Crew Spending Another Day in Russian Segment

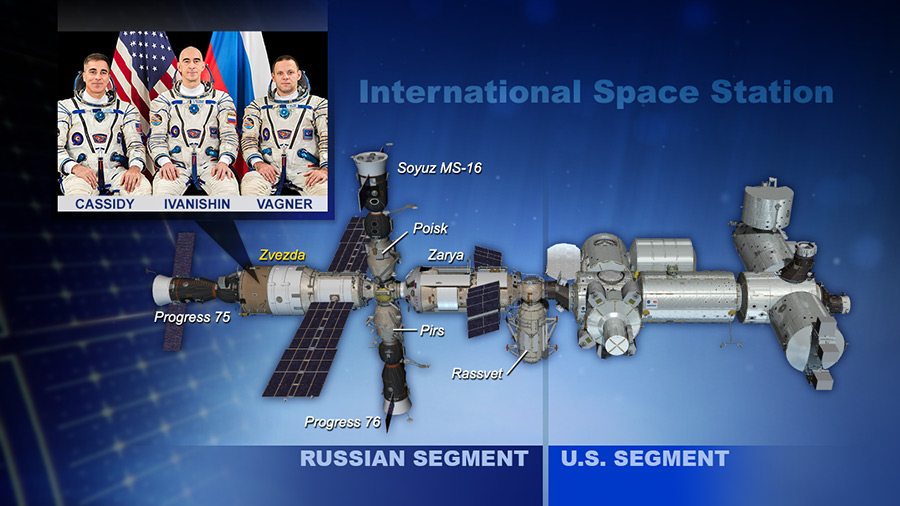
The three Expedition 63 crew members will spend another day inside the Russian segment of the International Space Station. Mission controllers are continuing their leak detection work today to collect more data.
All of the orbiting lab’s hatches will remain closed until Tuesday morning to give ground specialists additional time to collect data and monitor pressure readings in each module. The rate is still well within segment specifications and presents no danger to the crew or the space station.
The station’s atmosphere is maintained at pressure comfortable for the crew members, and a tiny bit of that air leaks over time, requiring routine repressurization from nitrogen tanks delivered on cargo resupply missions. In September 2019, NASA and its international partners first saw indications of a slight increase above the standard cabin air leak rate. Because of routine station operations like spacewalks and spacecraft arrivals and departures, it took time to gather enough data to characterize those measurements. That rate has slightly increased, so the teams are working a plan to isolate, identify and potentially repair the source.
Meanwhile, the station trio is staying comfortable in the Zvezda service module with access to the Poisk mini-research module, the Progress 76 cargo craft and their Soyuz MS-16 crew ship. Commander Chris Cassidy of NASA and Roscosmos Flight Engineers Anatoly Ivanishin and Ivan Vagner mainly focused on Earth photography Monday. The station’s Russian segment has a variety of windows the crew can look out with advanced camera gear for their Earth observation activities.
Mark Garcia
Powered by WPeMatico