NASA Data Reveals Possible Reason Some Exoplanets Are Shrinking
6 min read
NASA Data Reveals Possible Reason Some Exoplanets Are Shrinking

A new study could explain the ‘missing’ exoplanets between super-Earths and sub-Neptunes.
Some exoplanets seem to be losing their atmospheres and shrinking. In a new study using NASA’s retired Kepler Space Telescope, astronomers find evidence of a possible cause: The cores of these planets are pushing away their atmospheres from the inside out.
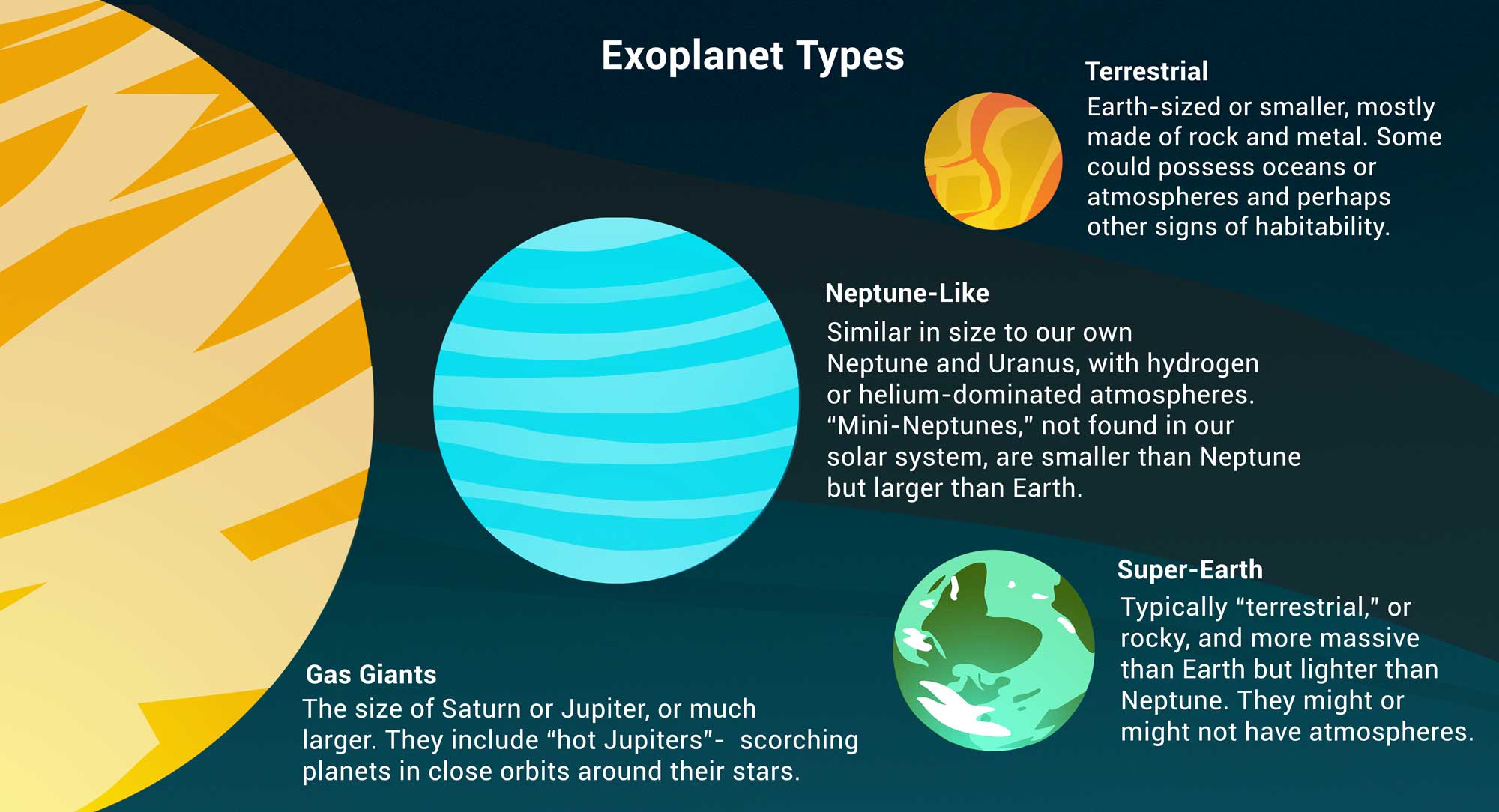
Exoplanets (planets outside our solar system) come in a variety of sizes, from small, rocky planets to colossal gas giants. In the middle lie rocky super-Earths and larger sub-Neptunes with puffy atmospheres. But there’s a conspicuous absence – a “size gap” – of planets that fall between 1.5 to 2 times the size of Earth (or in between super-Earths and sub-Neptunes) that scientists have been working to better understand.
