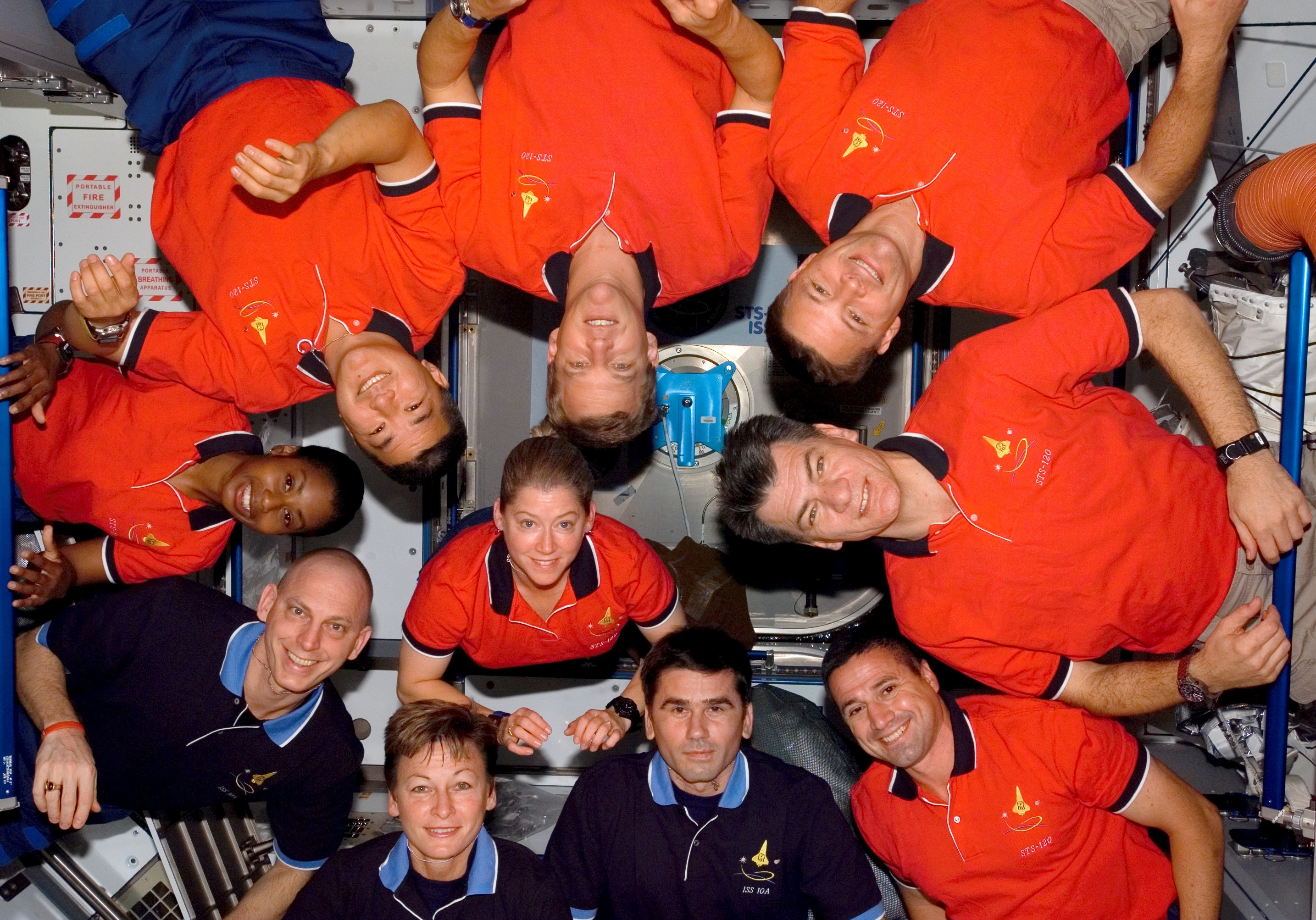
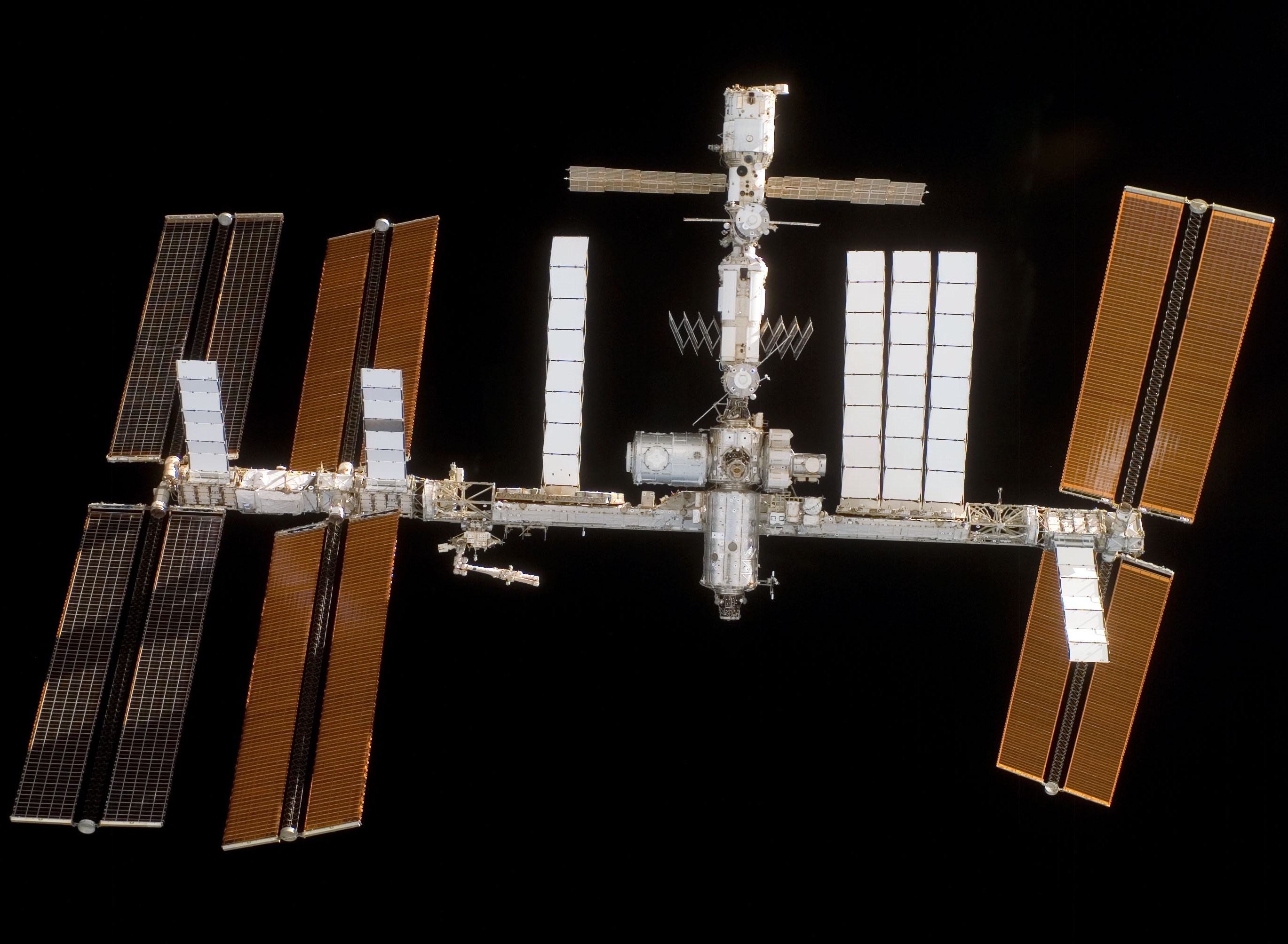



Left: NASA astronaut George D. Zamka holding the cufflink device used to repair the torn solar array. Middle: Zamka, lower right, with the STS-120 and Expedition 16 crews. Right: The space station as seen from STS-120 departing, showing the newly delivered Harmony Node 2 module temporarily berthed at the Unity Node 1 and the relocated and redeployed P6 truss segment and solar arrays at left.
When he returned to the orbiting lab in February 2010, Zamka did so as commander of space shuttle Endeavour’s STS-130 mission. After guiding the shuttle to a successful docking with the station, Zamka and his crewmates, along with the Expedition 22 crew, installed the Tranquility Node 3 module to Unity’s port side and activated the new element. The new module provided accommodations for life support and habitation facilities for the station’s six-person crew. The crew removed the Cupola from its launch position at the end of Tranquility and relocated it to the module’s Earth-facing port. The Cupola’s six trapezoidal and one circular center window provide crews not only visibility for approaching visiting vehicles, but also spectacular views of their home planet passing by below.
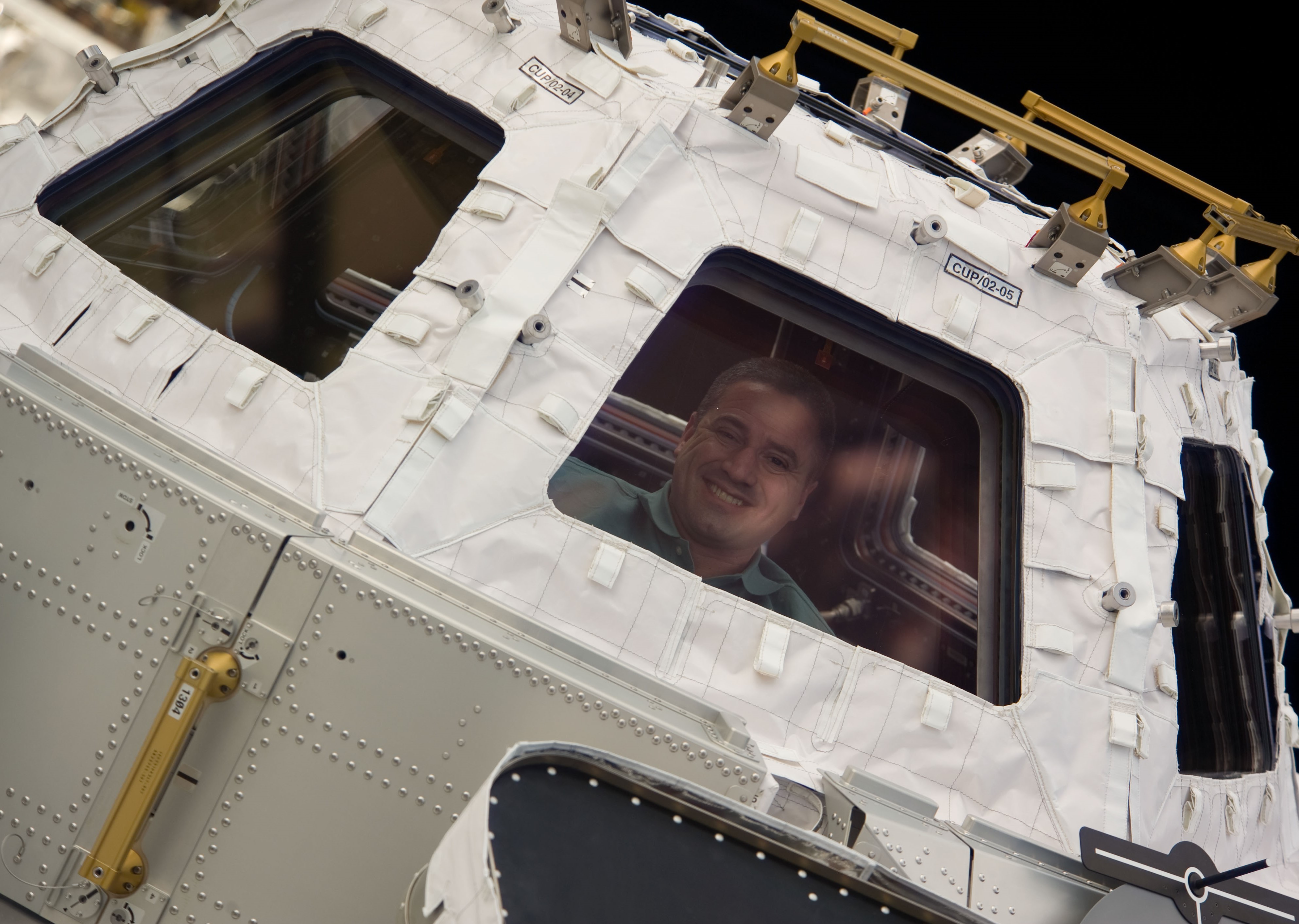
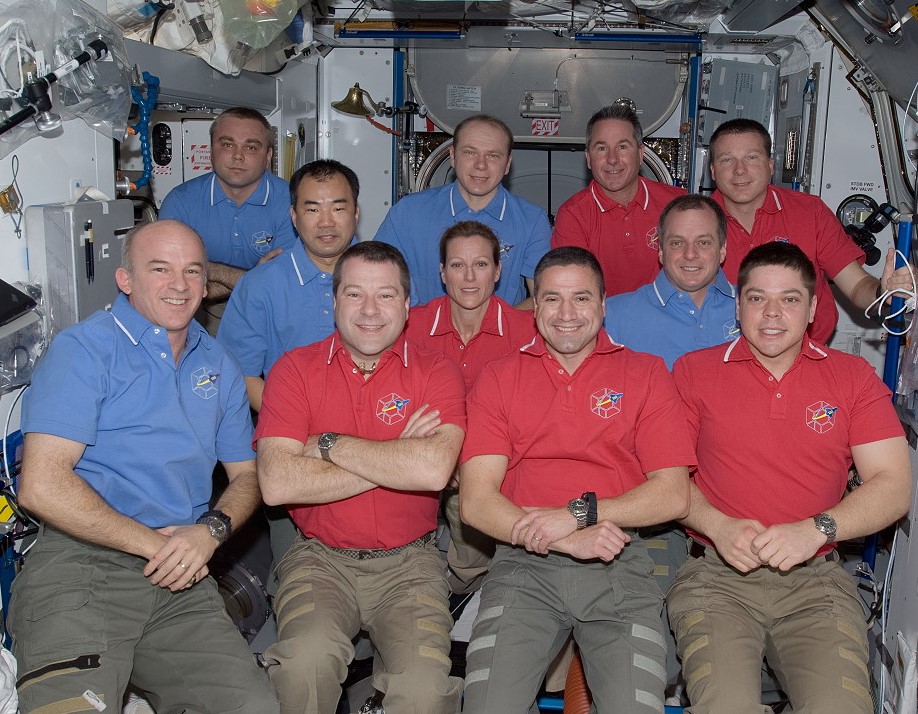
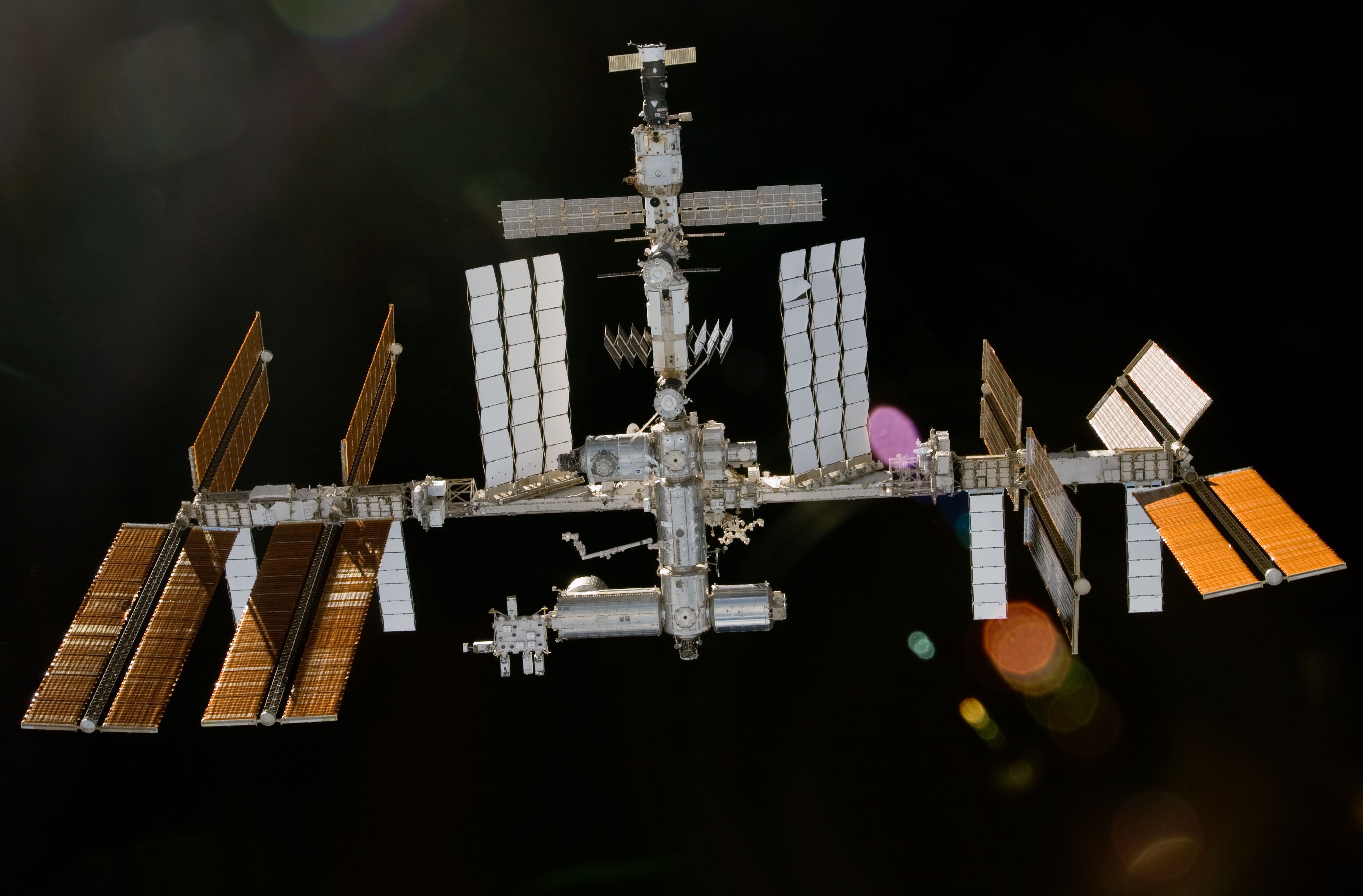



Left: NASA astronaut George D. Zamka peering through one of the Cupola’s windows. Middle: Zamka, front row second from right, with the STS-130 and Expedition 22 crews. Right: The space station as seem from the departing STS-130, showing the Tranquility Node 3 and Cupola berthed at the Unity Node 1, left of center.
