Boeing Crew Ship Preps for Launch as Crew Studies Space Biology

Boeing is ramping up for the launch of its first commercial crew vehicle to the International Space Station this week. The Expedition 61 crew is preparing for the new U.S. crew ship’s arrival while working human research and space biology today.
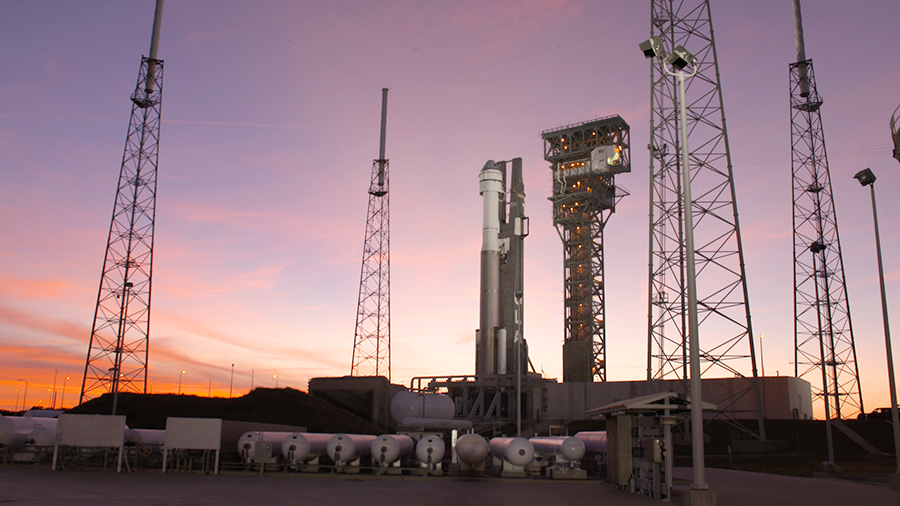
Boeing is targeting 6:36 a.m. EST Friday, Dec. 20, for the launch of its first CST-100 Starliner crew ship to the orbiting lab. It will dock to the forward-facing port of the Harmony module on Dec. 21 and return to Earth on Dec. 28. This will be an uncrewed orbital flight test of Boeing’s new spaceship and sets the stage for launching crews once again from the United States.
NASA Flight Engineer Christina Koch activated communications gear that will link up with the Boeing Starliner when it arrives Saturday. The C2V2 device (Common Communications for Visiting Vehicles) transmits telemetry from the approaching spacecraft to crew and ground controllers. The C2V2, used by the U.S. Dragon and Cygnus resupply ships, also enables an astronaut to remotely control a spacecraft if necessary.
ESA (European Space Agency) Commander Luca Parmitano and NASA Flight Engineer Andrew Morgan started Monday with hearing checks. The duo set up gear for the Acoustic Diagnostics study that measures hearing before, during and after a mission and assesses the noisy environment aboard the orbiting lab.
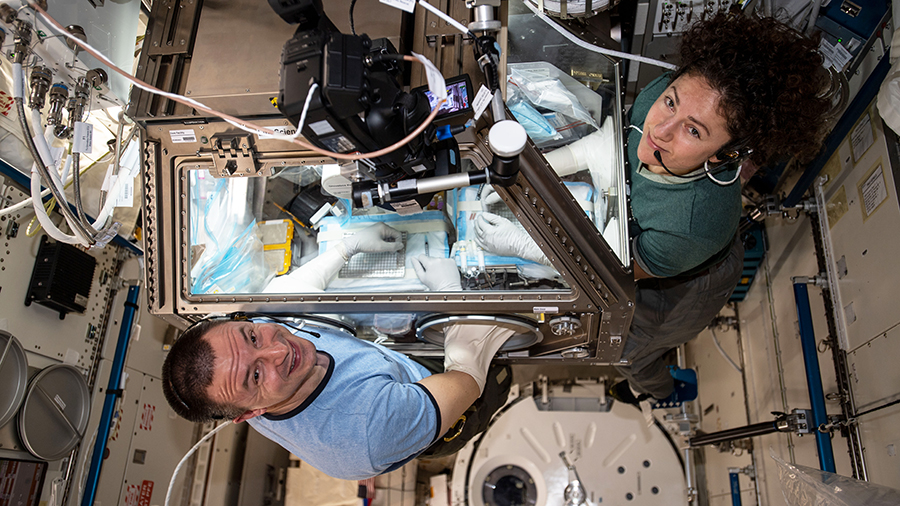
NASA astronaut Jessica Meir began her day on an exercise bike for a study measuring her aerobic and cardiovascular output. She then joined Koch in the afternoon feeding lab mice and cleaning their habitats.
Russian cosmonauts Alexander Skvortsov and Oleg Skripochka focused on life support and lab maintenance today. Skvortsov synchronized computers and cameras to station time and serviced an oxygen generator. Skripochka also checked out Russian laptop computers and radiation detection gear.
Catherine Williams
Powered by WPeMatico