“Scientists have now confirmed the detection of over 5,000 exoplanets, but there are fewer planets than expected with a diameter between 1.5 and 2 times that of Earth,” said Caltech/IPAC research scientist Jessie Christiansen, science lead for the NASA Exoplanet Archive and lead author of the new study in The Astronomical Journal. “Exoplanet scientists have enough data now to say that this gap is not a fluke. There’s something going on that impedes planets from reaching and/or staying at this size.”
Researchers think that this gap could be explained by certain sub-Neptunes losing their atmospheres over time. This loss would happen if the planet doesn’t have enough mass, and therefore gravitational force, to hold onto its atmosphere. So sub-Neptunes that aren’t massive enough would shrink to about the size of super-Earths, leaving the gap between the two sizes of planets.
But exactly how these planets are losing their atmospheres has remained a mystery. Scientists have settled on two likely mechanisms: One is called core-powered mass loss; and the other, photoevaporation. The study has uncovered new evidence supporting the first.
Solving the Mystery
Core-powered mass loss occurs when radiation emitted from a planet’s hot core pushes the atmosphere away from the planet over time, “and that radiation is pushing on the atmosphere from underneath,” Christiansen said.
The other leading explanation for the planetary gap, photoevaporation, happens when a planet’s atmosphere is essentially blown away by the hot radiation of its host star. In this scenario, “the high-energy radiation from the star is acting like a hair dryer on an ice cube,” she said.
While photoevaporation is thought to occur during a planet’s first 100 million years, core-powered mass loss is thought to happen much later – closer to 1 billion years into a planet’s life. But with either mechanism, “if you don’t have enough mass, you can’t hold on, and you lose your atmosphere and shrink down,” Christiansen added.
For this study, Chistiansen and her co-authors used data from NASA’s K2, an extended mission of the Kepler Space Telescope, to look at the star clusters Praesepe and Hyades, which are 600 million to 800 million years old. Because planets are generally thought to be the same age as their host star, the sub-Neptunes in this system would be past the age where photoevaporation could have taken place but not old enough to have experienced core-powered mass loss.
So if the team saw that there were a lot of sub-Neptunes in Praesepe and Hyades (as compared to older stars in other clusters), they could conclude that photoevaporation hadn’t taken place. In that case, core-powered mass loss would be the most likely explanation of what happens to less massive sub-Neptunes over time.
In observing Praesepe and Hyades, the researchers found that nearly 100% of stars in these clusters still have a sub-Neptune planet or planet candidate in their orbit. Judging from the size of these planets, the researchers think they have retained their atmospheres.
This differs from the other, older stars observed by K2 (stars more than 800 million years old), only 25% of which have orbiting sub-Neptunes. The older age of these stars is closer to the timeframe in which core-powered mass loss is thought to take place.
From these observations, the team concluded that photoevaporation could not have taken place in Praesepe and Hyades. If it had, it would have occurred hundreds of millions of years earlier, and these planets would have little, if any, atmosphere left. This leaves core-powered mass loss as the leading explanation for what likely happens to the atmospheres of these planets.
Christiansen’s team spent more than five years building the planet candidate catalog necessary for the study. But the research is far from complete, she said, and it is possible that the current understanding of photoevaporation and/or core-powered mass loss could evolve. The findings will likely be put to the test by future studies before anyone can declare the mystery of this planetary gap solved once and for all.
This study was conducted using the NASA Exoplanet Archive, which is operated by Caltech in Pasadena under contract with NASA as part of the Exoplanet Exploration Program, which is located at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. JPL is a division of Caltech.
More About the Mission
On Oct. 30, 2018, Kepler ran out of fuel and ended its mission after nine years, during which it discovered more than 2,600 confirmed planets around other stars along with thousands of additional candidates astronomers are working to confirm.
NASA’s Ames Research Center in Silicon Valley, California, manages the Kepler and K2 missions for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate. JPL managed Kepler mission development. Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corporation operated the flight system with support from the Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics at the University of Colorado in Boulder.
For more information about the Kepler and K2 missions, visit:
https://science.nasa.gov/mission/kepler
News Media Contacts
Calla Cofield
Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif.
626-808-2469
calla.e.cofield@jpl.nasa.gov
Karen Fox / Alise Fisher
NASA Headquarters, Washington
202-358-1257 / 202-358-2546
karen.c.fox@nasa.gov / alise.m.fisher@nasa.gov
Written by Chelsea Gohd
2023-169
Share
Details
Related Terms
Powered by WPeMatico
Get The Details…
Anthony Greicius