Joseph M. “Joe” Acaba
Joseph M. “Joe” Acaba was selected in 2004 as part of NASA’s Educator Astronaut Program and qualified as a mission specialist. His first flight into space was aboard STS-119 in March 2009. Discovery brought up the S6 final truss segment with the fourth and final set of solar arrays, bringing the U.S. segment of the station’s useable power generating capability between 42 and 60 kilowatts. Acaba completed two of the mission’s three spacewalks, one with fellow mission specialist Steven R. Swanson and the other with fellow educator-astronaut and mission specialist Richard R. “Ricky” Arnold. During the STS-119 mission, Koichi Wakata of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) replaced NASA astronaut Sandra H. Magnus as a member of the Expedition 18 crew.
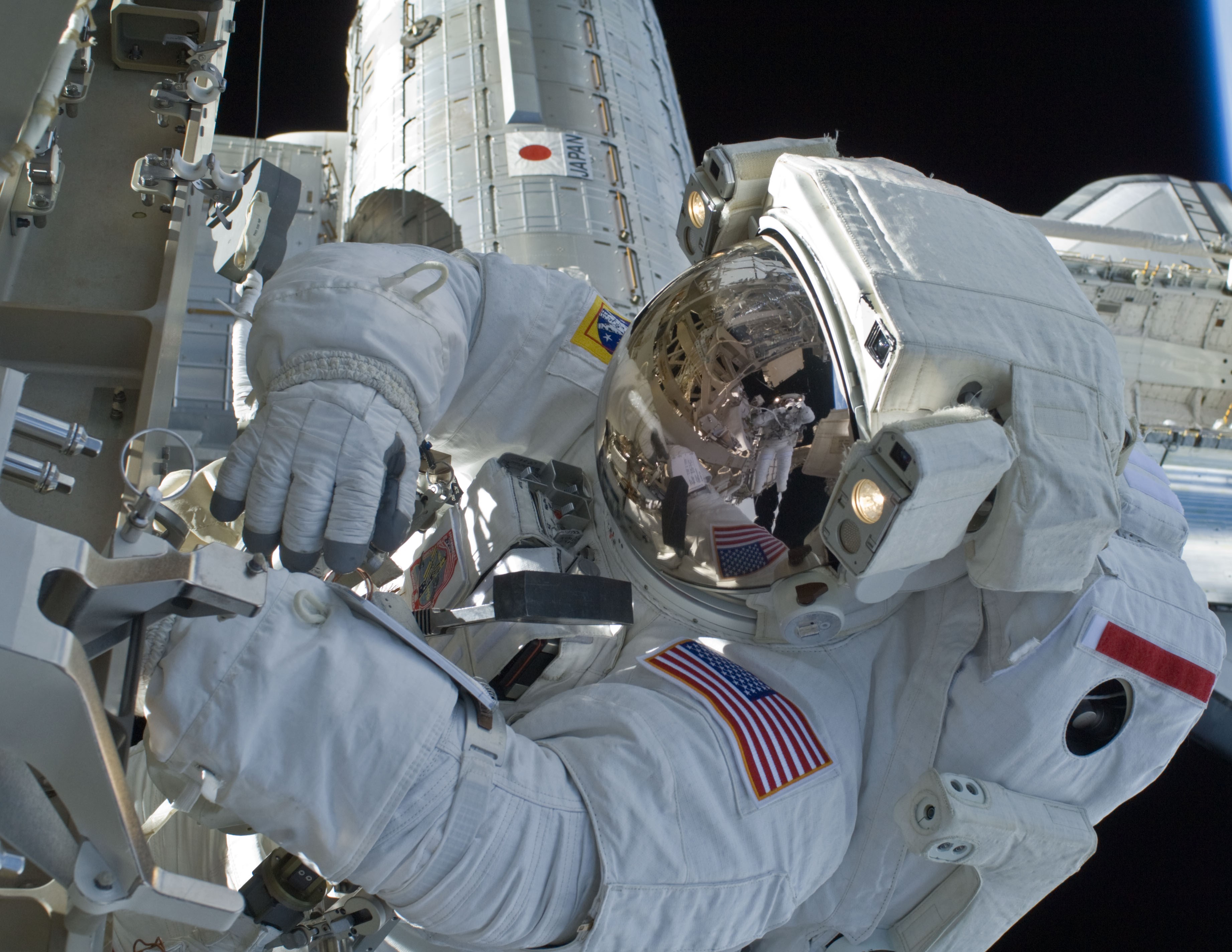
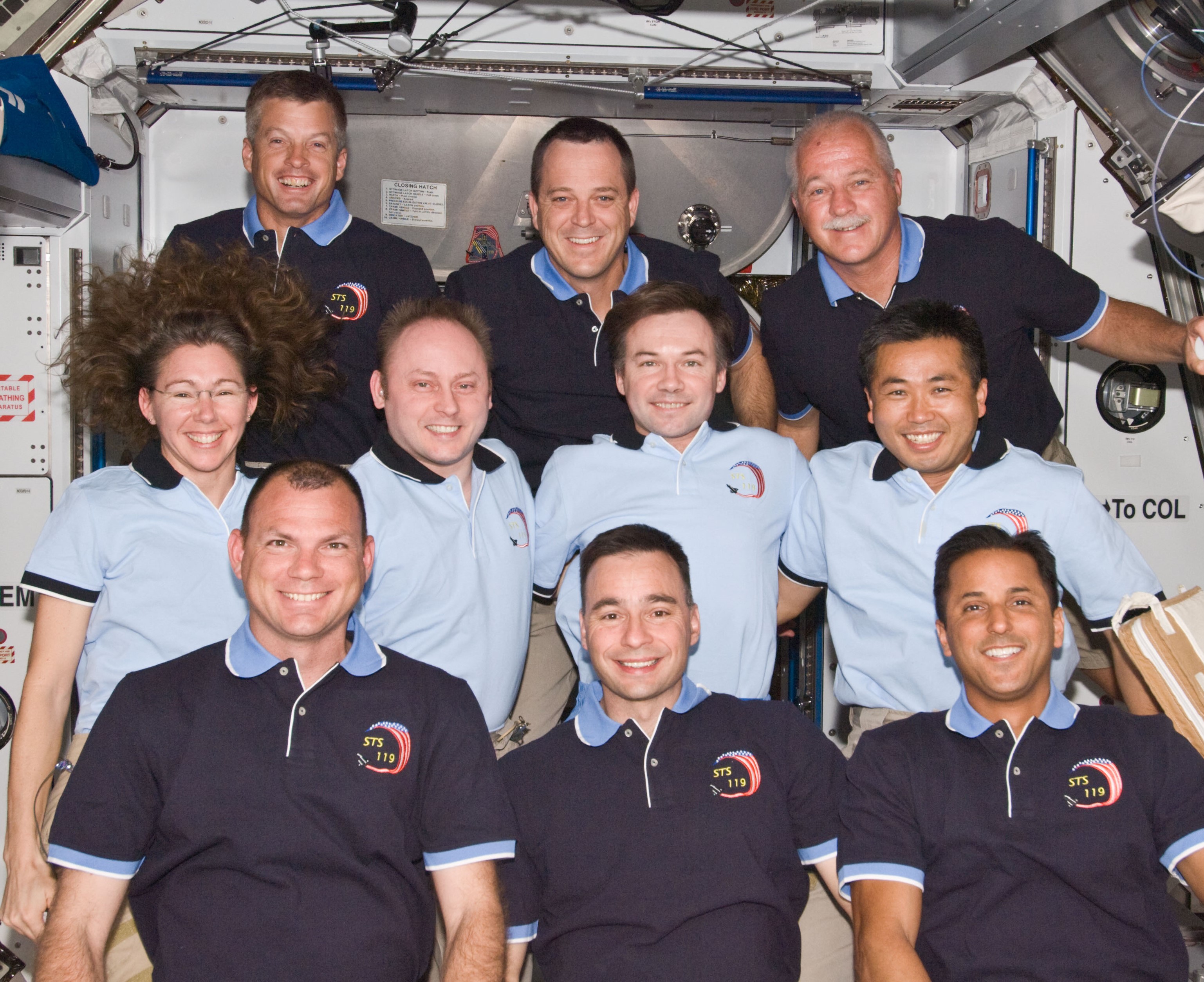


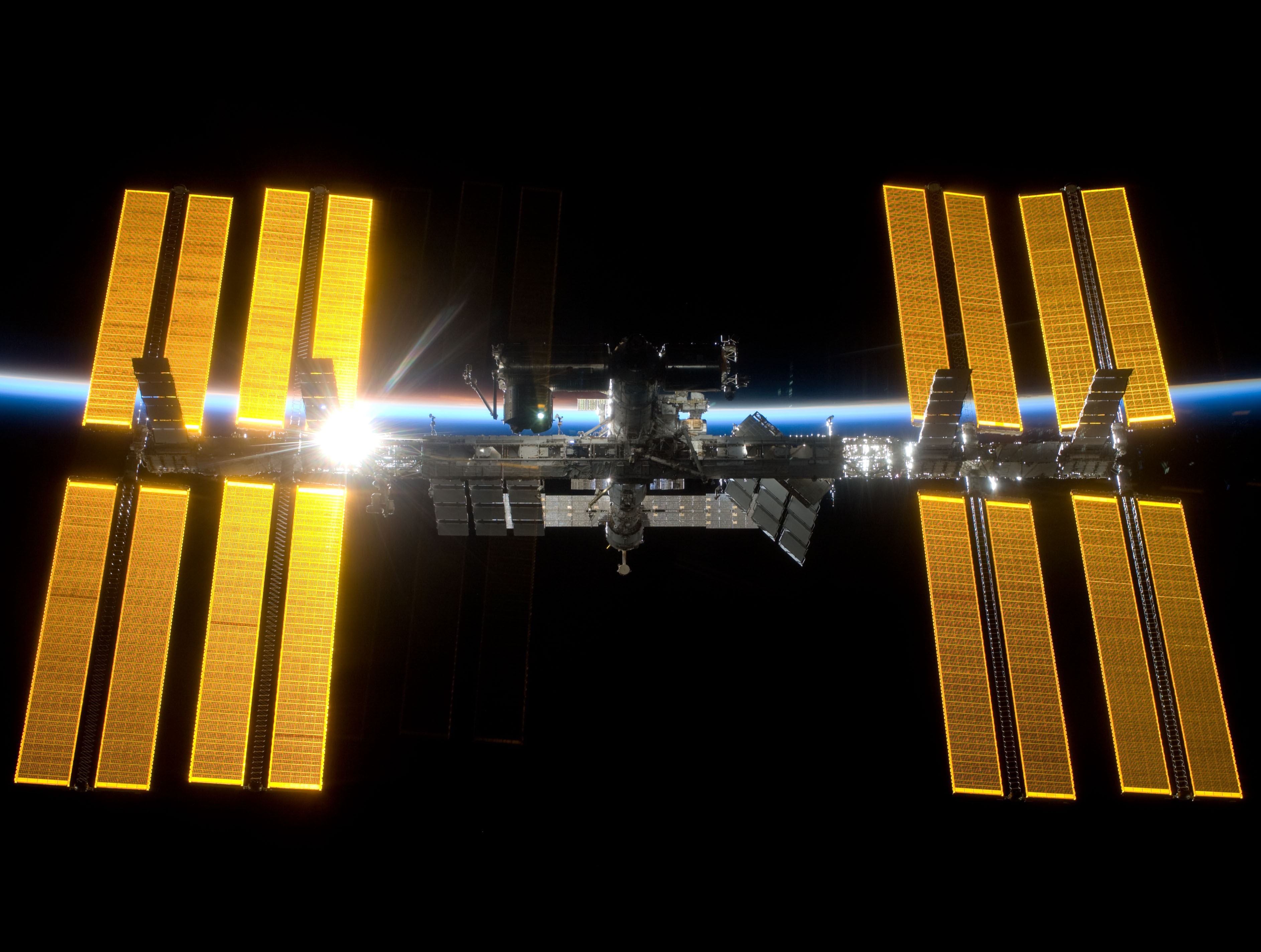
Left: NASA astronaut Joseph M. Acaba during the third STS-119 spacewalk. Middle: Acaba, front row at right, with the STS-119 and Expedition 18 crews. Right: The space station as seen from the departing STS-119, with the newly added S6 truss segment and solar arrays, at right.
For his second visit to the station, Acaba stayed for 125 days as part of Expeditions 31 and 32, launching in May 2012 from Kazakhstan aboard Soyuz TMA-04M. A week after arriving, Acaba and his crewmates welcomed the first commercial vehicle to dock with the space station, the SpaceX Dragon cargo resupply vehicle on its Demo-2 mission carrying food, water, scientific experiments and other supplies. The Expedition 31 crew loaded the Dragon spacecraft with cargo and experiment samples for return to Earth. The crew observed and photographed a rare celestial event, a transit of Venus across the Sun on June 5. In addition to conducting numerous science experiments, Acaba helped fire prevention icon Smokey the Bear celebrate his 68th birthday.
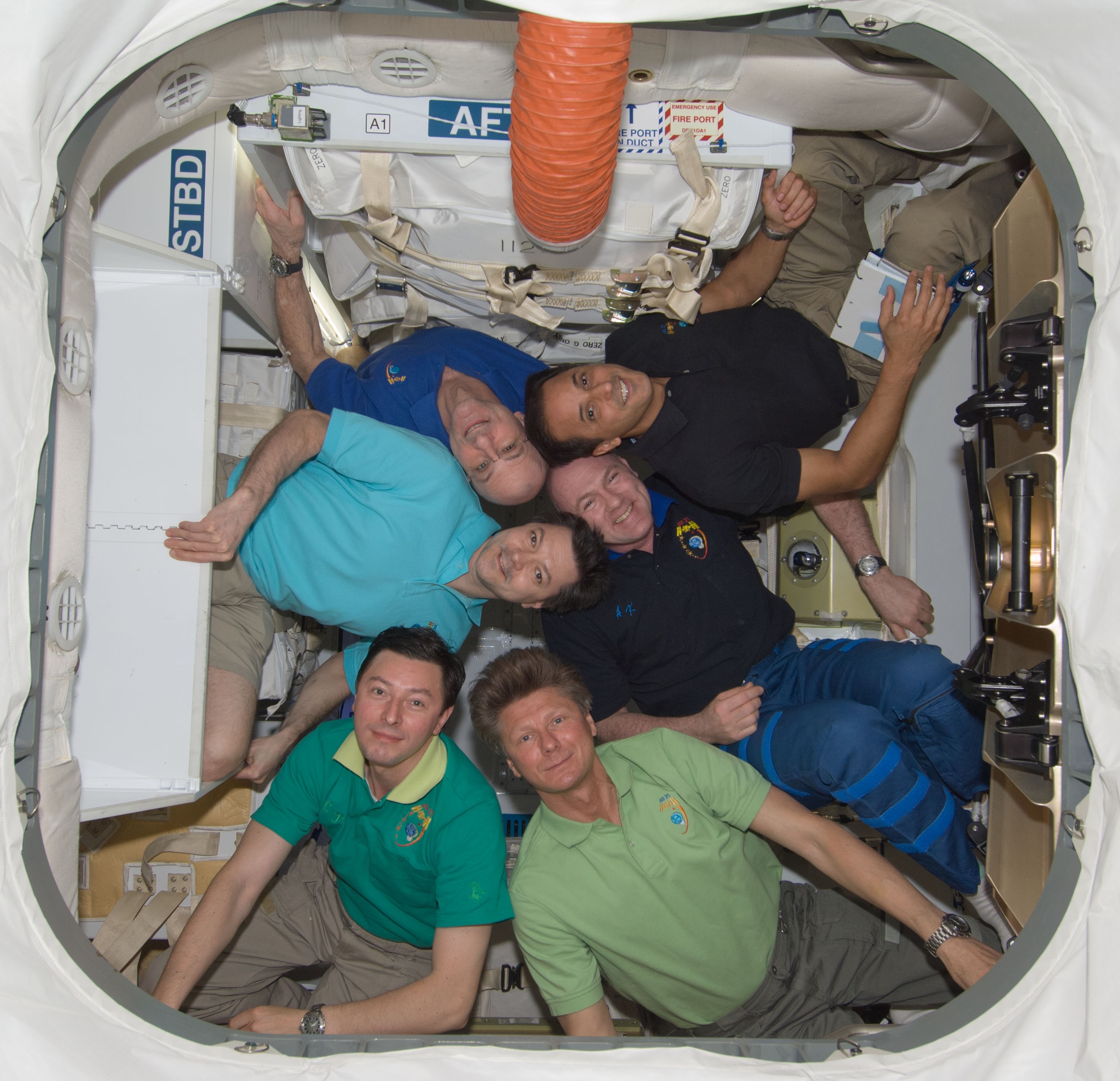
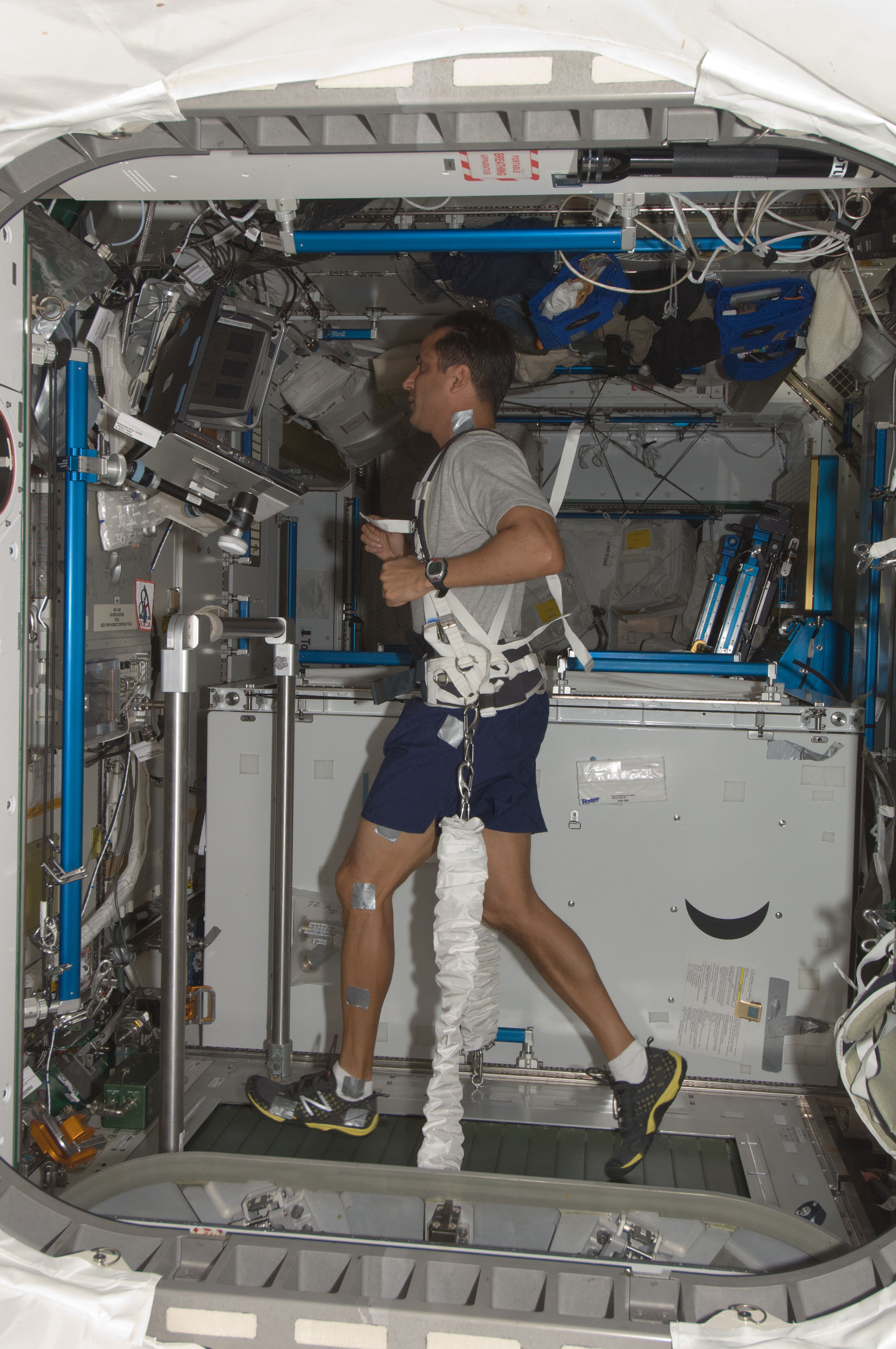


Left: NASA astronaut Joseph M. Acaba, top right, with his Expedition 31 crewmates inside the SpaceX Dragon resupply vehicle. Middle: Acaba running on the COLBERT treadmill. Right: Acaba refracted in a globule of water.
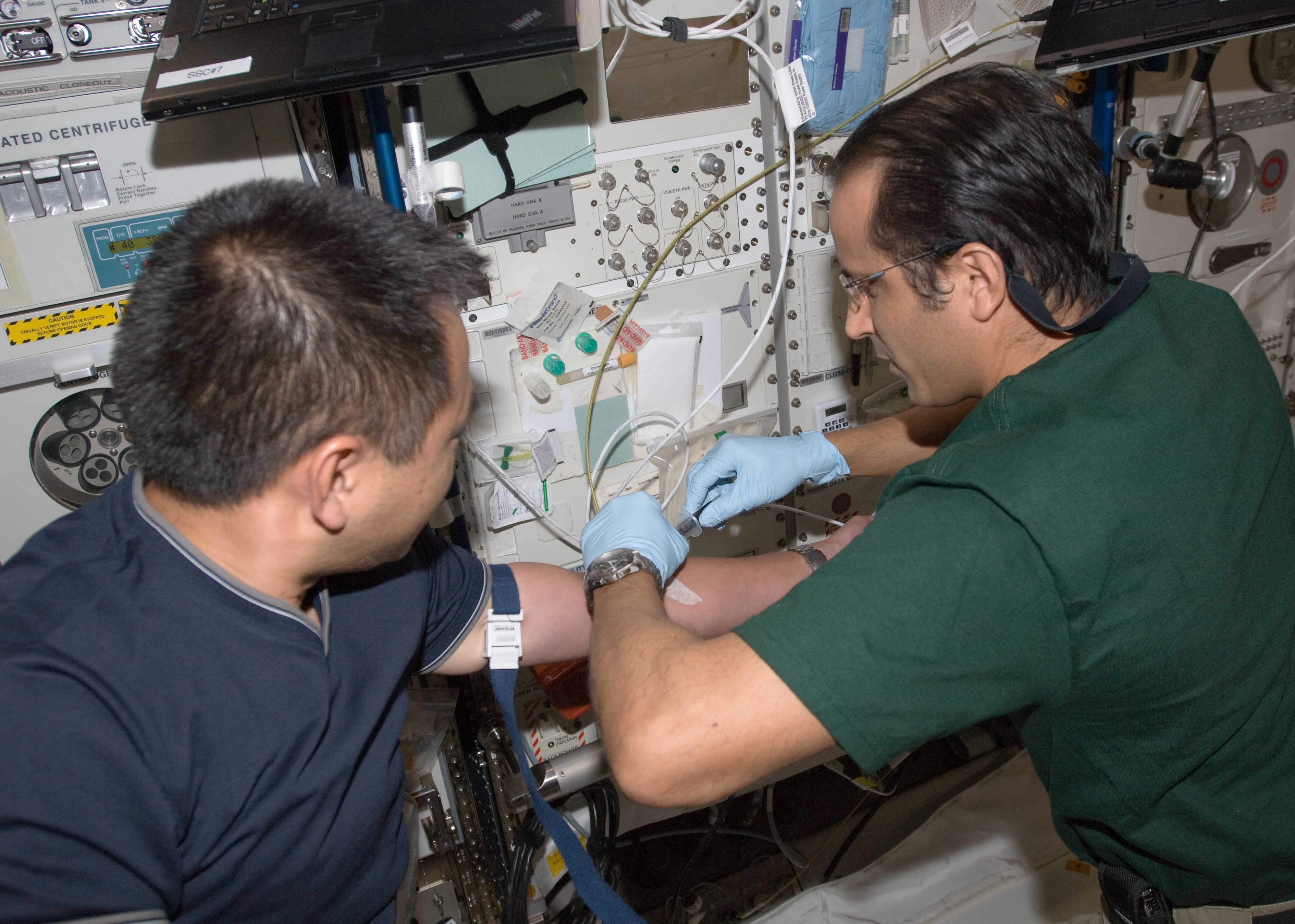
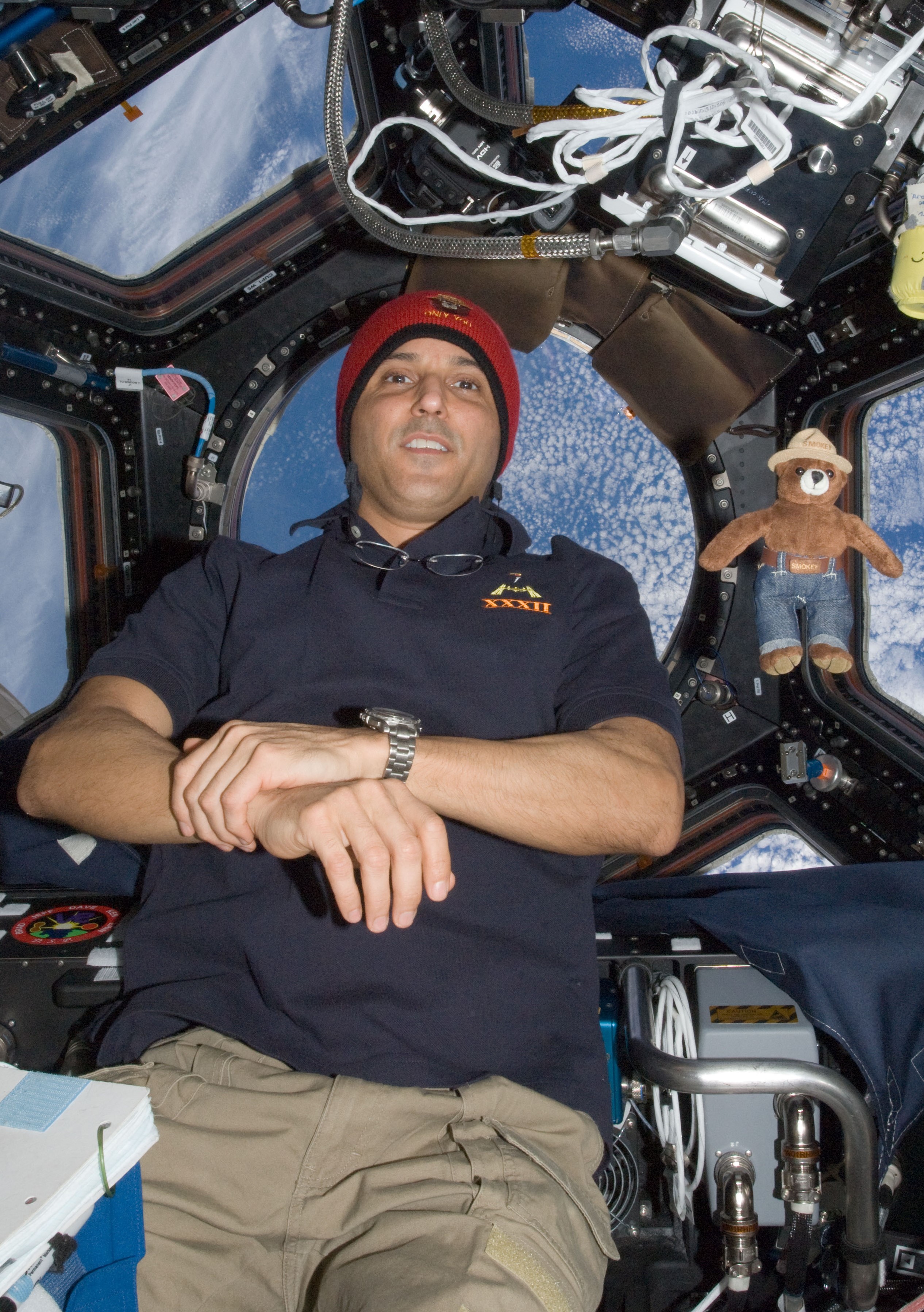
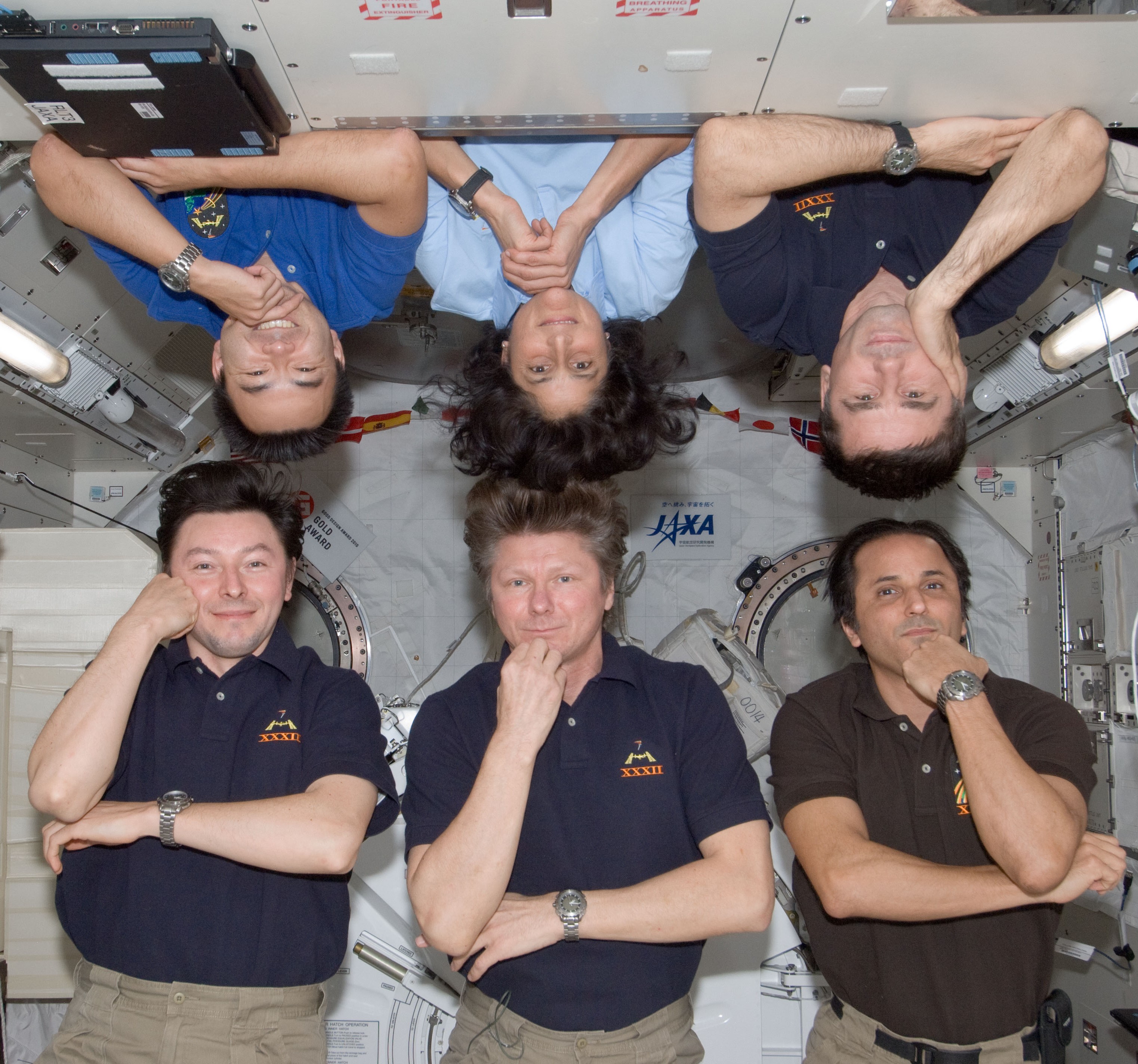



Left: NASA astronaut Joseph M. Acaba, right, drawing a blood sample from Akihiko Hoshide of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency. Middle: Acaba with a toy Smokey the Bear in the Cupola to help celebrate the forest fire prevention icon’s 68th birthday. Right: Acaba, lower right, with this Expedition 32 crewmates.
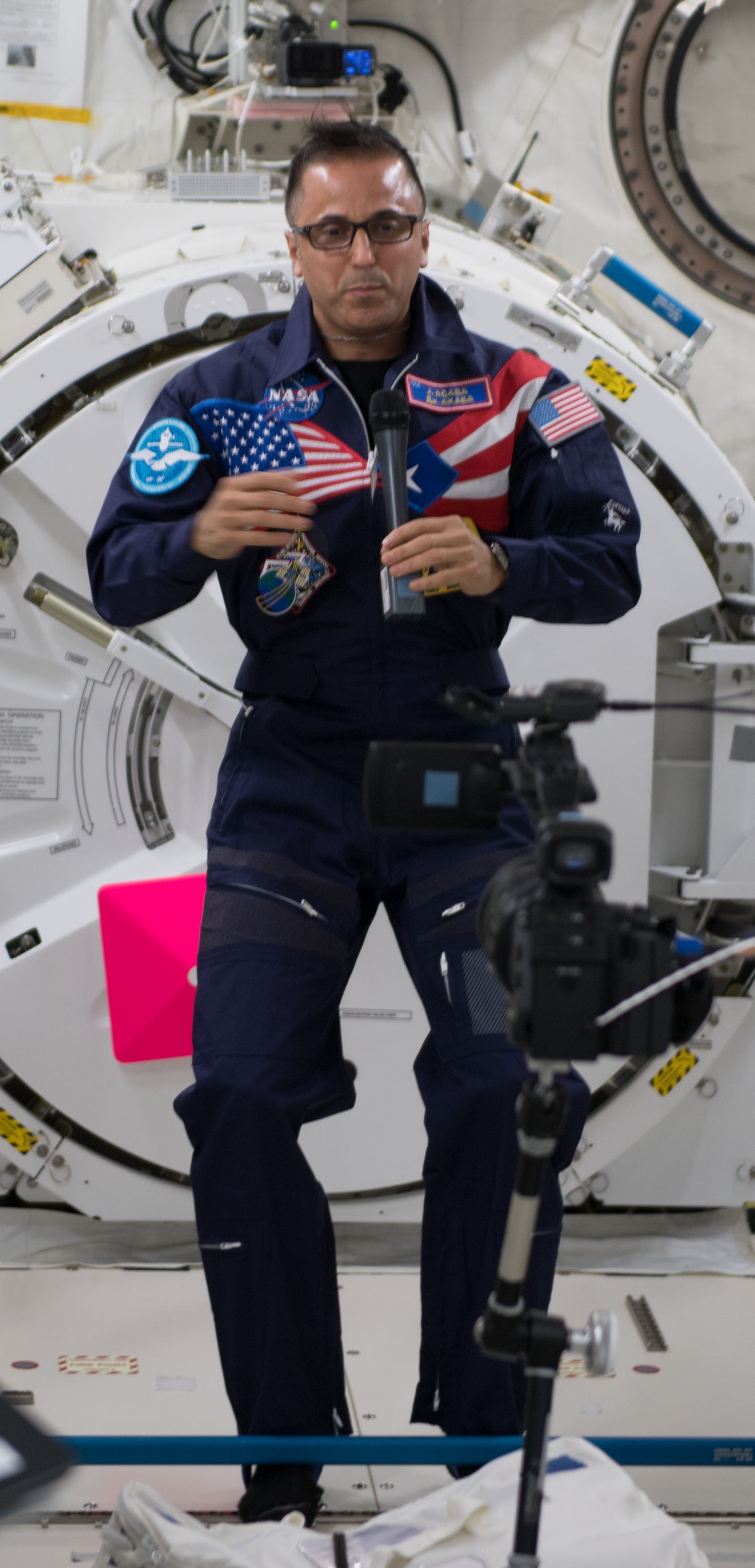
Acaba returned to the space station five years later as a member of Expedition 53 and 54, launching in September 2017, aboard Soyuz MS-06 Acaba joined NASA astronaut Randolph J. “Randy” Bresnik for a nearly seven-hour spacewalk to lubricate the newly installed replacement Latching End Effector on the SSRMS. Acaba continued with the research program and celebrated his Puerto Rican heritage with several events. He returned to Earth after a 168-day flight. Over his three missions, Acaba accumulated 306 days in space and nearly 20 hours in spacewalk time.
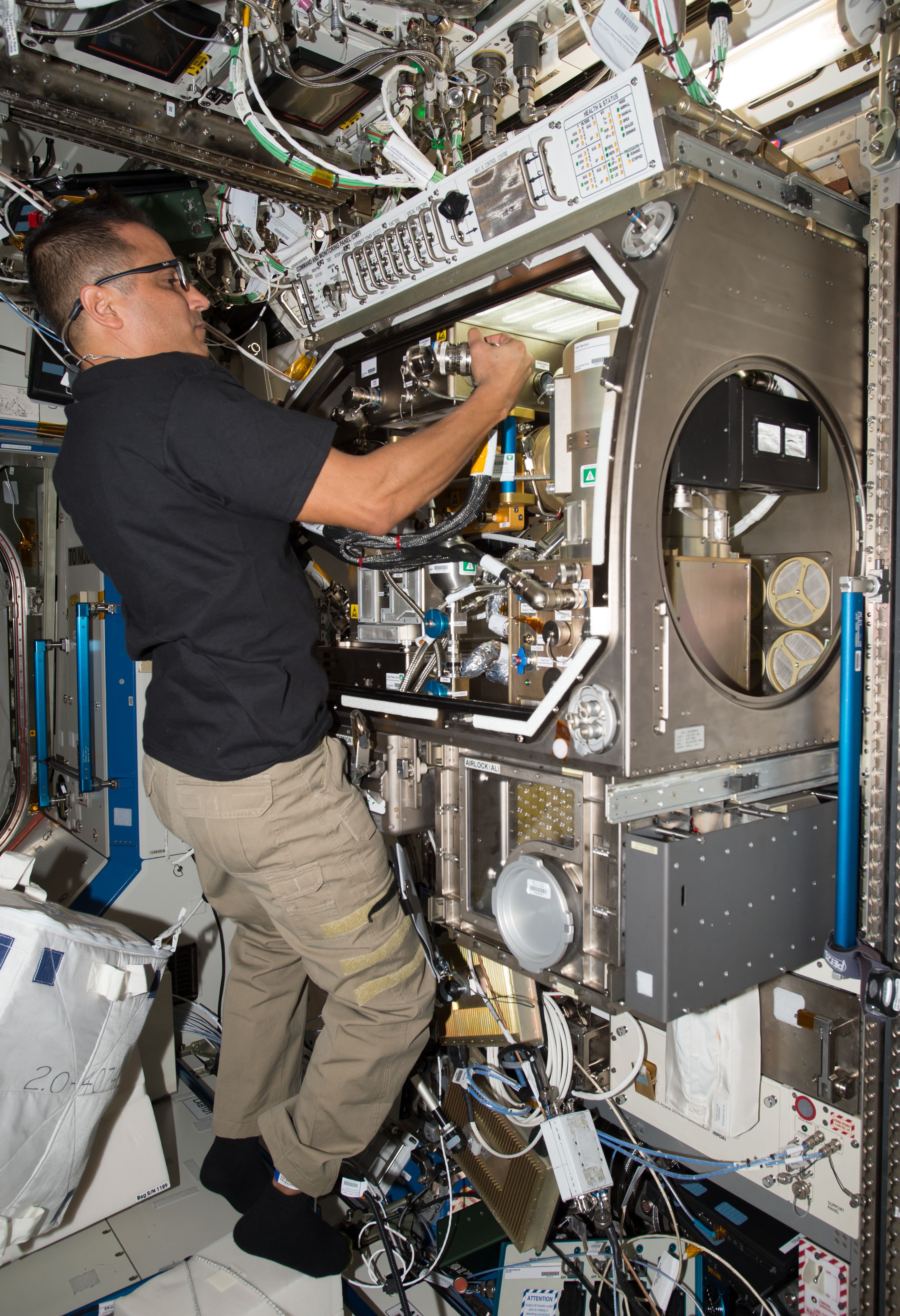
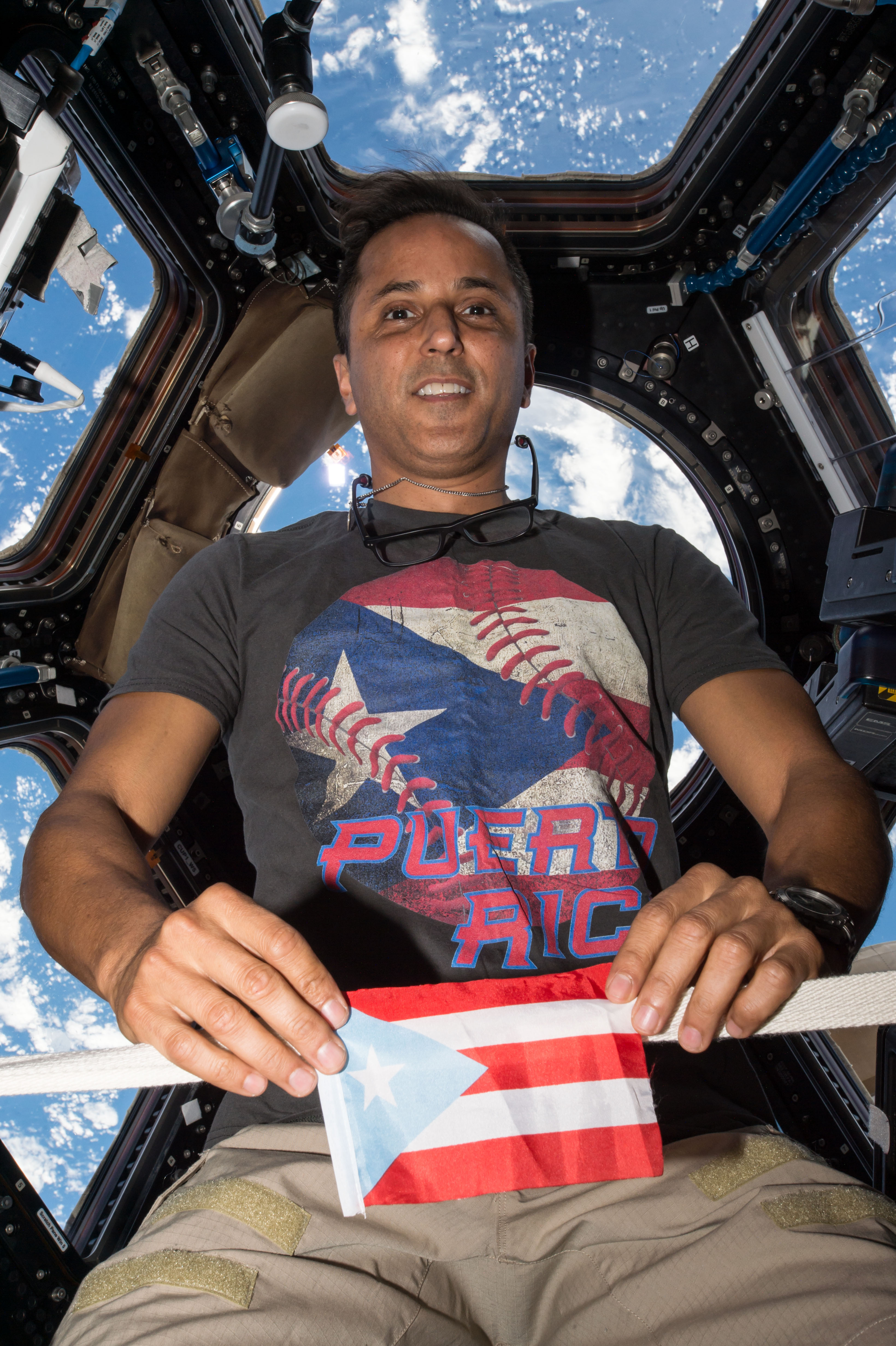
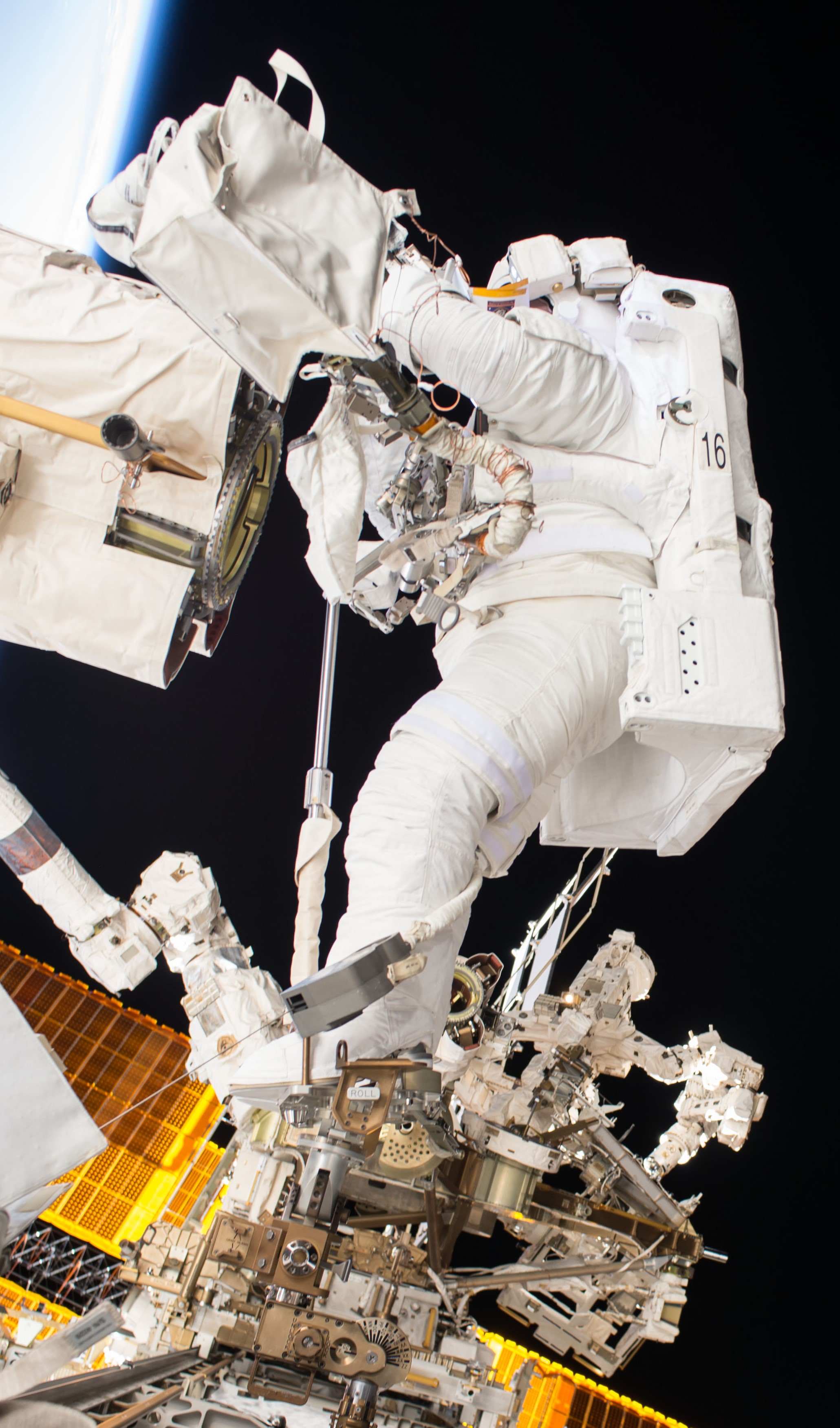
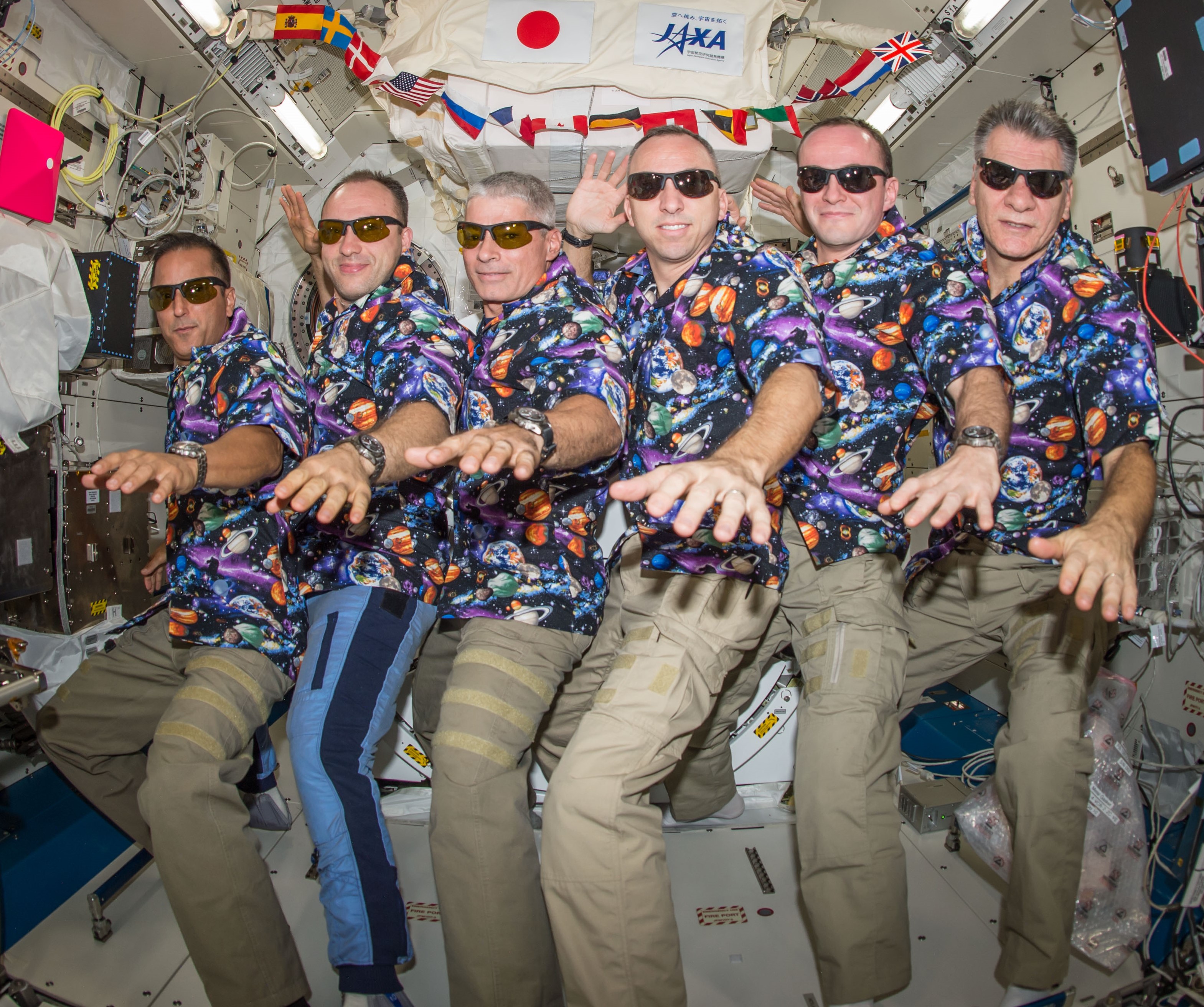




Left: NASA astronaut Joseph M. Acaba conducting an experiment in the Microgravity Sciences Glovebox. Middle left: In the Cupola, Acaba showing Puerto Rico pride. Middle right: During a spacewalk, Acaba is lubricating the Candarm2 Latching End Effector. Right: Acaba, left, with his Expedition 53 crewmates.
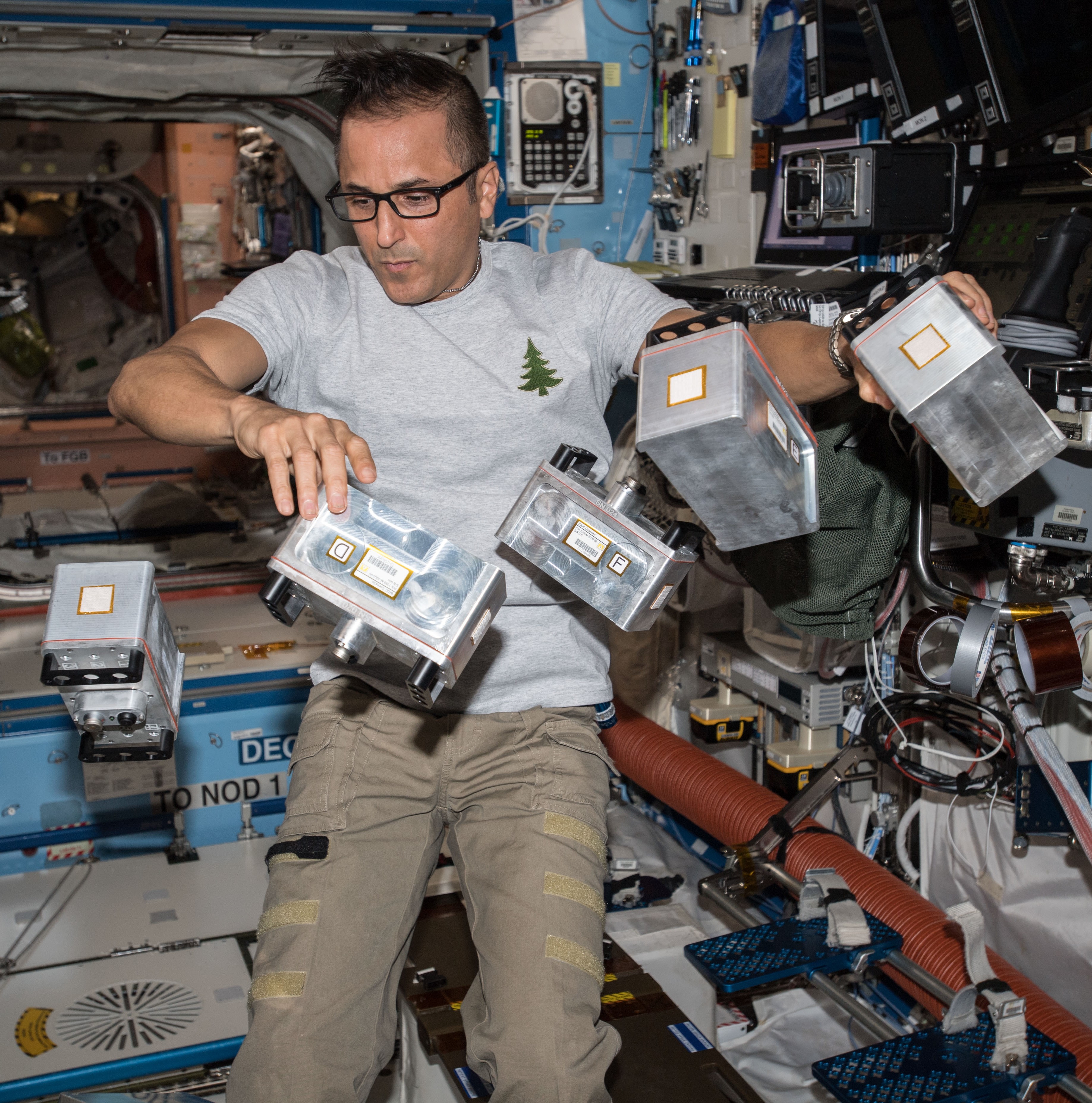
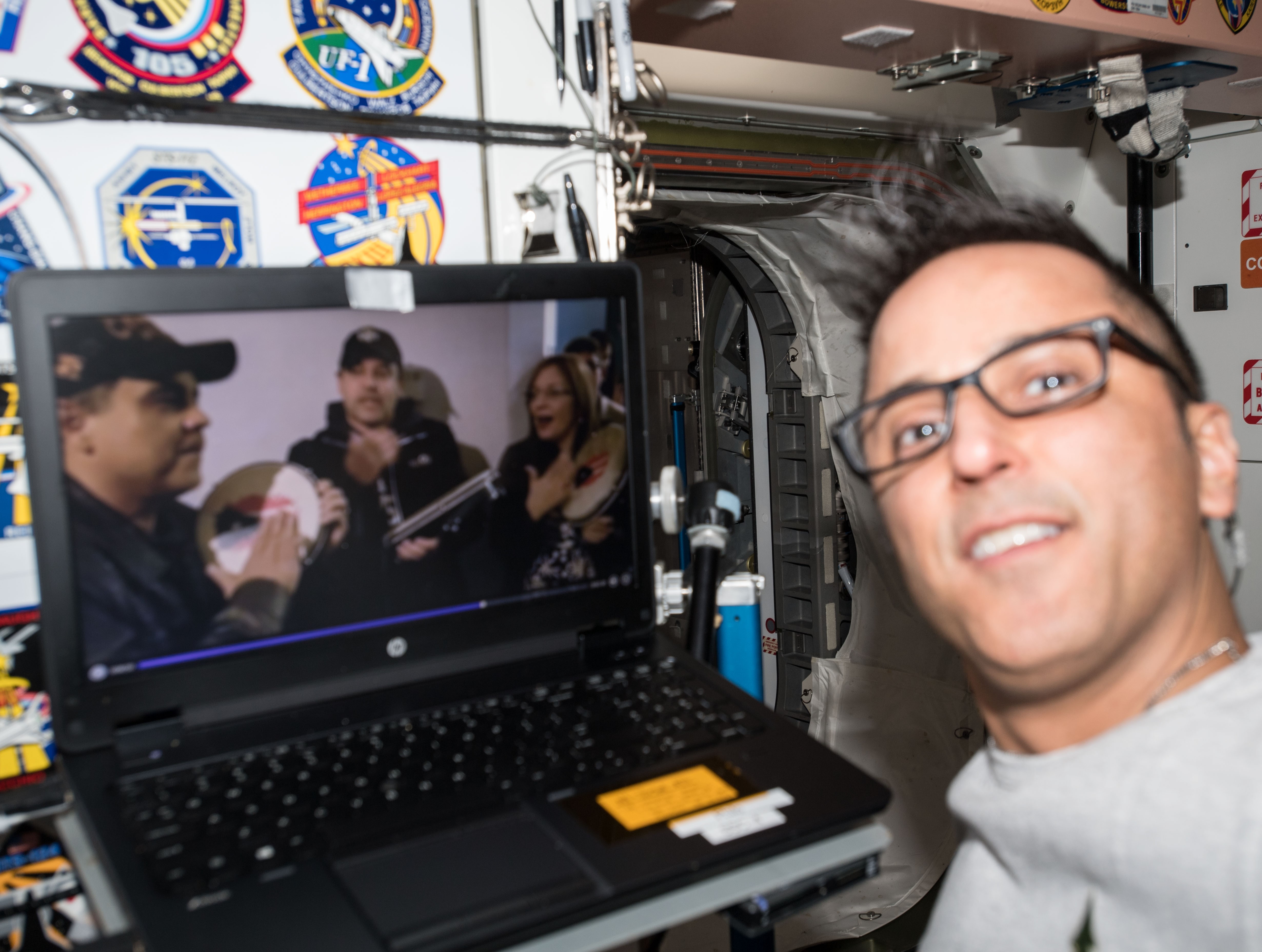




Left: NASA astronaut Joseph M. Acaba working with the Biological Research in Canisters experiment. Middle left: Acaba speaking with the Puerto Rico Institute of Robotics. Middle right: During the holidays, Acaba participating in a parranda by video. Right: Acaba, upper left, with his Expedition 54 crewmates.
José M. Hernández
Selected in 2004 as a NASA astronaut, José M. Hernández made his single visit to the space station during the STS-128 mission. Launched aboard space shuttle Discovery in August 2009, Hernández operated both the shuttle and station robotic arms to move the Leonardo MPLM back and forth and translate astronauts during the mission’s three spacewalks. He participated in the transfer and installation of the three systems racks and the three research racks aboard the orbiting laboratory. STS-128 also completed the final shuttle-based crew exchange, with Stott replacing Kopra as an Expedition 20 crew member. In collaboration with Amazon Studios, NASA is helping chronicle Hernández’ life and career through the film “A Million Miles Away,” telling the story of his journey from migrant farmer to NASA space explorer.
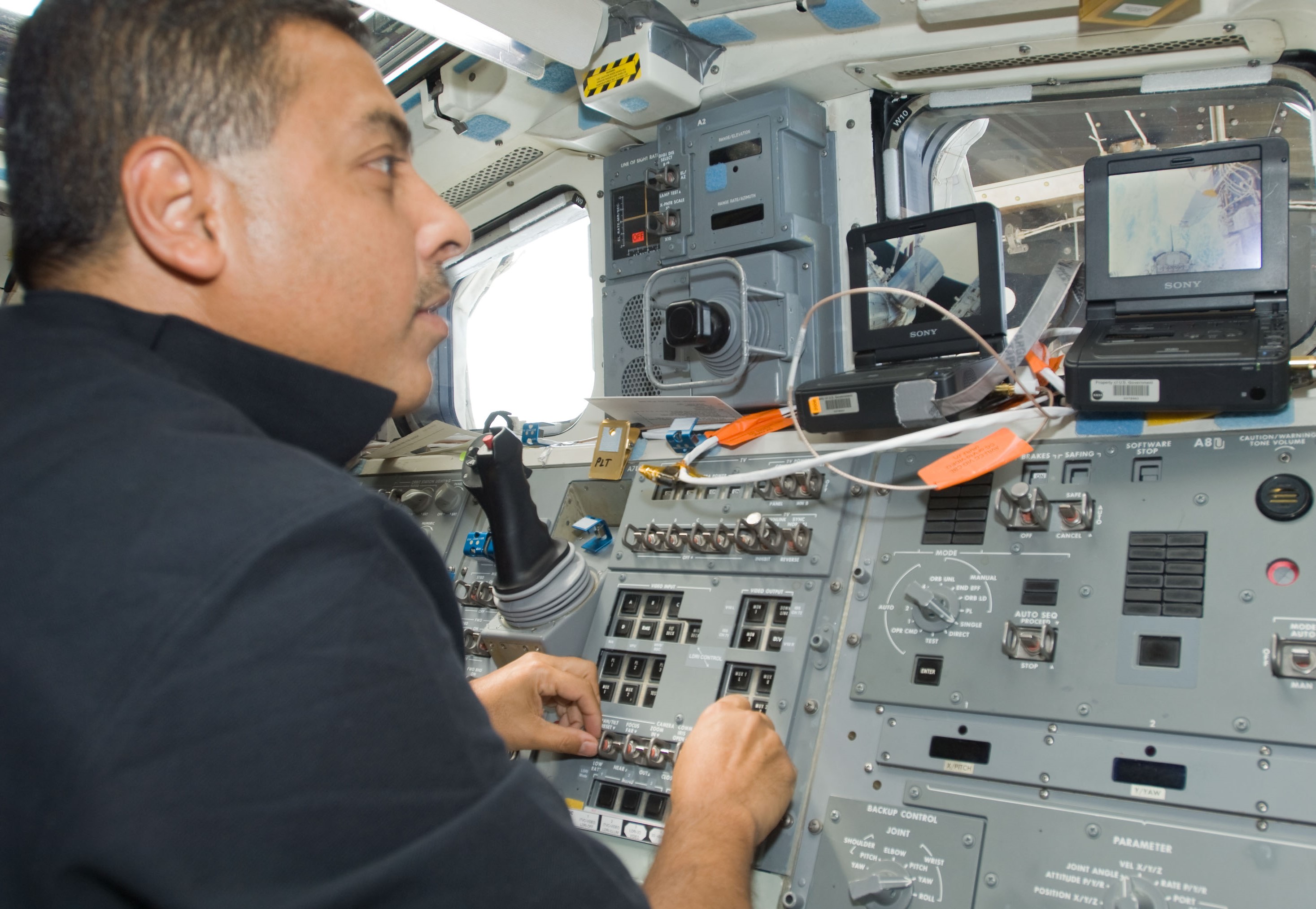
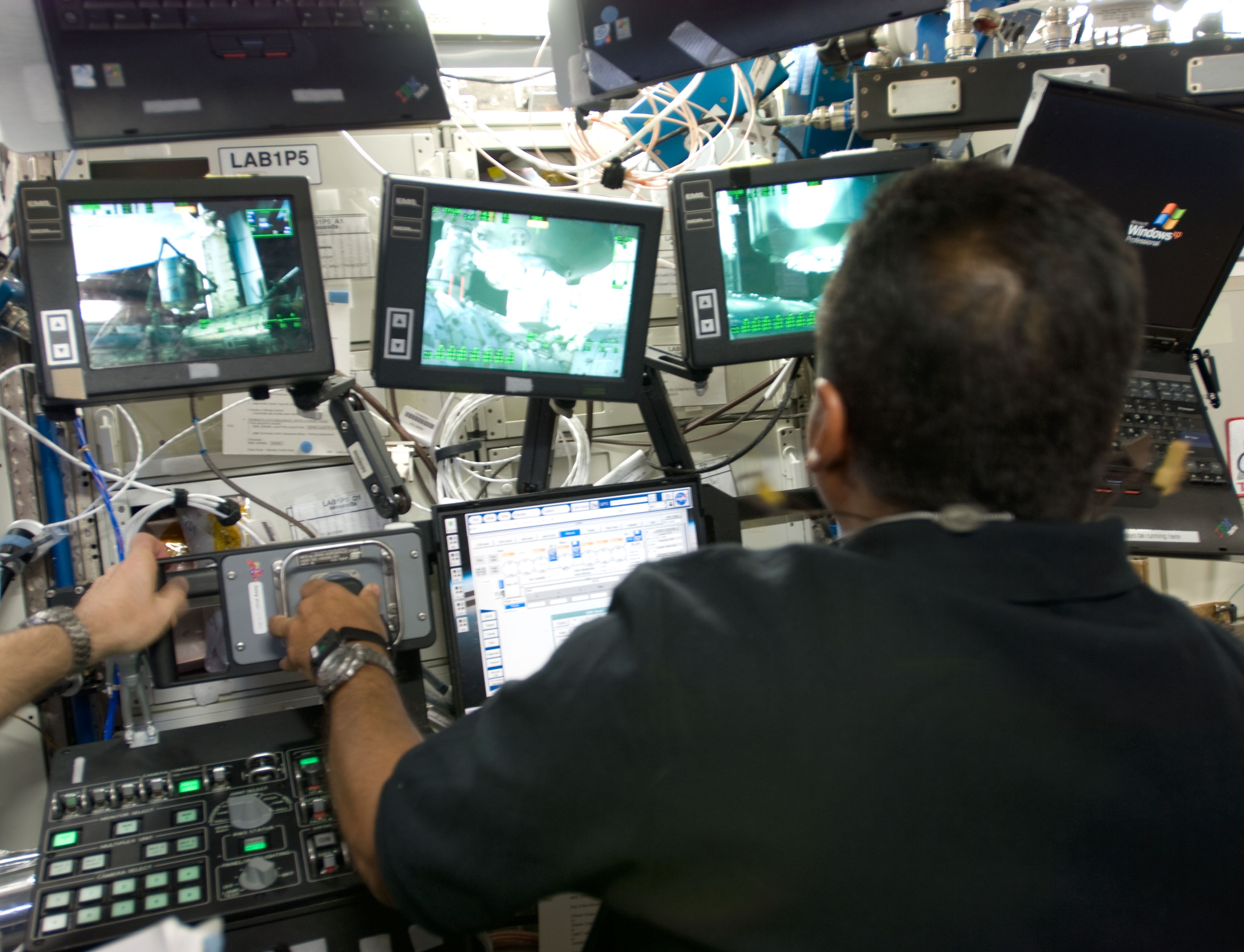
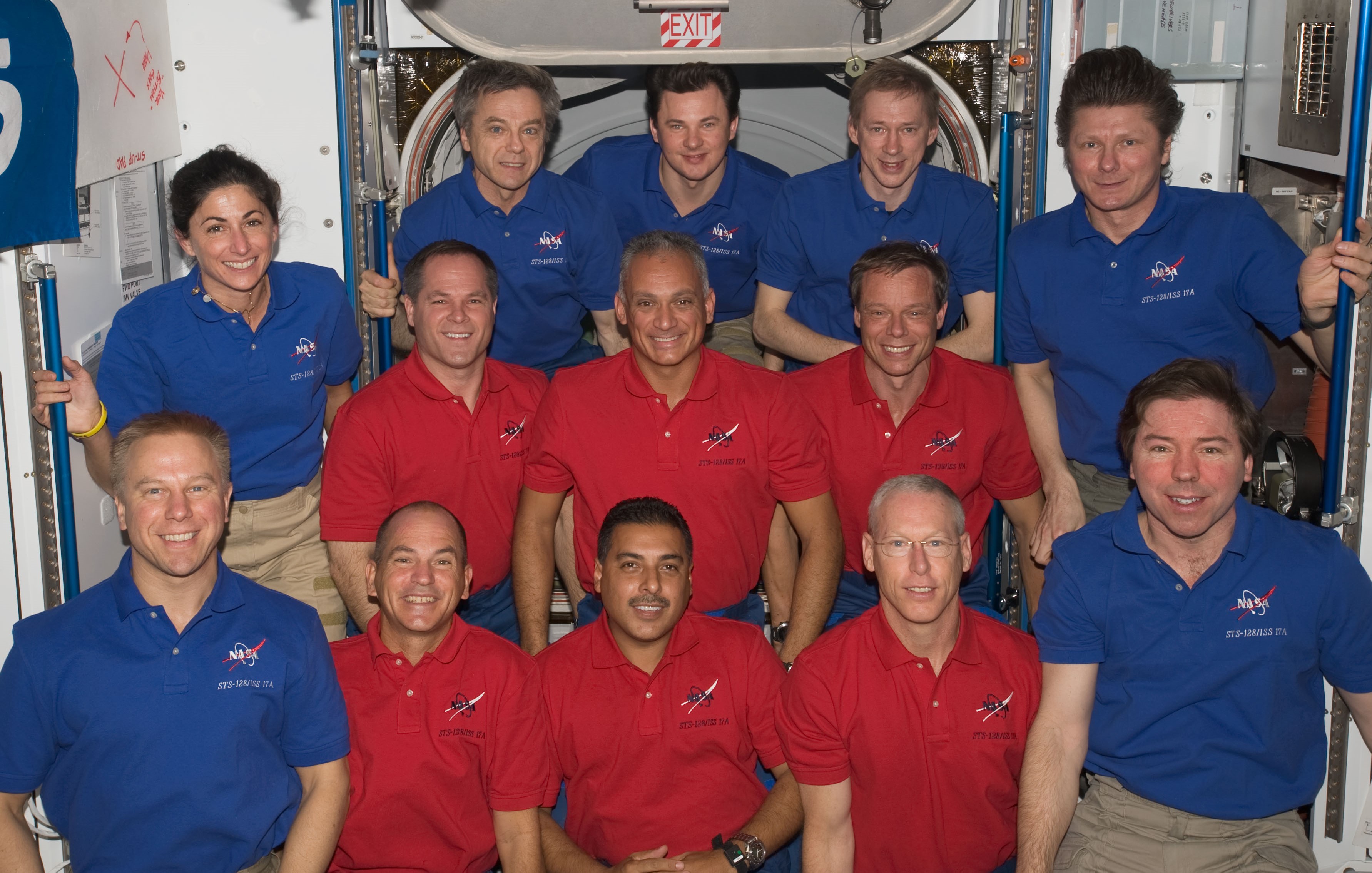



Left: NASA astronaut José M. Hernández operating the shuttle’s robotic arm to transfer the Leonardo Multipurpose Logistics Module (MPLM) to the station. Middle: Hernández operating the station’s robotic arm to return the MPLM to the shuttle’s payload bay. Right: Hernández, front row center, with the STS-128 and Expedition 20 crews.
Serena M. Auñón-Chancellor
Serena M. Auñón-Chancellor was selected as a member of NASA’s Astronaut Class of 2009 and made her first spaceflight nine years later. She launched aboard Soyuz MS-09 in June 2018and began work on the more than 300 research investigations she carried out during her stay aboard the orbiting laboratory. Auñón-Chancellor returned to Earth after completing a 197-day flight.
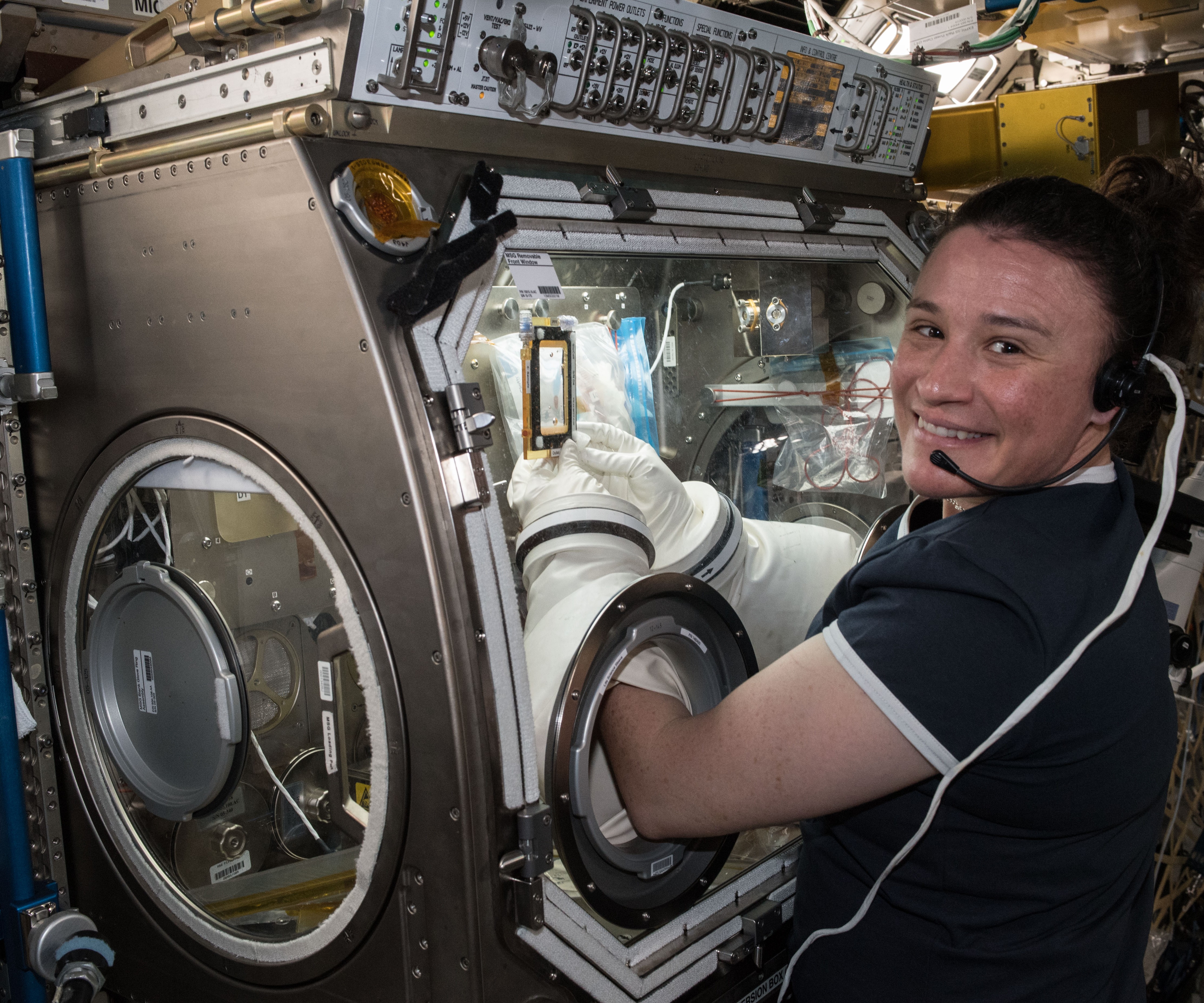
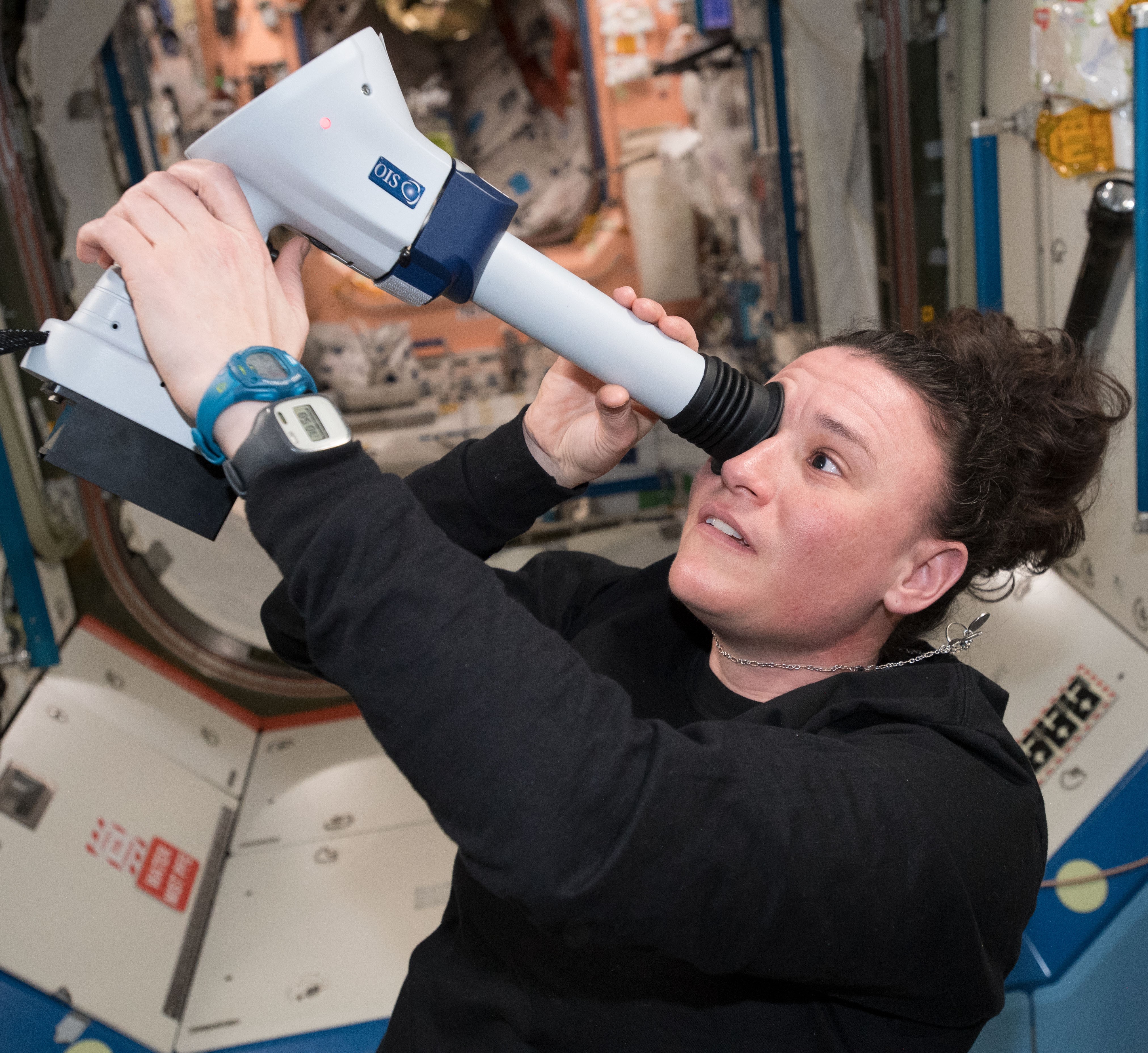
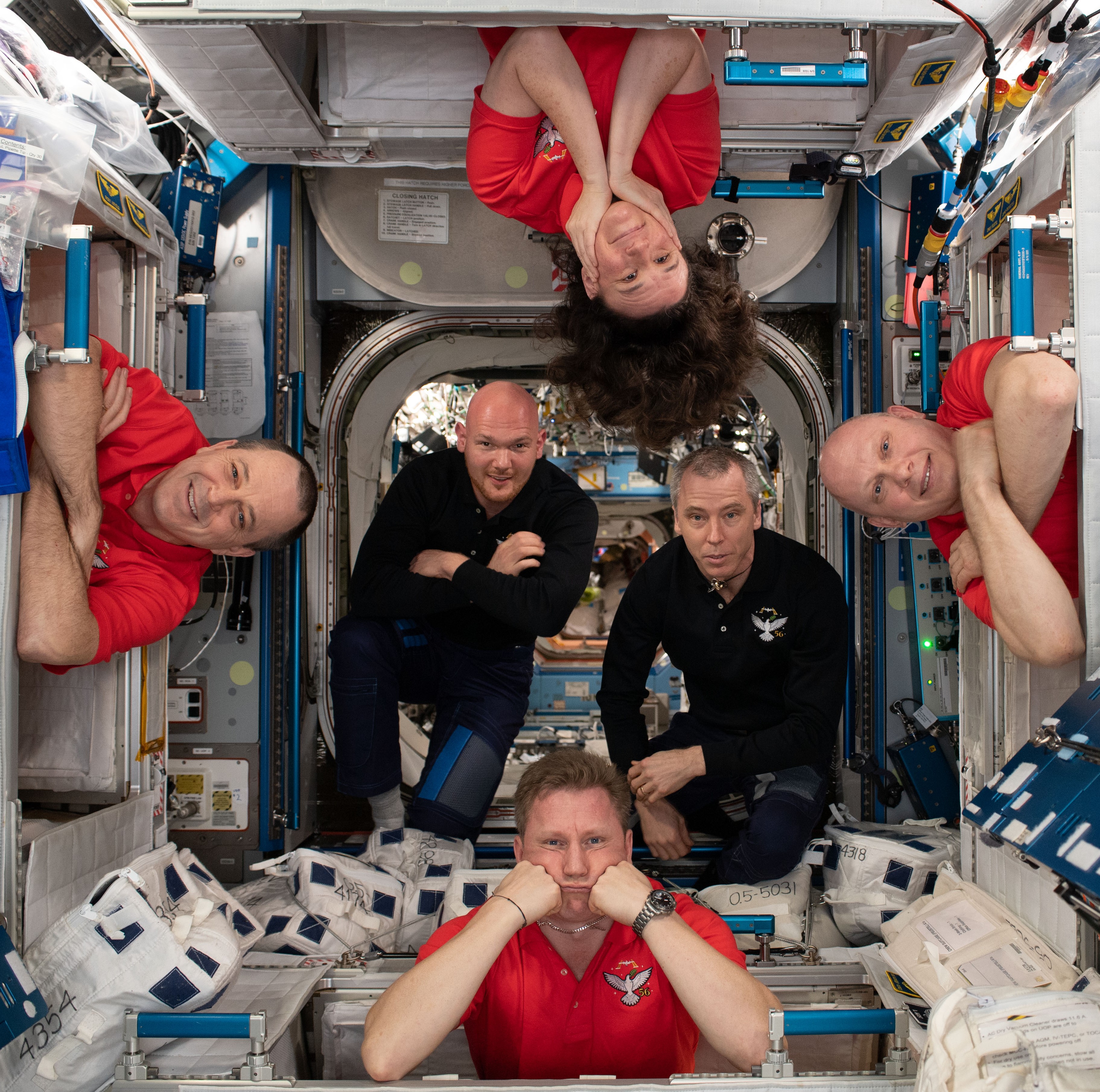



Left: NASA astronaut Serena M. Auñón-Chancellor conducting the AngieX Cancer Therapy experiment in the Microgravity Sciences Glovebox. Middle: Auñón-Chancellor completing a session of the Eye Exam – Fundoscope experiment to help understand vision changes in microgravity. Right: Auñón-Chancellor, top, posing with her Expedition 56 crewmates in the Harmony Node 2 module.
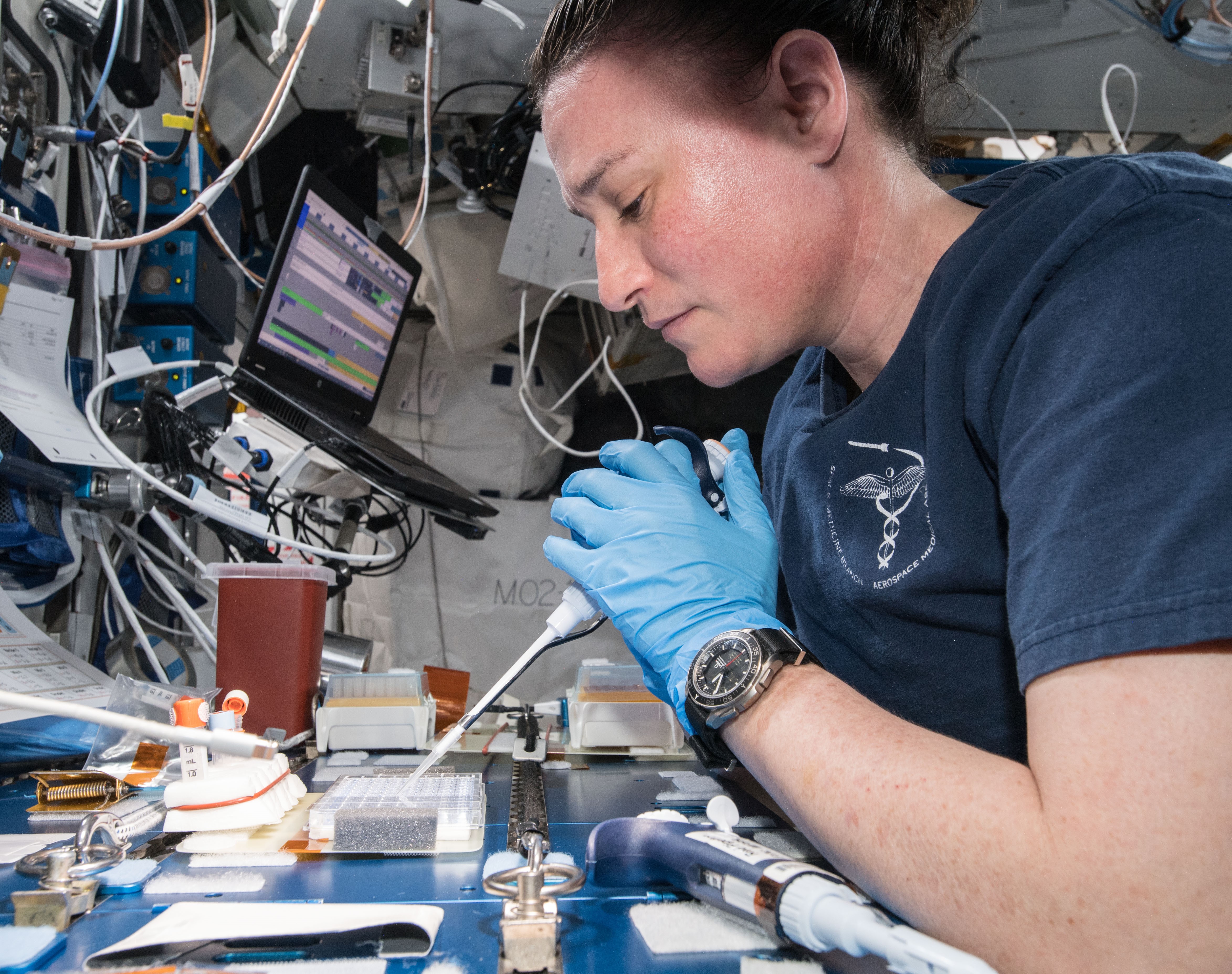
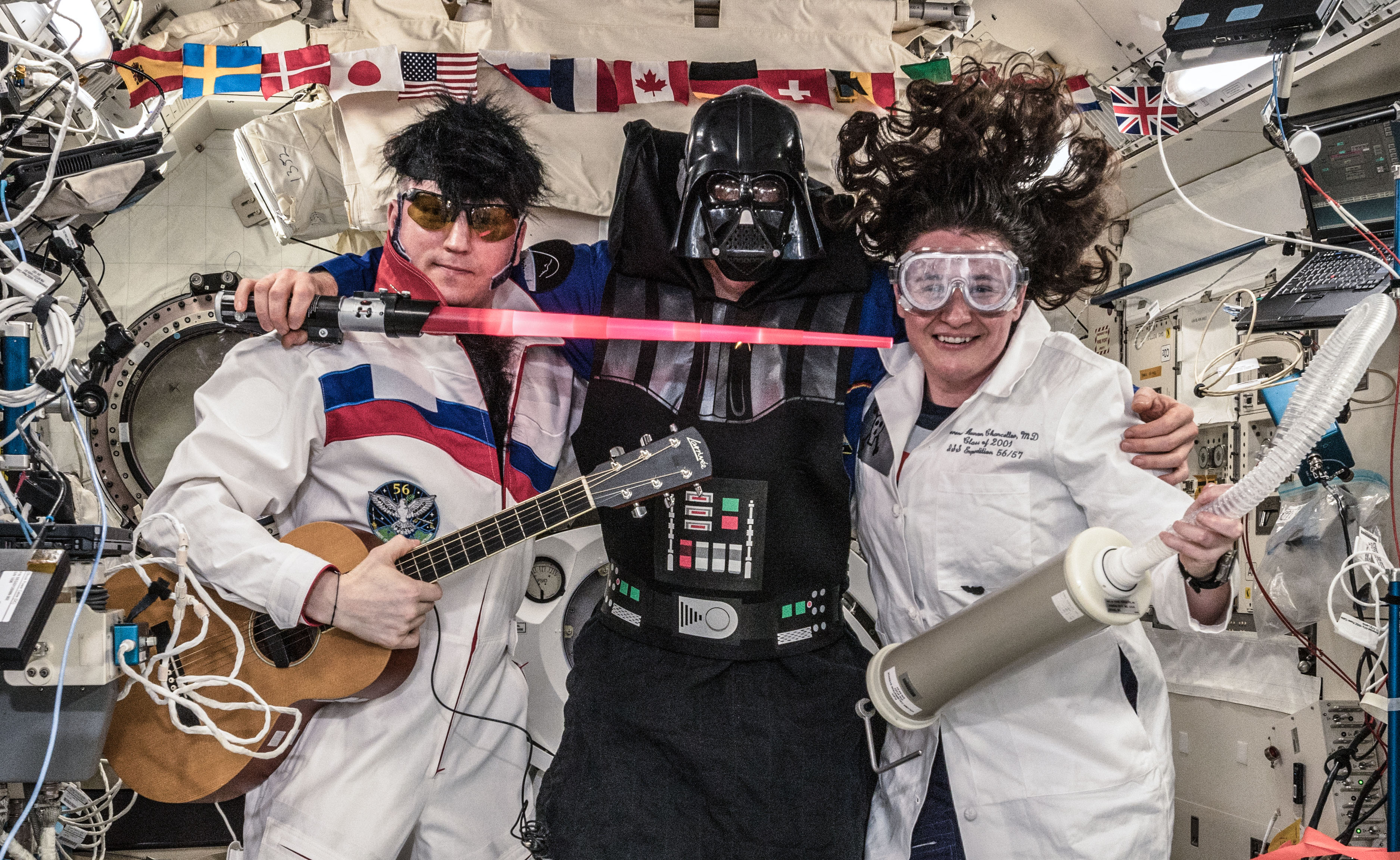
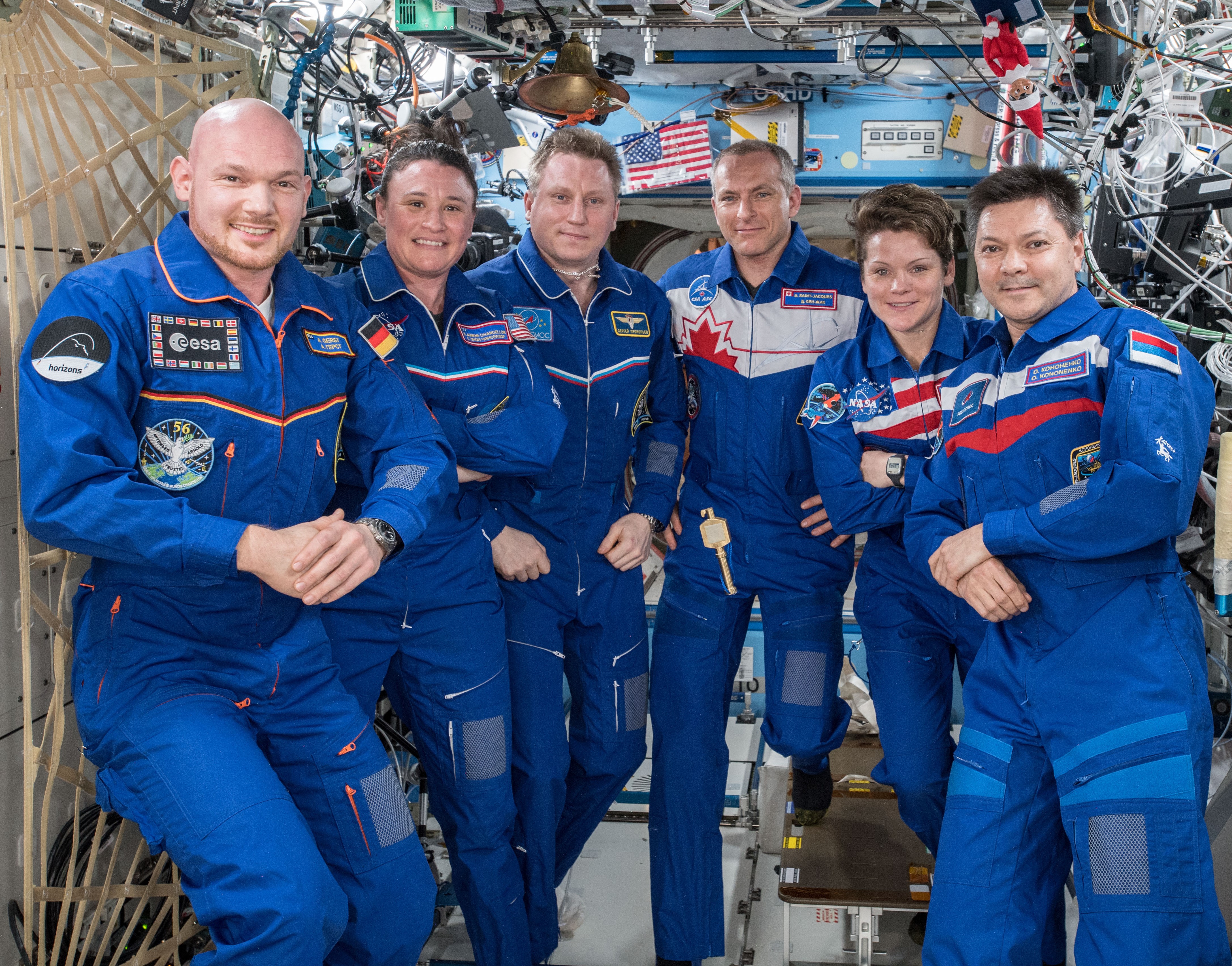



Left: NASA astronaut Serena M. Auñón-Chancellor working on the BioServe Protein Crystalography-1 experiment. Middle: Expedition 57 crew members in their best Halloween outfits – Sergei V. Prokopiev of Roscosmos, left, as Elvis, ESA astronaut Alexander Gerst as Darth Vader, and Auñón-Chancellor as a mad scientist. Right: Auñón-Chancellor and her Expedition 57 crewmates in the Destiny module.
Francisco “Frank” C. Rubio
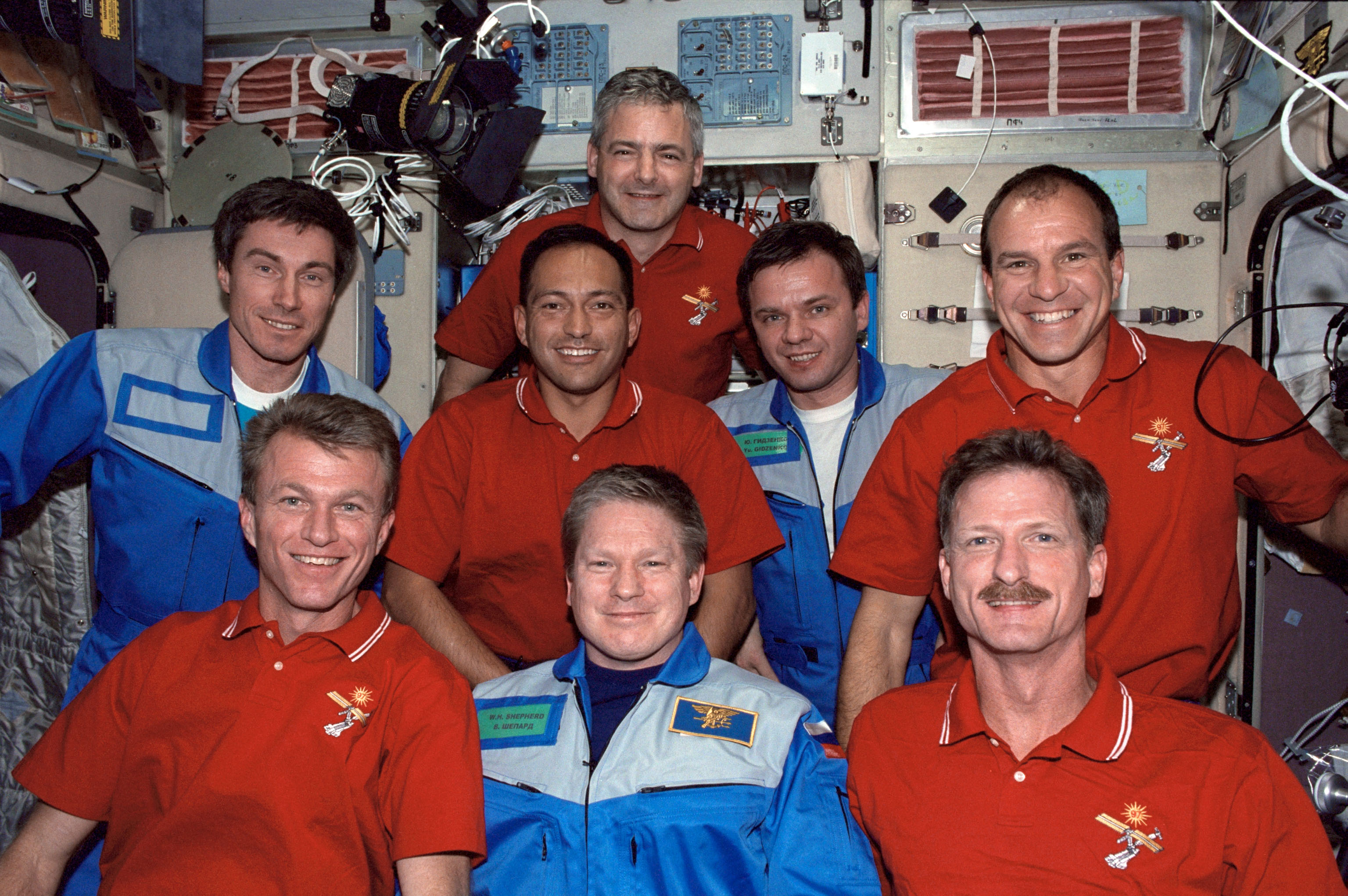
Selected as an astronaut by NASA in 2017, Dr. Francisco “Frank” C. Rubio began his first trip to space in September 2022, with Russian cosmonauts Sergei V. Prokopyev and Dmitri A. Petelin aboard Soyuz MS-22, for a planned six-month stay aboard the space station. A leak aboard their Soyuz MS-22 spacecraft in December resulted in the loss of its coolant, and they could no longer rely on it to return to Earth. Roscosmos sent the replacement Soyuz MS-23 to the station in February 2023. The incident extended their mission to over one year. On Sept. 11, Rubio broke the record of 355 days for the longest single flight by an American astronaut, set by Mark T. Vande Hei in March 2022. Prokopyev, Petelin, and Rubio landed on Sept. 27 after a 371-day flight, the longest aboard the space station.
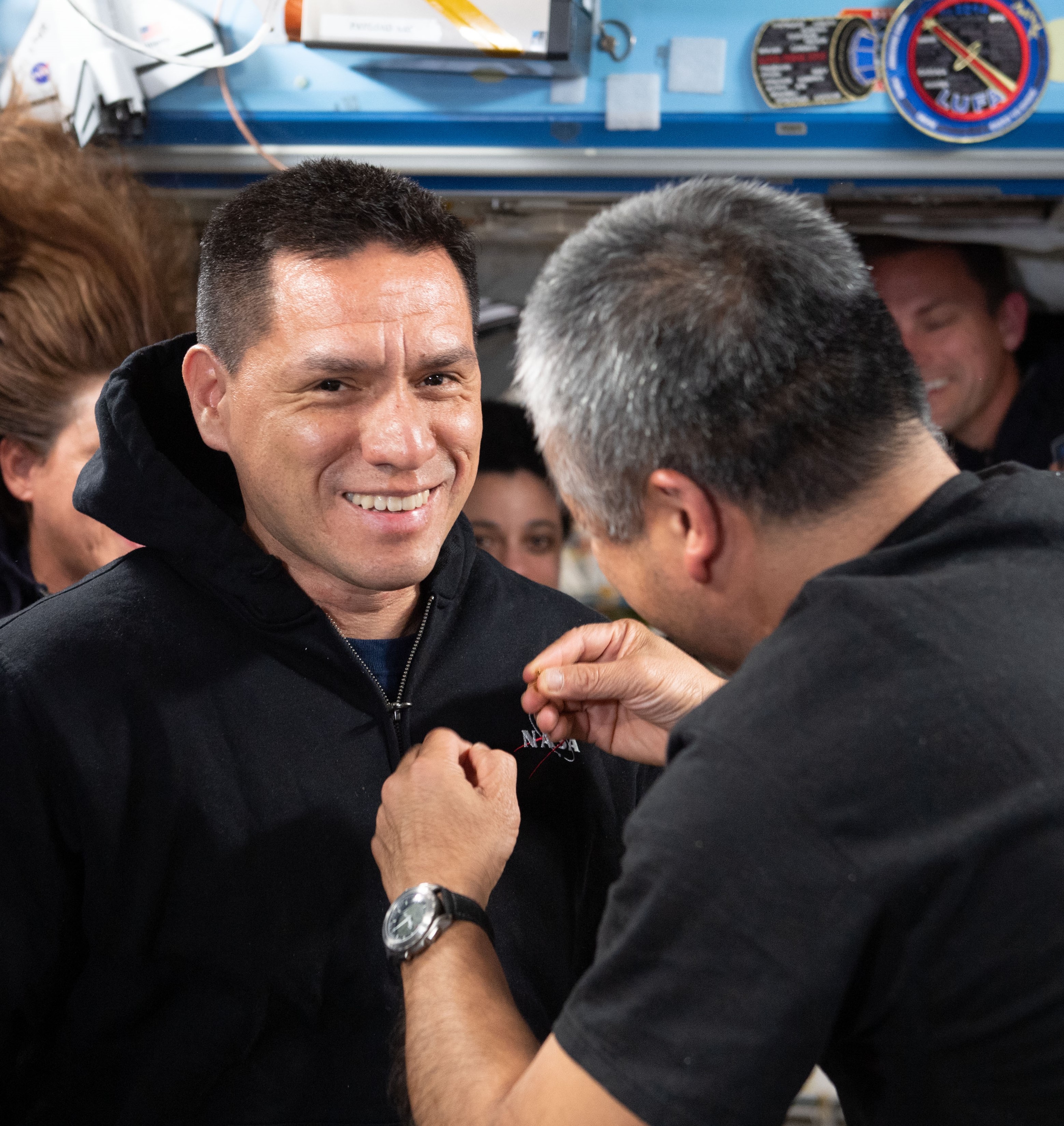
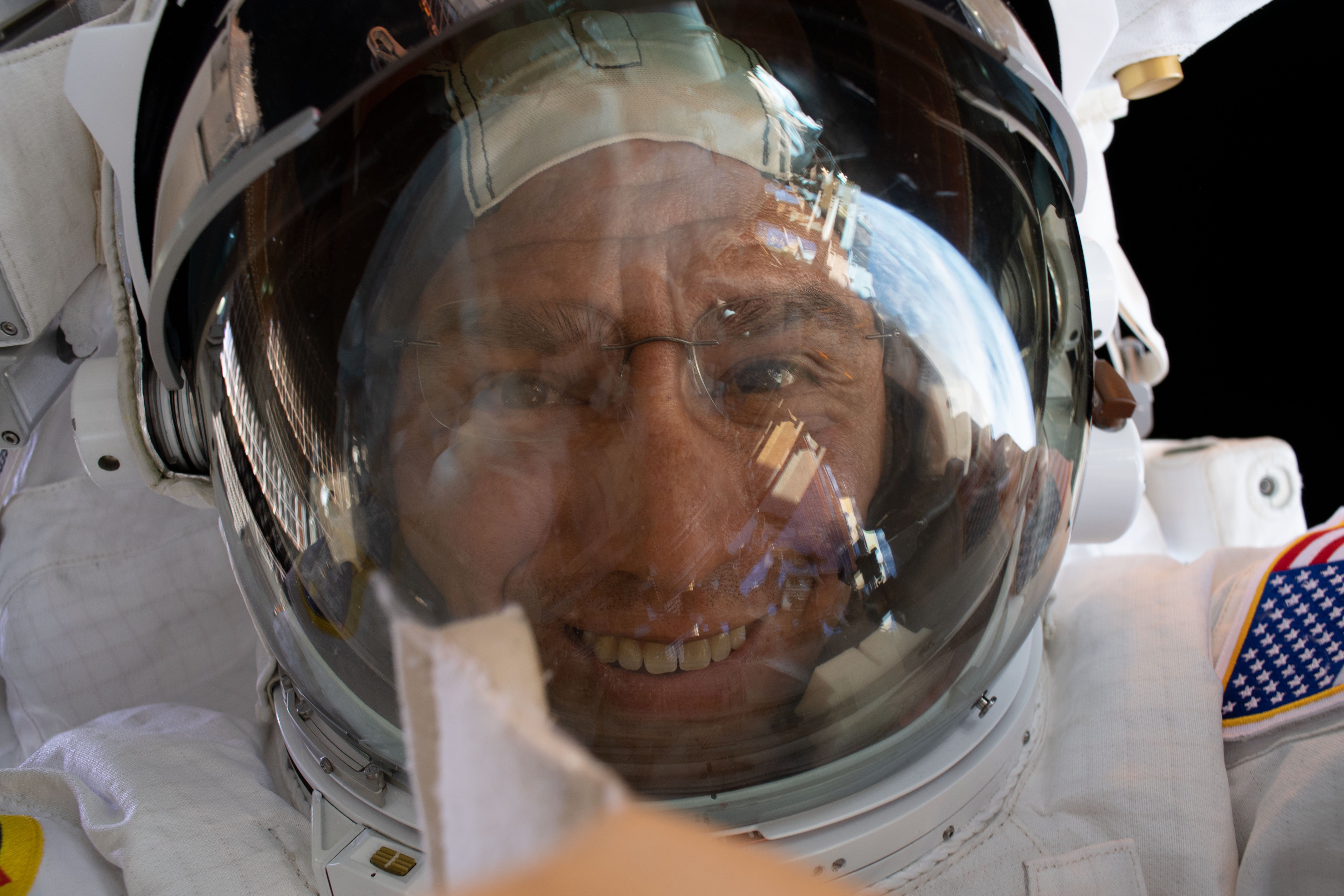
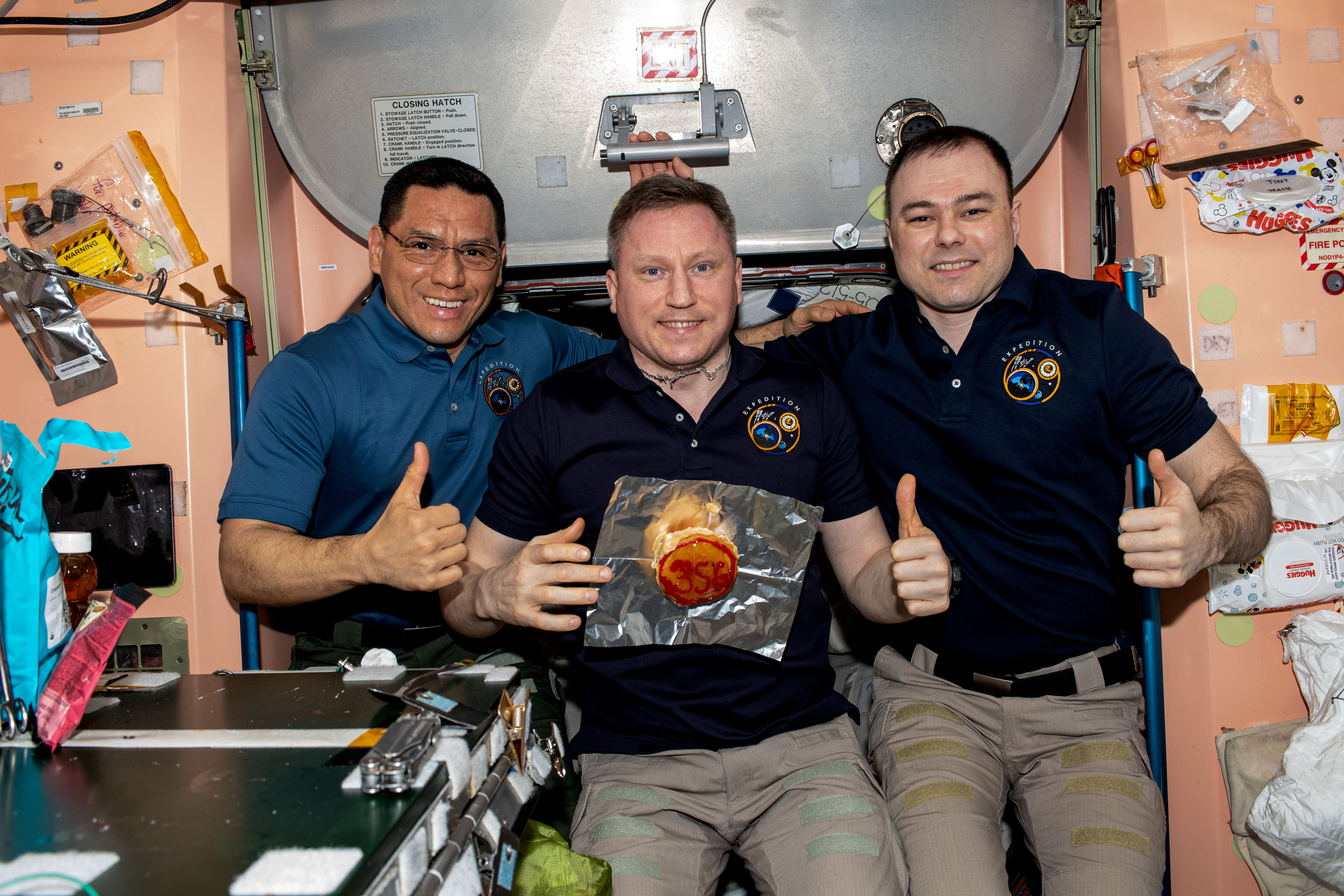



Left: Shortly after arriving at the space station, NASA astronaut Francisco “Frank” C. Rubio receives his gold astronaut pin from Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency astronaut and fellow Expedition 68 crew member Koichi Wakata. Middle: Rubio during one of his two spacewalks. Right: Rubio, left, with Russian cosmonauts Sergey V. Prokopyev and Dmitri A. Petelin with a cake with “356” written on it to signify they surpassed the previous record
of 355 days as the longest flight aboard the space station.
To be continued…
Powered by WPeMatico
Get The Details…
Kelli Mars